Scapular Dyskinesia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (59 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
The | Scapular dyskinesia (SD) is a term that describes a physical impairment in which the scapula's position and motion are altered. The words dyskinesia or dysrhythmia are often used instead of dyskinesia. <ref>Depreli Ö, Angın E. Review of scapular movement disorders among office workers having ergonomic risk. Journal of back and musculoskeletal rehabilitation. 2018 Jan 1;31(2):371-80.</ref><ref name=":11" /><ref name=":9" /> One of the other terms used for SD is [[Scapular Winging|scapular winging]], but it is a different condition that results in scapular dyskinesia usually after a [[Long Thoracic Nerve|long thoracic]] or [[Accessory Nerve Cranial Nerve 11|spinal accessory nerve]] injury. <ref>Humphrey CS, Sears BW, Curtin MJ. An anthropometric analysis to derive formulae for calculating the dimensions of anatomically shaped humeral heads. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2016 Sep 1;25(9):1532-41.</ref><ref>Kibler WB, Sciascia AD. Disorders of the scapula and their role in shoulder injury. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. 2017:128-30.</ref><ref>Didesch JT, Tang P. Anatomy, etiology, and management of scapular winging. The Journal of hand surgery. 2019 Apr 1;44(4):321-30.</ref> | ||
</ref> | |||
</ref> | |||
SD can be seen in overhead athletes or patients with shoulder pathology such as rotator cuff disease, glenohumeral instability, impingement syndrome, and labral tears as well as in healthy people. <ref>Teixeira DC, Alves L, Gutierres M. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8559559/ The role of scapular dyskinesis on rotator cuff tears: a narrative review of the current knowledge.] EFORT Open Reviews. 2021 Oct;6(10):932. | |||
</ref> <ref name=":2">Giuseppe LU, Laura RA, Berton A, Candela V, Massaroni C, Carnevale A, Stelitano G, Schena E, Nazarian A, DeAngelis J, Denaro V. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7215460/ Scapular dyskinesis: from basic science to ultimate treatment.] International journal of environmental research and public health. 2020 Apr;17(8):2974. | |||
</ref>Patients with shoulder pain have a higher incidence of SD, though whether SD causes shoulder pain or shoulder pain causes SD is unclear and requires further investigation. Some research suggests that SD can be predictive of future shoulder pain despite absence of symptoms at present<ref>Hickey D, Solvig V, Cavalheri V, Harrold M, Mckenna L. Scapular dyskinesis increases the risk of future shoulder pain by 43% in asymptomatic athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. British journal of sports [https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/bjsports/early/2017/07/22/bjsports-2017-097559.full.pdf?casa_token=GkkYpjRWDKcAAAAA:YBZetku4PyB6oUEJ3kcpQl5DmT218ByYPY6kA0oDPMyGCfBbX61iIYFsqIRu5HWhznPAWY067MuNnw medicine. 2017 Jul 22.]</ref>. | |||
== Scapular Biomechanics == | == Scapular Biomechanics == | ||
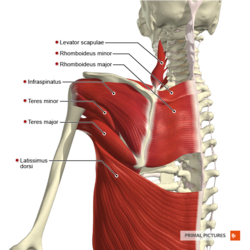
[[Image:Muscles_of_the_scapular_region_posterior_aspect_Primal.png|thumb|right|250px|© Primal Pictures]] | [[Image:Muscles_of_the_scapular_region_posterior_aspect_Primal.png|thumb|right|250px|© Primal Pictures]]Movements of the [[scapula]] can be broken up into 3 motions and 2 translations. | ||
The motions are: | |||
# Upward/downward rotation | |||
# Internal/ external rotation | |||
# Anterior/posterior tilt | |||
The translations are: | |||
# Upward/downward sliding on the thorax | |||
# Medial/lateral sliding around the curvature of the thorax | |||
< | Common patterns of the scapula are called scapular retraction (external rotation, posterior tilt, upward rotation and medial translation), protraction (internal rotation, anterior tilt, downward rotation and lateral translation), and shrug (upward translation, anterior tilt, and internal rotation). <ref>Barcia AM, Makovicka JL, Spenciner DB, Chamberlain AM, Jacofsky MC, Gabriel SM, Moroder P, von Rechenberg B, Sengun MZ, Tokish JM, MRAB Study Group. Scapular motion in the presence of rotator cuff tears: a systematic review. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2021 Jul 1;30(7):1679-92.</ref><ref name=":1" /> | ||
During the normal overhead upper extremity elevation with internal/external rotation being minimal until 100°, primary scapular movement is upward rotation and secondary scapular movement is posterior tilt. <ref name="Ludewig">Ludewig PM et al. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2657311/ Motion of the shoulder complex during multiplaner humeral elevation.] J Bone Joint Surg. Am.2009;91:378-389.</ref><ref name="McClure">McClure PW et al. Direct 3-dimentional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2001:10:269-277.</ref> | |||
The coordinated movement between the scapula and humerus which is necessary for efficient arm movement is termed [[Scapulohumeral Rhythm|scapulohumeral rhythm]]. <ref>Kibler WB, Ludewig PM, McClure PW, Michener LA, Bak K, Sciascia AD. Clinical implications of scapular dyskinesis in shoulder injury: the 2013 consensus statement from the ‘Scapular Summit’. British journal of sports medicine. 2013 Sep 1;47(14):877-85.</ref> An early study <ref>Inman VT, Saunders JD, Abbott LC. Observations on the function of the shoulder joint. JBJS. 1944 Jan 1;26(1):1-30.</ref> found an overall ratio of 2:1 between glenohumeral elevation and scapular upward rotation. Another study <ref name="McClure" /> found that during the scapular plane elevation of the arm, there was a consistent pattern of scapular upward rotation, posterior tilting, and external rotation along with clavicular elevation and retraction. | |||
The altered mechanics in SD are increased scapular anterior tilt, increased scapular internal rotation, and altered scapular upward rotation. <ref>Kibler WB, Stone AV, Zacharias A, Grantham WJ, Sciascia AD. Management of scapular dyskinesis in overhead athletes. Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine. 2021 Mar 1;29(1):150797.</ref> | |||
