Stroke Medical Management: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
The goal for the acute medical management of patients with stroke is to stabilize the patient and to complete initial evaluation and assessment, including imaging and laboratory studies, within a short time frame. Critical decisions focus on the need for intubation, blood pressure control, and determination of risk / benefit for thrombolytic intervention.<ref>Adams H, Adams R, Del Zoppo G, Goldstein LB. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: 2005 guidelines update a scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. Apr 2005;36(4):916-23.</ref> | The goal for the acute medical management of patients with stroke is to stabilize the patient and to complete initial evaluation and assessment, including imaging and laboratory studies, within a short time frame. Critical decisions focus on the need for intubation, blood pressure control, and determination of risk / benefit for thrombolytic intervention.<ref>Adams H, Adams R, Del Zoppo G, Goldstein LB. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: 2005 guidelines update a scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. Apr 2005;36(4):916-23.</ref> Patients presenting with Glasgow Coma Scale scores of 8 or less or rapidly decreasing Glasgow Coma Scale scores, require emergent airway control via intubation.<br> | ||
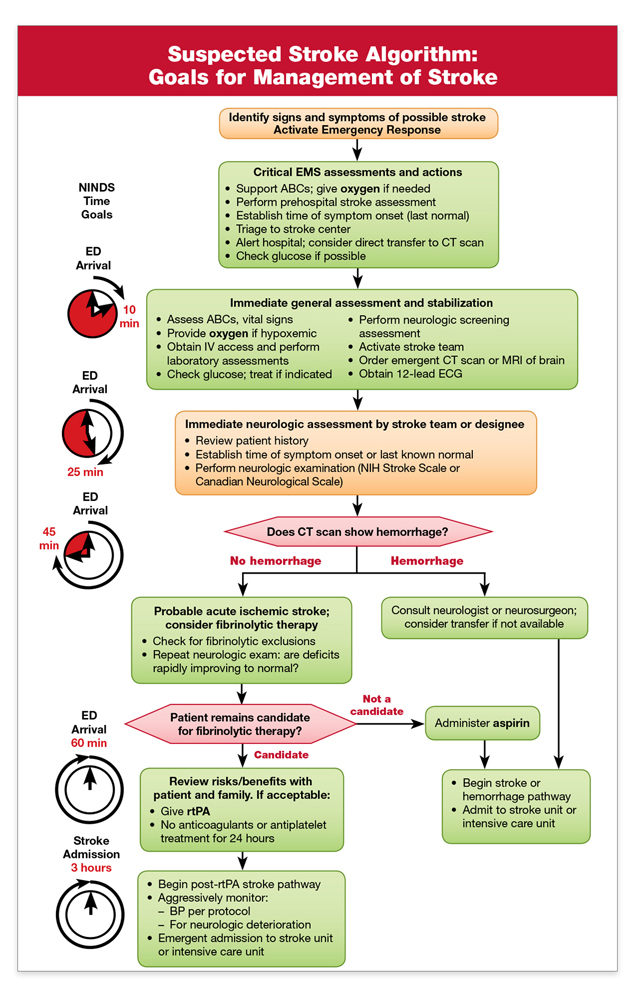
== Suspected Stroke Algorithm == | == Suspected Stroke Algorithm == | ||
[[Image:15-1043_l_1.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:15-1043_l_1.jpg]] | |||
== Imaging == | == Imaging == | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 6 May 2017
Original Editor - Naomi O'Reilly
Top Contributors - Naomi O'Reilly, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Admin, Karen Wilson, Claire Knott, Rucha Gadgil, Wanda van Niekerk and 127.0.0.1
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The goal for the acute medical management of patients with stroke is to stabilize the patient and to complete initial evaluation and assessment, including imaging and laboratory studies, within a short time frame. Critical decisions focus on the need for intubation, blood pressure control, and determination of risk / benefit for thrombolytic intervention.[1] Patients presenting with Glasgow Coma Scale scores of 8 or less or rapidly decreasing Glasgow Coma Scale scores, require emergent airway control via intubation.
Suspected Stroke Algorithm[edit | edit source]
Imaging[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Adams H, Adams R, Del Zoppo G, Goldstein LB. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: 2005 guidelines update a scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. Apr 2005;36(4):916-23.