Serratus Anterior: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
[[File:Download (1).jpg|thumb]] | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
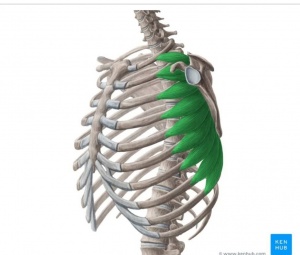
It originates on the top surface of the eight or nine upper ribs. <ref name=":0">https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/serratus-anterior-muscle#2</ref> | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
It inserts exactly at the front border of the scapula, or shoulder blade.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
The long thoracic nerve supplies the serratus anterior muscle. | |||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The function of the serratus anterior muscle is to allow the forward rotation of the arm and to pull the scapula forward and around the rib cage. The scapula is able to move laterally due to the serratus anterior muscle, which is vital for the elevation of the arm. The serratus anterior muscle also allows the upward rotation of the arm, which allows a person to lift items over their head.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Revision as of 00:06, 6 June 2018
Original Editor - Esraa Mohamed Abdullzaher
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kholoud Abd Elghany, Kim Jackson, Joao Costa, Lilian Ashraf, Esraa Mohamed Abdullzaher and Oyemi Sillo
Description[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
It originates on the top surface of the eight or nine upper ribs. [1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
It inserts exactly at the front border of the scapula, or shoulder blade.[1]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
The long thoracic nerve supplies the serratus anterior muscle.
Artery[edit | edit source]
Function[edit | edit source]
The function of the serratus anterior muscle is to allow the forward rotation of the arm and to pull the scapula forward and around the rib cage. The scapula is able to move laterally due to the serratus anterior muscle, which is vital for the elevation of the arm. The serratus anterior muscle also allows the upward rotation of the arm, which allows a person to lift items over their head.[1]