== Etiology == | |||
The causes of SD are many, but they can be looked at in these three groups: | |||
# Shoulder-related; | |||
# Neck-related; | |||
# Posture-related. <ref name=":0">Panagiotopoulos AC, Crowther IM. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6701878/ Scapular Dyskinesia, the forgotten culprit of shoulder pain and how to rehabilitate.] SICOT-J. 2019;5.</ref> | |||
''1. Shoulder-related:'' Shoulder pathologies associated with SD (acromioclavicular instability, shoulder impingement, rotator cuff injuries, glenoid labrum injuries, clavicle fractures <ref>Burkhart SS, Morgan CD, Kibler WB. The disabled throwing shoulder: spectrum of pathology Part I: pathoanatomy and biomechanics. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery. 2003 Apr 1;19(4):404-20. | |||
</ref><ref name=":1">Kibler WB, Sciascia A. Current concepts: scapular dyskinesis. British journal of sports medicine. 2010 Apr 1;44(5):300-5.</ref>), inflexibility of the pectoralis minor and short head of the biceps, and stiffness of the posterior glenohumeral capsule can be counted for this group. <ref>Borstad JD. Resting position variables at the shoulder: evidence to support a posture-impairment association. Physical Therapy. 2006 Apr 1;86(4):549-57.</ref><ref>Borstad JD, Ludewig PM. The effect of long versus short pectoralis minor resting length on scapular kinematics in healthy individuals. Journal of orthopaedic & sports physical therapy. 2005 Apr;35(4):227-38.</ref><ref name="McClure" /> | |||
''2. Neck-related:'' Mechanical neck pain syndromes and cervical nerve root-related syndromes. <ref name=":0" /> | |||
''3. Posture-related:'' Excessive thoracic kyphosis and cervical lordosis, which are the changes that athletes are more tend to show are related causes of SD. <ref>Crosbie J, Kilbreath SL, Hollmann L, York S. Scapulohumeral rhythm and associated spinal motion. Clinical biomechanics. 2008 Feb 1;23(2):184-92.</ref> | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | |||
Patients with SD can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. <ref>Pires ED, Camargo PR. Analysis of the kinetic chain in asymptomatic individuals with and without scapular dyskinesis. Clinical Biomechanics. 2018 May 1;54:8-15.</ref> Symptoms of SD can be one or a combination of the following: <ref name=":10">Burkhart SS, Morgan CD, Kibler WB. The disabled throwing shoulder: spectrum of pathology Part III: The SICK scapula, scapular dyskinesis, the kinetic chain, and rehabilitation. Arthroscopy. 2003 Jul 1;19(6):641-61.</ref> | |||
* Anterior shoulder pain | |||
* Posterosuperior scapular pain (may radiate into the ipsilateral para spinous cervical region or radicular/thoracic outlet-type symptoms in the affected upper extremity can be found) | |||
* Superior shoulder pain | |||
* Proximal lateral arm pain | |||
== | == Clinical Examination == | ||
There is no standard clinical assessment of SD. However, some assessment methods have proven to be reliable: <ref name=":2" /> | |||
'' | ==='''Classification of Dyskinesia Types'''=== | ||
Noting shoulder assymmetry is generally reliable. Based on visual observation, one of the three types of dyskinesia can be determined during arm movements in terms of the presence of SD: <ref>Uhl TL, Kibler WB, Gecewich B, Tripp BL. Evaluation of clinical assessment methods for scapular dyskinesis. Arthroscopy: the journal of arthroscopic & related surgery. 2009 Nov 1;25(11):1240-8.</ref> <ref>Kibler WB, Uhl TL, Maddux JW, Brooks PV, Zeller B, McMullen J. Qualitative clinical evaluation of scapular dysfunction: a reliability study. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2002 Nov 1;11(6):550-6.</ref> | |||
* Type 1: Inferior angle prominence (i.e. anterior tilt of the scapula) | |||
* Type 2: Medial border prominence (i.e. [[Scapular Winging|winging]] of the scapula) | |||
* Type 3: Early scapular elevation or excessive/insufficient upward rotation during arm elevation | |||
=== | === Manually Assisted Movements of Scapula === | ||
To determine the role of the scapula position in shoulder pain two tests that apply manual assistance to the scapula are [[Scapular Assistance Test|The Scapular Assistance Test]] (SAT) and [[Scapular Retraction Test|The Scapular Reposition (Retraction) Test]] (SRT). <ref>Kopkow C, Lange T, Schmitt J, Kasten P. Interrater reliability of the modified scapular assistance test with and without handheld weights. Manual therapy. 2015 Dec 1;20(6):868-74.</ref> | |||
In the [[Scapular Assistance Test|SAT]], the patient is asked to do arm flexion or abduction and rate their pain on the [[Numeric Pain Rating Scale|numerical pain rating scale]]. The same process is repeated while the examiner pushes upward and laterally on the inferior angle to facilitate upward rotation, and pulls the superior aspect of the scapula to produce posterior tilt. If two or more points of pain decrease after assisted movement, the test is positive. <ref>Kibler WB, Sciascia AD. Introduction to the second international conference on scapular dyskinesis in shoulder injury—the ‘Scapular summit’report of 2013. British journal of sports medicine. 2013 Sep 1;47(14):874-. | |||
</ref><ref>Kibler BW, McMullen J. Scapular dyskinesis and its relation to shoulder pain. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2003 Mar 1;11(2):142-51.</ref><ref>Kibler WB. The scapula in rotator cuff disease. Rotator Cuff Tear. 2012;57:27-40.</ref><ref>Rabin A, Irrgang JJ, Fitzgerald GK, Eubanks A. The intertester reliability of the scapular assistance test. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 2006 Sep;36(9):653-60.</ref><ref>Rabin A, Chechik O, Dolkart O, Goldstein Y, Maman E. A positive scapular assistance test is equally present in various shoulder disorders but more commonly found among patients with scapular dyskinesis. Physical Therapy in Sport. 2018 Nov 1;34:129-35.</ref> This suggests that scapula dyskinesia has a role in influencing the patient's pain. Taping techniques can then be used to recreate this same effect of improving scapula kinematics<ref>Shih YF, Lee YF, Chen WY. Effects of Kinesiology Taping on Scapular Reposition Accuracy, Kinematics, and Muscle Activity in Athletes With Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. J Sport Rehabil. 2018 Nov 1;27(6):560-569. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2017-0043. Epub 2018 Oct 15. PMID: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29364027/ 29364027.]</ref><ref>Ozer ST, Karabay D, Yesilyaprak SS. Taping to Improve Scapular Dyskinesis, Scapular Upward Rotation, and Pectoralis Minor Length in Overhead Athletes. J Athl Train. 2018 Nov;53(11):1063-1070. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-342-17. Epub 2019 Jan 7. PMID: 30615491; [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30615491/ PMCID: PMC6333226.]</ref>. | |||
