Stroke Medical Management
Original Editor - Naomi O'Reilly
Top Contributors - Naomi O'Reilly, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, Admin, Simisola Ajeyalemi, 127.0.0.1, Karen Wilson, Claire Knott, Rucha Gadgil and Wanda van Niekerk
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The goal for the acute medical management of patients with stroke is to stabilize the patient and to complete initial evaluation and assessment, including imaging and laboratory studies, within a short time frame. Critical decisions focus on the need for intubation, blood pressure control, and determination of risk / benefit for thrombolytic intervention.[1] Patients presenting with Glasgow Coma Scale scores of 8 or less or rapidly decreasing Glasgow Coma Scale scores, require emergent airway control via intubation.
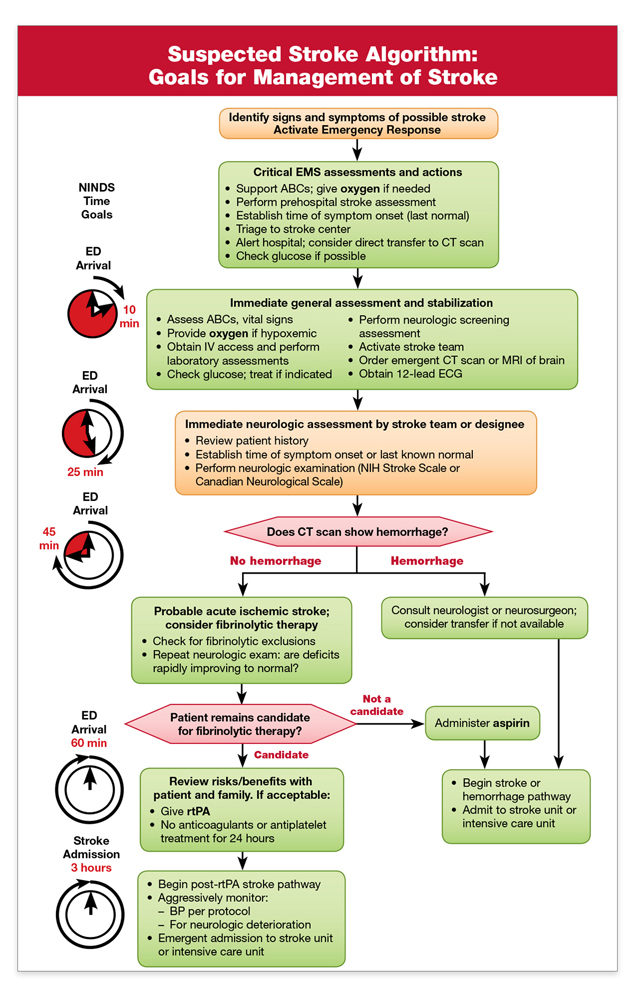
Suspected Stroke Algorithm[edit | edit source]
Ischemic Stroke[edit | edit source]
In the case of an Ischemic Stroke, the more rapidly blood flow is restrored, the ore likely for improved recovery and fewer brain cell deaths. Primary treatment is aimed at breaking down the clot through means of medication (Thrombolysis) or mechanical removal of clot (Thrombectomy). Other treatments aim to minimisethe clot becoming larger or prevention of new clot formation by means of anticoagulant type medications such as Aspirin, Clopidogrel or Dipyridamole. In conjunction with this, overall patient medical condition should be managed including montoring of blood sugars, oxygen levels and hydration and providing adequate treatment for same.
Thrombolysis[edit | edit source]
Thrombectomy[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Adams H, Adams R, Del Zoppo G, Goldstein LB. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: 2005 guidelines update a scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. Apr 2005;36(4):916-23.