Rectus Abdominis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User: | '''Original Editor '''- [[User: Asma Alshehri |Asma Alshehri]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== | == Introduction == | ||
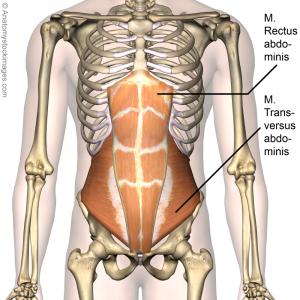
[[File:Torso-rectus-abdominis-transversus-abdominis.png|right|frameless]] | |||
The Rectus Abdominis makes up the top layer of your abdominal muscles, commonly referred to as your "six-pack." It is two flat and parallel muscles separated by linea alba (a connective tissue). It acts to flex the spinal column, tense the anterior wall of the [[Abdominal Muscle Anatomy|abdomen]] and assist in compressing the contents of the abdomen. | |||
Rectus | * The [[Rectus Sheath]] is a multilayered aponeurosis, being a durable, resilient, fibrous compartment that contains both the rectus abdominis muscle and the pyramidalis muscle<ref>Sevensma KE, Leavitt L, Pihl KD. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Rectus Sheath.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537153/ (accessed 19.12.2021)</ref>. | ||
== Origin and Insertion == | |||
Originating from the [[Pubis|pubic crest]] (between pubic tubercle and pubic symphysis) at the lower end the muscle inserts with the help of fibers to the 5th to 7th coastal [[cartilage]] and the xiphoid process of the sternum. The [[muscle]] is interrupted (but not all the way through) by three (or more) fibrous bands called the tendinous intersections, | |||
# The most superior intersection is generally at the level of the xiphoid, | |||
# The lower intersection is at the level of umbilicus | |||
# The middle one is at the midway between them<ref name="Anatomy">Helen J.Hislop Jacqueline Montgomery,Muscle Testing,2007,8th edition.</ref>. | |||
=== Nerve === | |||
[[Thoracic Spinal Nerves|Spinal nerves T7 to T12]] (ventral rami) . T7 innervates fibers above the superior tendinous intersection, T8 innervates fibers between the superior and middle intersections and T9 innervates fibers between the middle and lower intersection. | |||
=== Artery === | |||
Superior and inferior epigastric [[arteries]]. (Also, small terminal branches from the lower three posterior intercostal arteries, subcostal artery, posterior lumbar arteries and the deep circumflex artery may provide some contributions)<ref>Rectus Abdominis,https://www.mananatomy.com/body-systems/muscular-system/rectus-abdominis, (accessed 23 April 2017)</ref> | |||
== Function == | |||
The main actions for rectus abdominis are: | |||
* Flexion of the trunk (flexion of thoracic and lumber spine), while it works by drawing pubic symphysis and sternum toward each other. | |||
* Tense the anterior wall of the [[Abdominal Muscle Anatomy|abdomen]] and assist in compressing the contents of the abdomen | |||
* It works on posterior [[Pelvic Tilt|pelvic tilt]] with other abdominal muscles.<ref name="Anatomy" /> | |||
* Play a role in core stability. | |||
== Physiotherapy Relevance == | |||
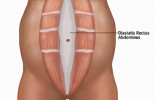
Are part of the core muscles abdominalis recti play a role in [[Core Stability|core stability]]. The core muscles include the rectus abdominis, [[Transversus Abdominis|transversus abdominis]], [[Erector Spinae|erector spinae]] and [[External Abdominal Oblique|obliques]], which together act like a natural weight belt to protect the lower back from injury. Weak core muscles can predispose persons to spinal problems.[[Image:Diastasis 18.png|right|200x100px|alt=|frameless]][[Diastasis Recti]] Abdominis is a midline separation at the linea alba. A palpable midline gap of more than 2.5 cm or any visible bulging on exertion is considered as a diastasis and commonly occurs around the umbilicus, but can occur anywhere between the xiphoid process and pubic bone.<ref>Diastasis recti abdominis, https://www.coreconcepts.com.sg/condition/diastasis-recti-abdominis/ (accessed 14 April 2017)</ref> | |||
Newborn babies also can have this belly spread and it should go away on its own.<ref name="Most">Abdominal separation (diastasis recti), http://www.webmd.com/baby/guide/abdominal-separation-diastasis-recti (accessed 14 April 2017)</ref> It is most seen often in premature and African American infants.<ref>Diastasis recti, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001602.htm (accessed 14 April 2017)</ref> | |||
== | == Assessment == | ||
Palpation: | |||
Have the patient in a supine lying position with a pillow under knees to ensure the relaxation of the muscle, palpation will be along the muscle starting from the xiphoid process and the adjacent ribs with going down to the pubis bone on both sides. Ask the patient to raise (or try to raise) the trunk and then relax. | |||
Muscle power: | |||
We mainly need to assess the strength of the abdominal muscles rather than its flexibility because having weak abdominal muscles will come out later with serious of problems. | We mainly need to assess the strength of the abdominal muscles rather than its flexibility because having weak abdominal muscles will come out later with serious of problems. | ||
MMT for rectus abdominis is usually done by asking the patient to bring his/her trunk against gravity from supine position until the inferior angles of the scapula are off the table, and the therapist will start grading according to the patient’s performance and ability to do the movement as instructed. | [[Muscle Strength Testing|MMT]] for rectus abdominis is usually done by asking the patient to bring his/her trunk against gravity from supine position until the inferior angles of the scapula are off the table, and the therapist will start grading according to the patient’s performance and ability to do the movement as instructed. | ||