In [[Scapular Retraction Test|SRT]], the patient is asked to do 90 degrees of flexion with shoulder internal rotation while the examiner stabilizes the medial scapular border with one hand. Then the patient is asked to hold the position while the examiner is applying resistance with the other hand. If the pain felt by the patient is decreased or the strength is increased with the assistance the test is positive. <ref name=":7" /> This test is described by Kibler et al <ref>Kibler WB, Sciascia A, Dome D. Evaluation of apparent and absolute supraspinatus strength in patients with shoulder injury using the scapular retraction test. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Oct;34(10):1643-7.</ref> to establish the scapular retraction stabilization on the improvement of supraspinatus strength deficits in patients with SD. <ref>Smith J, Dietrich CT, Kotajarvi BR, Kaufman KR. The effect of scapular protraction on isometric shoulder rotation strength in normal subjects. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2006 May 1;15(3):339-43.</ref><ref>Khazzam M, Gates ST, Tisano BK, Kukowski N. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6172943/ Diagnostic accuracy of the scapular retraction test in assessing the status of the rotator cuff.] Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 2018 Sep 25;6(10):2325967118799308.</ref> | |||
''' | ==='''Assessment of Surrounding Structures'''=== | ||
The structures around the scapula can be assessed for pain, loss of function, soft tissue laxity and muscle power. <ref name=":7" /> | |||
The [[Sternoclavicular Joint|sternoclavicular]] (SC) and [[Acromioclavicular Joint|acromioclavicular]] (AC) joints should be assessed for instability. [[Acromioclavicular Joint|AC joint]] can be assessed for anterior-posterior (AP) laxity by mobilizing the acromion in an AP direction while stabilizing the clavicle. <ref name=":7">Kilber WB, Sciascia A (2010) Current concepts: scapular dyskinesis. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 44, 300–305. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]</ref><ref name=":11">Kibler BW, Sciascia A, Wilkes T. Scapular dyskinesis and its relation to shoulder injury. JAAOS-journal of the American academy of orthopaedic surgeons. 2012 Jun 1;20(6):364-72.</ref> Manual muscle tests for rotator cuff/biceps muscles can be applied. The [[Infraspinatus Test|infraspinatus strength test]] shows good reliability to assess infraspinatus weakness due to SD. <ref name=":2" /> | |||
=== | === Muscle Tests === | ||
Three specific muscle tests that the clinician observes the scapula position and considers the scapular muscle weakness if the break in the position and scapular movement occurs are: <ref name=":9" /> | |||
==== | * Manual resistance of the arm at 130° of flexion (for the serratus anterior) <ref name=":8">Michener LA, Boardman ND, Pidcoe PE, Frith AM. Scapular muscle tests in subjects with shoulder pain and functional loss: reliability and construct validity. Physical therapy. 2005 Nov 1;85(11):1128-38.</ref><ref>Ekstrom RA, Soderberg GL, Donatelli RA. Normalization procedures using maximum voluntary isometric contractions for the serratus anterior and trapezius muscles during surface EMG analysis. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2005 Aug 1;15(4):418-28.</ref> | ||
* Manual resistance of the arm at 130-150° of abduction (for the lower and middle trapezius) <ref name=":8" /> | |||
* Extension of the arm at the side (for the rhomboid) <ref>Ginn KA, Halaki M, Cathers I. [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jor.21488 Revision of the Shoulder Normalization Tests is required to include rhomboid major and teres major.] Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2011 Dec;29(12):1846-9.</ref> | |||
==='''Core Evaluation'''=== | |||
With the low row test, if core and hip strength facilitate the scapular motion can be assessed. The examiner stands behind the patient. The patient is asked to do slight arm extension and resist the movement of the arm into flexion. The same movement is repeated with gluteal muscle contraction. If the strength increase with gluteal contraction core/lower extremity strengthening can be added to the treatment plan. <ref name=":9">Sciascia A, Kibler WB. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8805107/ Current Views of Scapular Dyskinesis and its Possible Clinical Relevance. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy.] 2022;17(2):117.</ref> | |||
[ | === Outcome Measures === | ||
[http://orthopaedicscore.com/scorepages/disabilities_of_arm_shoulder_hand_score_dash.html DASH] is a measure that includes 30 items and assesses the disability and symptoms of the upper limb in patients with musculoskeletal disorders. <ref>Franchignoni F, Vercelli S, Giordano A, Sartorio F, Bravini E, Ferriero G. Minimal clinically important difference of the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand outcome measure (DASH) and its shortened version (QuickDASH). Journal of orthopaedic & sports physical therapy. 2014 Jan;44(1):30-9.</ref> | |||
== Physiotherapy Management == | == Physiotherapy Management == | ||
Treatment of SD aims at the restoration of scapular retraction, posterior tilt and external rotation. Specific exercises for scapular rehabilitation are <ref name=":2" />: | |||
Specific exercises for scapular rehabilitation | |||
