Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
== Clinical relevance<ref>Harrison M. Common problems. Neurological Skills. 1987;:63-99.</ref> == | == Clinical relevance<ref>Harrison M. Common problems. Neurological Skills. 1987;:63-99.</ref> == | ||
* [[carpal tunel syndrome]]. | * [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome|carpal tunel syndrome]]. | ||
* Median and [[Ulnar Nerve|ulnar]] nerve lesion. | * Median and [[Ulnar Nerve|ulnar]] nerve lesion. | ||
* [[Syringomyelia]] | * [[Syringomyelia]] | ||
* [[Motor neurone disease]] | * [[Motor Neurone Disease MND|Motor neurone disease]] | ||
* [[Peripheral neuropathy]] | * [[Neuropathic Pain|Peripheral neuropathy]] | ||
== Assessment<ref>UC San Diego's Practical Guide to Clinical Medicine [Internet]. Meded.ucsd.edu. 2020 [cited 22 September 2020]. Available from: <nowiki>https://meded.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/joints3.html</nowiki></ref> == | == Assessment<ref>UC San Diego's Practical Guide to Clinical Medicine [Internet]. Meded.ucsd.edu. 2020 [cited 22 September 2020]. Available from: <nowiki>https://meded.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/joints3.html</nowiki></ref> == | ||
Revision as of 00:02, 23 September 2020
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Anneta Adamou, Saumya Srivastava, Chrysolite Jyothi Kommu and Kim Jackson
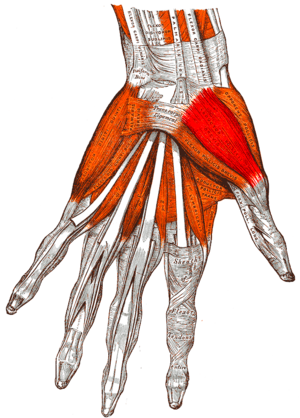
Description[1][edit | edit source]
Abductor pollicis brevis muscle is the most lateral and superficial of the three muscles forming the thenar emirence.
Origin[2][edit | edit source]
It takes its origin from the front of transverse carpal ligament, extending into the tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium with an occasional contribution from the tendon of abductor pollicis longus.
Insertion[3][edit | edit source]
The muscle has a short tendon which attaches to the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Nerve[4][edit | edit source]
Median nerve C8, T1.
Artery[4][edit | edit source]
Princeps pollicis artery.
Function[5][edit | edit source]
It acts to abduct the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb.
Clinical relevance[6][edit | edit source]
- carpal tunel syndrome.
- Median and ulnar nerve lesion.
- Syringomyelia
- Motor neurone disease
- Peripheral neuropathy
Assessment[7][edit | edit source]
Function can be tested by providing resistance to abduction up and away from the plane of the palm.
StrengthTips[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Cael C. Functional anatomy. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2011.
- ↑ Palastanga N, Field D, Soames R. Anatomy and human movement. 4th ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2002.
- ↑ Lippert L, Lippert L. Clinical kinesiology and anatomy. 4th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis; 2006.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Tiwana MS, Sinkler MA, Bordoni B. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Triceps Muscle. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 May 30.
- ↑ The Muscles of the Hand - Thenar - Hypothenar - TeachMeAnatomy [Internet]. Teachmeanatomy.info. 2020 [cited 21 September 2020]. Available from: https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/muscles/hand/?fbclid=IwAR12pBXShD88Na_jqJc6bSMhslR1-4F573kwF60ZHdV3C67U7380Itmqgxk#Lumbricals
- ↑ Harrison M. Common problems. Neurological Skills. 1987;:63-99.
- ↑ UC San Diego's Practical Guide to Clinical Medicine [Internet]. Meded.ucsd.edu. 2020 [cited 22 September 2020]. Available from: https://meded.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/joints3.html