Splenius Capitis: Difference between revisions
m (deleted pubmed) |
Ahmed Nasr (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Description | == Description == | ||
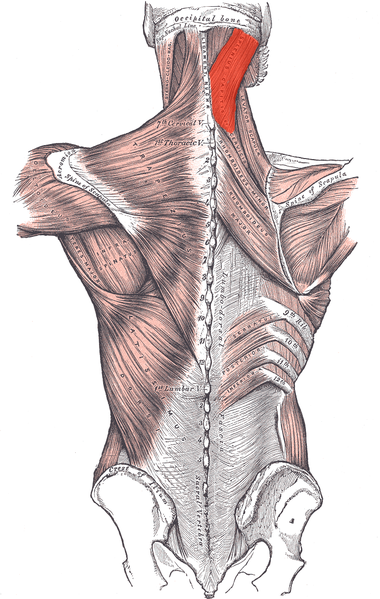
Musculus splenius capitis is one of the deep (or intrinsic) muscles of the back. It is a broad strap-like muscle in the back of the neck. Deep to Sternocleidomastoid at the mastoid process.<ref name="gray">Gray's Anatomy of Human Body, Bartleby.com edition. New York: 2000.fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/115.html</ref> <br> | Musculus splenius capitis is one of the deep (or intrinsic) muscles of the back. It is a broad strap-like muscle in the back of the neck. Deep to Sternocleidomastoid at the mastoid process.<ref name="gray">Gray's Anatomy of Human Body, Bartleby.com edition. New York: 2000.fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/115.html</ref> <br> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Lower half of | Lower half of [[ligamentum nuchae]] (C4-C6) and spinous process of C7-T3<ref name="ae">http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5203/</ref><ref name="wh">Wheeless`textbook of orthopedic, splenius capitis , available from:http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/splenius_capitis | ||
< | (24july 2019 ) | ||
</ref> | |||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
Superior nuchal line, Mastoid process of temporal bone, and rough surface adjoining occipital bone<ref name="ae" /><ref name="wh" /> | Superior nuchal line, Mastoid process of temporal bone, and rough surface adjoining occipital bone<ref name="ae" /><ref name="wh" /> | ||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Dorsal ramus of spinal nerves C3-C6<ref name="ae" /> | Dorsal ramus of spinal nerves C3-C6<ref name="ae" /> | ||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
| Line 38: | Line 35: | ||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Acting bilaterally: extension of the head and | Acting bilaterally: extension of the head and cervical spine <br>Acting unilaterally: lateral flexion of the head and neck and rotation the head to the same side. <ref name="wh" /> | ||
== Function == | |||
= | It also assists in supporting the head in the erect position<ref name="gray" /> | ||
In people with neck pain it has shown that over activity of superficial muscles and splenius capitis and inhibition of [[Semispinalis Cervicis]]<ref>J Schomacher, J Erlenwein, A Dieterich, F Petzke, F Petzkeb, D Falla. Can neck exercises enhance the activation of the semispinalis cervicis relative to the splenius capitis at specific spinal levels? Manual therapy, October 2015:20: 694-702.</ref> | |||
So in management of neck pain we have to focus on exercises that has more specification to activate [[Semispinalis Cervicis]] and to perform stretch and myofascial release to splenius capitis . | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 02:29, 24 July 2019
Original Editor - Venus Pagare
Top Contributors - Rachel Vogel, Lucinda hampton, Oyemi Sillo, Venus Pagare, WikiSysop, Kim Jackson, Ahmed Nasr and Tarina van der Stockt
Description[edit | edit source]
Musculus splenius capitis is one of the deep (or intrinsic) muscles of the back. It is a broad strap-like muscle in the back of the neck. Deep to Sternocleidomastoid at the mastoid process.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Lower half of ligamentum nuchae (C4-C6) and spinous process of C7-T3[2][3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Superior nuchal line, Mastoid process of temporal bone, and rough surface adjoining occipital bone[2][3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal ramus of spinal nerves C3-C6[2]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Muscular branches of the occipital artery from the external carotid artery. [2]
Action[edit | edit source]
Acting bilaterally: extension of the head and cervical spine
Acting unilaterally: lateral flexion of the head and neck and rotation the head to the same side. [3]
Function[edit | edit source]
It also assists in supporting the head in the erect position[1]
In people with neck pain it has shown that over activity of superficial muscles and splenius capitis and inhibition of Semispinalis Cervicis[4]
So in management of neck pain we have to focus on exercises that has more specification to activate Semispinalis Cervicis and to perform stretch and myofascial release to splenius capitis .
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gray's Anatomy of Human Body, Bartleby.com edition. New York: 2000.fckLRhttp://www.bartleby.com/107/115.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5203/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Wheeless`textbook of orthopedic, splenius capitis , available from:http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/splenius_capitis (24july 2019 )
- ↑ J Schomacher, J Erlenwein, A Dieterich, F Petzke, F Petzkeb, D Falla. Can neck exercises enhance the activation of the semispinalis cervicis relative to the splenius capitis at specific spinal levels? Manual therapy, October 2015:20: 694-702.