Flexibility exercises: To increase the flexibility of the [[Pectoralis Minor|pectoralis minor]] and the external rotation and posterior tilt of the scapula, shoulder horizontal abduction at 90 degrees and 150 degrees of elevation. <ref name=":3">Umehara J, Nakamura M, Nishishita S, Tanaka H, Kusano K, Ichihashi N. Scapular kinematic alterations during arm elevation with decrease in pectoralis minor stiffness after stretching in healthy individuals. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2018 Jul 1;27(7):1214-20. | |||
</ref><ref name=":4">Umehara J, Nakamura M, Fujita K, Kusano K, Nishishita S, Araki K, Tanaka H, Yanase K, Ichihashi N. Shoulder horizontal abduction stretching effectively increases shear elastic modulus of pectoralis minor muscle. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2017 Jul 1;26(7):1159-65. | |||
</ref> <ref name=":4">Umehara J, Nakamura M, Fujita K, Kusano K, Nishishita S, Araki K, Tanaka H, Yanase K, Ichihashi N. Shoulder horizontal abduction stretching effectively increases shear elastic modulus of pectoralis minor muscle. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2017 Jul 1;26(7):1159-65. | </ref><ref>Morais N, Cruz J. The pectoralis minor muscle and shoulder movement-related impairments and pain: Rationale, assessment and management. Physical Therapy in Sport. 2016 Jan 1;17:1-3.</ref> | ||
Stabilization exercises based on stretching and strengthening to optimize scapular kinematics, and improve muscle strength and joint position sense <ref name=":6">Struyf F, Nijs J, Meeus M, Roussel NA, Mottram S, Truijen S, Meeusen R. Does scapular positioning predict shoulder pain in recreational overhead athletes?. International journal of sports medicine. 2013 Jul 3:75-82.</ref> <ref>Başkurt Z, Başkurt F, Gelecek N, Özkan MH. The effectiveness of scapular stabilization exercise in the patients with subacromial impingement syndrome. Journal of back and musculoskeletal rehabilitation. 2011 Jan 1;24(3):173-9.</ref> <ref name=":5">Turgut E, Duzgun I, Baltaci G. Effects of scapular stabilization exercise training on scapular kinematics, disability, and pain in subacromial impingement: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2017 Oct 1;98(10):1915-23.</ref>: Closed and open kinetic chain exercises, including [[Pushups|push-ups]], lawnmower exercises, and resisted scapular retraction. <ref name=":6" /> <ref name=":5" /> | |||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|Ns6-J8MMMcw|250}} </div> | <div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|Ns6-J8MMMcw|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>MoveMend Rehab and Performance. Lawnmower Shoulder Exercise - Physical Therapy Exercises for Shoulder Rehabilitation Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ns6-J8MMMcw</ref></div></div> | ||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|3AZ_iF-_RFE|250}} </div> | <div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|3AZ_iF-_RFE|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>stoneclinicPT. Shoulder Scapular Retraction Exercise. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3AZ_iF-_RFE</ref></div></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
The serratus anterior and trapezius muscles play a key role in scapular stabilisation. They act as a force couple during upper extremity movements and are particularly important in the overhead position. <ref>Magee DJ. [https://books.google.com.tr/books?hl=en&lr=&id=cxu0BQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Magee+DJ.+Orthopedic+Physical+Assessment-E-Book.+Elsevier+Health+Sciences%3B+2013+Dec+1.&ots=mrFMzSzzZr&sig=tsQeI7gDR-_PTzqLRX6W395FGC4&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false Orthopedic Physical Assessment-E-Book.] Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013 Dec 1.</ref><ref>BAGG SD, FORREST WJ. Electromyographic study of the scapular rotators during arm abduction in the scapular plane. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 1986 Jun 1;65(3):111-24.</ref> <ref>Magarey ME, Jones MA. Dynamic evaluation and early management of altered motor control around the shoulder complex. Manual therapy. 2003 Nov 1;8(4):195-206.</ref> Also, they are the main muscles that cause dyskinesia, <ref name=":0" /> so they should be considered well in rehabilitation. | |||
The [[Pushups|push-ups]] on a stable surface stretch the serratus anterior and improve the general muscle strength with a Red Cord sling. The push-ups on an unstable surface increase the trapezius activation while decreasing the serratus anterior activation. <ref>De Mey, K.; Danneels, L.; Cagnie, B.; Borms, D.; T’Jonck, Z.; Van Damme, E.; Cools, A.M. [https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/fulltext/2014/06000/shoulder_muscle_activation_levels_during_four.17.aspx Shoulder muscle activation levels during four closed kinetic chain exercises with and without Redcord slings.] J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1626–1635. [CrossRef]</ref><ref>Pirauá AL, Pitangui AC, Silva JP, dos Passos MH, de Oliveira VM, Batista LD, de Araújo RC. Electromyographic analysis of the serratus anterior and trapezius muscles during push-ups on stable and unstable bases in subjects with scapular dyskinesis. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2014 Oct 1;24(5):675-81. | |||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
Shrug exercises activate the upper and lower trapezius and increase the upward rotation angle. So they are useful for the patient with SD and corresponding scapular downward rotation syndrome. <ref>Pizzari T, Wickham J, Balster S, Ganderton C, Watson L. Modifying a shrug exercise can facilitate the upward rotator muscles of the scapula. Clinical biomechanics. 2014 Feb 1;29(2):201-5.</ref><ref>Lee JH, Cynn HS, Choi WJ, Jeong HJ, Yoon TL. Various shrug exercises can change scapular kinematics and scapular rotator muscle activities in subjects with scapular downward rotation syndrome. Human movement science. 2016 Feb 1;45:119-29.</ref> But, this exercise should not be in the first 4-6 weeks of rehabilitation, or it can delay the restoration of scapular muscle balance. <ref name=":9" /> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|YT6qn6HVQyE}} | {{#ev:youtube|YT6qn6HVQyE}}<ref>Rehab My Patient. How to do shoulder shrugs. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YT6qn6HVQyE</ref> | ||
A review article about the effects of [[Kinesio Taping|Kinesio taping]] <ref name=":2" /> concluded that Kinesio taping over the upper and lower trapezius could improve the scapular muscle balance and increase the upward scapular rotation in patients with type 2 SD. <ref>Huang TS, Ou HL, Lin JJ. Effects of trapezius kinesio taping on scapular kinematics and associated muscular activation in subjects with scapular dyskinesis. Journal of Hand Therapy. 2019 Jul 1;32(3):345-52.</ref> | |||
== Presentations == | == Presentations == | ||
Latest revision as of 04:05, 26 January 2024
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Scapular dyskinesia (SD) is a term that describes a physical impairment in which the scapula's position and motion are altered. The words dyskinesia or dysrhythmia are often used instead of dyskinesia. [1][2][3] One of the other terms used for SD is scapular winging, but it is a different condition that results in scapular dyskinesia usually after a long thoracic or spinal accessory nerve injury. [4][5][6]
SD can be seen in overhead athletes or patients with shoulder pathology such as rotator cuff disease, glenohumeral instability, impingement syndrome, and labral tears as well as in healthy people. [7] [8]Patients with shoulder pain have a higher incidence of SD, though whether SD causes shoulder pain or shoulder pain causes SD is unclear and requires further investigation. Some research suggests that SD can be predictive of future shoulder pain despite absence of symptoms at present[9].
Scapular Biomechanics[edit | edit source]
Movements of the scapula can be broken up into 3 motions and 2 translations.
The motions are:
- Upward/downward rotation
- Internal/ external rotation
- Anterior/posterior tilt
The translations are:
- Upward/downward sliding on the thorax
- Medial/lateral sliding around the curvature of the thorax
Common patterns of the scapula are called scapular retraction (external rotation, posterior tilt, upward rotation and medial translation), protraction (internal rotation, anterior tilt, downward rotation and lateral translation), and shrug (upward translation, anterior tilt, and internal rotation). [10][11]
During the normal overhead upper extremity elevation with internal/external rotation being minimal until 100°, primary scapular movement is upward rotation and secondary scapular movement is posterior tilt. [12][13]
The coordinated movement between the scapula and humerus which is necessary for efficient arm movement is termed scapulohumeral rhythm. [14] An early study [15] found an overall ratio of 2:1 between glenohumeral elevation and scapular upward rotation. Another study [13] found that during the scapular plane elevation of the arm, there was a consistent pattern of scapular upward rotation, posterior tilting, and external rotation along with clavicular elevation and retraction.
The altered mechanics in SD are increased scapular anterior tilt, increased scapular internal rotation, and altered scapular upward rotation. [16]
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The causes of SD are many, but they can be looked at in these three groups:
- Shoulder-related;
- Neck-related;
- Posture-related. [17]
1. Shoulder-related: Shoulder pathologies associated with SD (acromioclavicular instability, shoulder impingement, rotator cuff injuries, glenoid labrum injuries, clavicle fractures [18][11]), inflexibility of the pectoralis minor and short head of the biceps, and stiffness of the posterior glenohumeral capsule can be counted for this group. [19][20][13]
2. Neck-related: Mechanical neck pain syndromes and cervical nerve root-related syndromes. [17]
3. Posture-related: Excessive thoracic kyphosis and cervical lordosis, which are the changes that athletes are more tend to show are related causes of SD. [21]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with SD can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. [22] Symptoms of SD can be one or a combination of the following: [23]
- Anterior shoulder pain
- Posterosuperior scapular pain (may radiate into the ipsilateral para spinous cervical region or radicular/thoracic outlet-type symptoms in the affected upper extremity can be found)
- Superior shoulder pain
- Proximal lateral arm pain
Clinical Examination[edit | edit source]
There is no standard clinical assessment of SD. However, some assessment methods have proven to be reliable: [8]
Classification of Dyskinesia Types[edit | edit source]
Noting shoulder assymmetry is generally reliable. Based on visual observation, one of the three types of dyskinesia can be determined during arm movements in terms of the presence of SD: [24] [25]
- Type 1: Inferior angle prominence (i.e. anterior tilt of the scapula)
- Type 2: Medial border prominence (i.e. winging of the scapula)
- Type 3: Early scapular elevation or excessive/insufficient upward rotation during arm elevation
Manually Assisted Movements of Scapula[edit | edit source]
To determine the role of the scapula position in shoulder pain two tests that apply manual assistance to the scapula are The Scapular Assistance Test (SAT) and The Scapular Reposition (Retraction) Test (SRT). [26]
In the SAT, the patient is asked to do arm flexion or abduction and rate their pain on the numerical pain rating scale. The same process is repeated while the examiner pushes upward and laterally on the inferior angle to facilitate upward rotation, and pulls the superior aspect of the scapula to produce posterior tilt. If two or more points of pain decrease after assisted movement, the test is positive. [27][28][29][30][31] This suggests that scapula dyskinesia has a role in influencing the patient's pain. Taping techniques can then be used to recreate this same effect of improving scapula kinematics[32][33].
In SRT, the patient is asked to do 90 degrees of flexion with shoulder internal rotation while the examiner stabilizes the medial scapular border with one hand. Then the patient is asked to hold the position while the examiner is applying resistance with the other hand. If the pain felt by the patient is decreased or the strength is increased with the assistance the test is positive. [34] This test is described by Kibler et al [35] to establish the scapular retraction stabilization on the improvement of supraspinatus strength deficits in patients with SD. [36][37]
Assessment of Surrounding Structures[edit | edit source]
The structures around the scapula can be assessed for pain, loss of function, soft tissue laxity and muscle power. [34]
The sternoclavicular (SC) and acromioclavicular (AC) joints should be assessed for instability. AC joint can be assessed for anterior-posterior (AP) laxity by mobilizing the acromion in an AP direction while stabilizing the clavicle. [34][2] Manual muscle tests for rotator cuff/biceps muscles can be applied. The infraspinatus strength test shows good reliability to assess infraspinatus weakness due to SD. [8]
Muscle Tests[edit | edit source]
Three specific muscle tests that the clinician observes the scapula position and considers the scapular muscle weakness if the break in the position and scapular movement occurs are: [3]
- Manual resistance of the arm at 130° of flexion (for the serratus anterior) [38][39]
- Manual resistance of the arm at 130-150° of abduction (for the lower and middle trapezius) [38]
- Extension of the arm at the side (for the rhomboid) [40]
Core Evaluation[edit | edit source]
With the low row test, if core and hip strength facilitate the scapular motion can be assessed. The examiner stands behind the patient. The patient is asked to do slight arm extension and resist the movement of the arm into flexion. The same movement is repeated with gluteal muscle contraction. If the strength increase with gluteal contraction core/lower extremity strengthening can be added to the treatment plan. [3]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
DASH is a measure that includes 30 items and assesses the disability and symptoms of the upper limb in patients with musculoskeletal disorders. [41]
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
Treatment of SD aims at the restoration of scapular retraction, posterior tilt and external rotation. Specific exercises for scapular rehabilitation are [8]:
Flexibility exercises: To increase the flexibility of the pectoralis minor and the external rotation and posterior tilt of the scapula, shoulder horizontal abduction at 90 degrees and 150 degrees of elevation. [42][43][44]
Stabilization exercises based on stretching and strengthening to optimize scapular kinematics, and improve muscle strength and joint position sense [45] [46] [47]: Closed and open kinetic chain exercises, including push-ups, lawnmower exercises, and resisted scapular retraction. [45] [47]
The serratus anterior and trapezius muscles play a key role in scapular stabilisation. They act as a force couple during upper extremity movements and are particularly important in the overhead position. [50][51] [52] Also, they are the main muscles that cause dyskinesia, [17] so they should be considered well in rehabilitation.
The push-ups on a stable surface stretch the serratus anterior and improve the general muscle strength with a Red Cord sling. The push-ups on an unstable surface increase the trapezius activation while decreasing the serratus anterior activation. [53][54]
Shrug exercises activate the upper and lower trapezius and increase the upward rotation angle. So they are useful for the patient with SD and corresponding scapular downward rotation syndrome. [55][56] But, this exercise should not be in the first 4-6 weeks of rehabilitation, or it can delay the restoration of scapular muscle balance. [3]
A review article about the effects of Kinesio taping [8] concluded that Kinesio taping over the upper and lower trapezius could improve the scapular muscle balance and increase the upward scapular rotation in patients with type 2 SD. [58]
Presentations[edit | edit source]
 |
Advanced Exercises for the Upper Quarter: A How To Guide for Scapular Motor Control Rehabilitation
This presentation, created by Stephanie Pascoe as part of the OMPT Fellowship in 2010, describes a how to guide for scapulothoracic rehabilitation. It includes some great animations! |
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Depreli Ö, Angın E. Review of scapular movement disorders among office workers having ergonomic risk. Journal of back and musculoskeletal rehabilitation. 2018 Jan 1;31(2):371-80.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kibler BW, Sciascia A, Wilkes T. Scapular dyskinesis and its relation to shoulder injury. JAAOS-journal of the American academy of orthopaedic surgeons. 2012 Jun 1;20(6):364-72.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Sciascia A, Kibler WB. Current Views of Scapular Dyskinesis and its Possible Clinical Relevance. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy. 2022;17(2):117.
- ↑ Humphrey CS, Sears BW, Curtin MJ. An anthropometric analysis to derive formulae for calculating the dimensions of anatomically shaped humeral heads. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2016 Sep 1;25(9):1532-41.
- ↑ Kibler WB, Sciascia AD. Disorders of the scapula and their role in shoulder injury. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. 2017:128-30.
- ↑ Didesch JT, Tang P. Anatomy, etiology, and management of scapular winging. The Journal of hand surgery. 2019 Apr 1;44(4):321-30.
- ↑ Teixeira DC, Alves L, Gutierres M. The role of scapular dyskinesis on rotator cuff tears: a narrative review of the current knowledge. EFORT Open Reviews. 2021 Oct;6(10):932.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Giuseppe LU, Laura RA, Berton A, Candela V, Massaroni C, Carnevale A, Stelitano G, Schena E, Nazarian A, DeAngelis J, Denaro V. Scapular dyskinesis: from basic science to ultimate treatment. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2020 Apr;17(8):2974.
- ↑ Hickey D, Solvig V, Cavalheri V, Harrold M, Mckenna L. Scapular dyskinesis increases the risk of future shoulder pain by 43% in asymptomatic athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. British journal of sports medicine. 2017 Jul 22.
- ↑ Barcia AM, Makovicka JL, Spenciner DB, Chamberlain AM, Jacofsky MC, Gabriel SM, Moroder P, von Rechenberg B, Sengun MZ, Tokish JM, MRAB Study Group. Scapular motion in the presence of rotator cuff tears: a systematic review. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2021 Jul 1;30(7):1679-92.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Kibler WB, Sciascia A. Current concepts: scapular dyskinesis. British journal of sports medicine. 2010 Apr 1;44(5):300-5.
- ↑ Ludewig PM et al. Motion of the shoulder complex during multiplaner humeral elevation. J Bone Joint Surg. Am.2009;91:378-389.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 McClure PW et al. Direct 3-dimentional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2001:10:269-277.
- ↑ Kibler WB, Ludewig PM, McClure PW, Michener LA, Bak K, Sciascia AD. Clinical implications of scapular dyskinesis in shoulder injury: the 2013 consensus statement from the ‘Scapular Summit’. British journal of sports medicine. 2013 Sep 1;47(14):877-85.
- ↑ Inman VT, Saunders JD, Abbott LC. Observations on the function of the shoulder joint. JBJS. 1944 Jan 1;26(1):1-30.
- ↑ Kibler WB, Stone AV, Zacharias A, Grantham WJ, Sciascia AD. Management of scapular dyskinesis in overhead athletes. Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine. 2021 Mar 1;29(1):150797.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Panagiotopoulos AC, Crowther IM. Scapular Dyskinesia, the forgotten culprit of shoulder pain and how to rehabilitate. SICOT-J. 2019;5.
- ↑ Burkhart SS, Morgan CD, Kibler WB. The disabled throwing shoulder: spectrum of pathology Part I: pathoanatomy and biomechanics. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery. 2003 Apr 1;19(4):404-20.
- ↑ Borstad JD. Resting position variables at the shoulder: evidence to support a posture-impairment association. Physical Therapy. 2006 Apr 1;86(4):549-57.
- ↑ Borstad JD, Ludewig PM. The effect of long versus short pectoralis minor resting length on scapular kinematics in healthy individuals. Journal of orthopaedic & sports physical therapy. 2005 Apr;35(4):227-38.
- ↑ Crosbie J, Kilbreath SL, Hollmann L, York S. Scapulohumeral rhythm and associated spinal motion. Clinical biomechanics. 2008 Feb 1;23(2):184-92.
- ↑ Pires ED, Camargo PR. Analysis of the kinetic chain in asymptomatic individuals with and without scapular dyskinesis. Clinical Biomechanics. 2018 May 1;54:8-15.
- ↑ Burkhart SS, Morgan CD, Kibler WB. The disabled throwing shoulder: spectrum of pathology Part III: The SICK scapula, scapular dyskinesis, the kinetic chain, and rehabilitation. Arthroscopy. 2003 Jul 1;19(6):641-61.
- ↑ Uhl TL, Kibler WB, Gecewich B, Tripp BL. Evaluation of clinical assessment methods for scapular dyskinesis. Arthroscopy: the journal of arthroscopic & related surgery. 2009 Nov 1;25(11):1240-8.
- ↑ Kibler WB, Uhl TL, Maddux JW, Brooks PV, Zeller B, McMullen J. Qualitative clinical evaluation of scapular dysfunction: a reliability study. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2002 Nov 1;11(6):550-6.
- ↑ Kopkow C, Lange T, Schmitt J, Kasten P. Interrater reliability of the modified scapular assistance test with and without handheld weights. Manual therapy. 2015 Dec 1;20(6):868-74.
- ↑ Kibler WB, Sciascia AD. Introduction to the second international conference on scapular dyskinesis in shoulder injury—the ‘Scapular summit’report of 2013. British journal of sports medicine. 2013 Sep 1;47(14):874-.
- ↑ Kibler BW, McMullen J. Scapular dyskinesis and its relation to shoulder pain. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2003 Mar 1;11(2):142-51.
- ↑ Kibler WB. The scapula in rotator cuff disease. Rotator Cuff Tear. 2012;57:27-40.
- ↑ Rabin A, Irrgang JJ, Fitzgerald GK, Eubanks A. The intertester reliability of the scapular assistance test. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 2006 Sep;36(9):653-60.
- ↑ Rabin A, Chechik O, Dolkart O, Goldstein Y, Maman E. A positive scapular assistance test is equally present in various shoulder disorders but more commonly found among patients with scapular dyskinesis. Physical Therapy in Sport. 2018 Nov 1;34:129-35.
- ↑ Shih YF, Lee YF, Chen WY. Effects of Kinesiology Taping on Scapular Reposition Accuracy, Kinematics, and Muscle Activity in Athletes With Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. J Sport Rehabil. 2018 Nov 1;27(6):560-569. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2017-0043. Epub 2018 Oct 15. PMID: 29364027.
- ↑ Ozer ST, Karabay D, Yesilyaprak SS. Taping to Improve Scapular Dyskinesis, Scapular Upward Rotation, and Pectoralis Minor Length in Overhead Athletes. J Athl Train. 2018 Nov;53(11):1063-1070. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-342-17. Epub 2019 Jan 7. PMID: 30615491; PMCID: PMC6333226.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Kilber WB, Sciascia A (2010) Current concepts: scapular dyskinesis. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 44, 300–305. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ↑ Kibler WB, Sciascia A, Dome D. Evaluation of apparent and absolute supraspinatus strength in patients with shoulder injury using the scapular retraction test. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Oct;34(10):1643-7.
- ↑ Smith J, Dietrich CT, Kotajarvi BR, Kaufman KR. The effect of scapular protraction on isometric shoulder rotation strength in normal subjects. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2006 May 1;15(3):339-43.
- ↑ Khazzam M, Gates ST, Tisano BK, Kukowski N. Diagnostic accuracy of the scapular retraction test in assessing the status of the rotator cuff. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 2018 Sep 25;6(10):2325967118799308.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Michener LA, Boardman ND, Pidcoe PE, Frith AM. Scapular muscle tests in subjects with shoulder pain and functional loss: reliability and construct validity. Physical therapy. 2005 Nov 1;85(11):1128-38.
- ↑ Ekstrom RA, Soderberg GL, Donatelli RA. Normalization procedures using maximum voluntary isometric contractions for the serratus anterior and trapezius muscles during surface EMG analysis. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2005 Aug 1;15(4):418-28.
- ↑ Ginn KA, Halaki M, Cathers I. Revision of the Shoulder Normalization Tests is required to include rhomboid major and teres major. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2011 Dec;29(12):1846-9.
- ↑ Franchignoni F, Vercelli S, Giordano A, Sartorio F, Bravini E, Ferriero G. Minimal clinically important difference of the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand outcome measure (DASH) and its shortened version (QuickDASH). Journal of orthopaedic & sports physical therapy. 2014 Jan;44(1):30-9.
- ↑ Umehara J, Nakamura M, Nishishita S, Tanaka H, Kusano K, Ichihashi N. Scapular kinematic alterations during arm elevation with decrease in pectoralis minor stiffness after stretching in healthy individuals. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2018 Jul 1;27(7):1214-20.
- ↑ Umehara J, Nakamura M, Fujita K, Kusano K, Nishishita S, Araki K, Tanaka H, Yanase K, Ichihashi N. Shoulder horizontal abduction stretching effectively increases shear elastic modulus of pectoralis minor muscle. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2017 Jul 1;26(7):1159-65.
- ↑ Morais N, Cruz J. The pectoralis minor muscle and shoulder movement-related impairments and pain: Rationale, assessment and management. Physical Therapy in Sport. 2016 Jan 1;17:1-3.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Struyf F, Nijs J, Meeus M, Roussel NA, Mottram S, Truijen S, Meeusen R. Does scapular positioning predict shoulder pain in recreational overhead athletes?. International journal of sports medicine. 2013 Jul 3:75-82.
- ↑ Başkurt Z, Başkurt F, Gelecek N, Özkan MH. The effectiveness of scapular stabilization exercise in the patients with subacromial impingement syndrome. Journal of back and musculoskeletal rehabilitation. 2011 Jan 1;24(3):173-9.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Turgut E, Duzgun I, Baltaci G. Effects of scapular stabilization exercise training on scapular kinematics, disability, and pain in subacromial impingement: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2017 Oct 1;98(10):1915-23.
- ↑ MoveMend Rehab and Performance. Lawnmower Shoulder Exercise - Physical Therapy Exercises for Shoulder Rehabilitation Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ns6-J8MMMcw
- ↑ stoneclinicPT. Shoulder Scapular Retraction Exercise. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3AZ_iF-_RFE
- ↑ Magee DJ. Orthopedic Physical Assessment-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013 Dec 1.
- ↑ BAGG SD, FORREST WJ. Electromyographic study of the scapular rotators during arm abduction in the scapular plane. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 1986 Jun 1;65(3):111-24.
- ↑ Magarey ME, Jones MA. Dynamic evaluation and early management of altered motor control around the shoulder complex. Manual therapy. 2003 Nov 1;8(4):195-206.
- ↑ De Mey, K.; Danneels, L.; Cagnie, B.; Borms, D.; T’Jonck, Z.; Van Damme, E.; Cools, A.M. Shoulder muscle activation levels during four closed kinetic chain exercises with and without Redcord slings. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1626–1635. [CrossRef]
- ↑ Pirauá AL, Pitangui AC, Silva JP, dos Passos MH, de Oliveira VM, Batista LD, de Araújo RC. Electromyographic analysis of the serratus anterior and trapezius muscles during push-ups on stable and unstable bases in subjects with scapular dyskinesis. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2014 Oct 1;24(5):675-81.
- ↑ Pizzari T, Wickham J, Balster S, Ganderton C, Watson L. Modifying a shrug exercise can facilitate the upward rotator muscles of the scapula. Clinical biomechanics. 2014 Feb 1;29(2):201-5.
- ↑ Lee JH, Cynn HS, Choi WJ, Jeong HJ, Yoon TL. Various shrug exercises can change scapular kinematics and scapular rotator muscle activities in subjects with scapular downward rotation syndrome. Human movement science. 2016 Feb 1;45:119-29.
- ↑ Rehab My Patient. How to do shoulder shrugs. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YT6qn6HVQyE
- ↑ Huang TS, Ou HL, Lin JJ. Effects of trapezius kinesio taping on scapular kinematics and associated muscular activation in subjects with scapular dyskinesis. Journal of Hand Therapy. 2019 Jul 1;32(3):345-52.