Grading from 5 to 1 will be based on the level of ability to bear the resistance (the resistance here is generated by the patient's arms behind the head, arms crossed over chest or arms overstretched above the plane of the body<ref name="Anatomy" />) to only minimal contraction felt by the examiner's hand. | Grading from 5 to 1 will be based on the level of ability to bear the resistance (the resistance here is generated by the patient's arms behind the head, arms crossed over chest or arms overstretched above the plane of the body<ref name="Anatomy" />) to only minimal contraction felt by the examiner's hand. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Strengthening exercises: | Strengthening exercises: | ||
*Sit up exercise: Requires raising the trunk against gravity to the midline and slowly lower it down repeatedly in multiple sets. In order to isolate the rectus abdominis, do the exercise while bending the knees to minimize the engagement of hip flexors. (For rectus abdominis, raising the trunk should be performed straightly) | |||
== References == | |||
= References = | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:01, 19 December 2021
Original Editor - Asma Alshehri
Top Contributors - Asma Alshehri, Lucinda hampton, Admin, WikiSysop and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The Rectus Abdominis makes up the top layer of your abdominal muscles, commonly referred to as your "six-pack." It is two flat and parallel muscles separated by linea alba (a connective tissue). It acts to flex the spinal column, tense the anterior wall of the abdomen and assist in compressing the contents of the abdomen.
- The Rectus Sheath is a multilayered aponeurosis, being a durable, resilient, fibrous compartment that contains both the rectus abdominis muscle and the pyramidalis muscle[1].
Origin and Insertion[edit | edit source]
Originating from the pubic crest (between pubic tubercle and pubic symphysis) at the lower end the muscle inserts with the help of fibers to the 5th to 7th coastal cartilage and the xiphoid process of the sternum. The muscle is interrupted (but not all the way through) by three (or more) fibrous bands called the tendinous intersections,
- The most superior intersection is generally at the level of the xiphoid,
- The lower intersection is at the level of umbilicus
- The middle one is at the midway between them[2].
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Spinal nerves T7 to T12 (ventral rami) . T7 innervates fibers above the superior tendinous intersection, T8 innervates fibers between the superior and middle intersections and T9 innervates fibers between the middle and lower intersection.
Artery[edit | edit source]
Superior and inferior epigastric arteries. (Also, small terminal branches from the lower three posterior intercostal arteries, subcostal artery, posterior lumbar arteries and the deep circumflex artery may provide some contributions)[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
The main actions for rectus abdominis are:
- Flexion of the trunk (flexion of thoracic and lumber spine), while it works by drawing pubic symphysis and sternum toward each other.
- Tense the anterior wall of the abdomen and assist in compressing the contents of the abdomen
- It works on posterior pelvic tilt with other abdominal muscles.[2]
- Play a role in core stability.
Physiotherapy Relevance[edit | edit source]
Are part of the core muscles abdominalis recti play a role in core stability. The core muscles include the rectus abdominis, transversus abdominis, erector spinae and obliques, which together act like a natural weight belt to protect the lower back from injury. Weak core muscles can predispose persons to spinal problems.
Diastasis Recti Abdominis is a midline separation at the linea alba. A palpable midline gap of more than 2.5 cm or any visible bulging on exertion is considered as a diastasis and commonly occurs around the umbilicus, but can occur anywhere between the xiphoid process and pubic bone.[4]
Newborn babies also can have this belly spread and it should go away on its own.[5] It is most seen often in premature and African American infants.[6]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation:
Have the patient in a supine lying position with a pillow under knees to ensure the relaxation of the muscle, palpation will be along the muscle starting from the xiphoid process and the adjacent ribs with going down to the pubis bone on both sides. Ask the patient to raise (or try to raise) the trunk and then relax.
Muscle power:
We mainly need to assess the strength of the abdominal muscles rather than its flexibility because having weak abdominal muscles will come out later with serious of problems.
MMT for rectus abdominis is usually done by asking the patient to bring his/her trunk against gravity from supine position until the inferior angles of the scapula are off the table, and the therapist will start grading according to the patient’s performance and ability to do the movement as instructed.
Grading from 5 to 1 will be based on the level of ability to bear the resistance (the resistance here is generated by the patient's arms behind the head, arms crossed over chest or arms overstretched above the plane of the body[2]) to only minimal contraction felt by the examiner's hand.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Strengthening exercises:
- Sit up exercise: Requires raising the trunk against gravity to the midline and slowly lower it down repeatedly in multiple sets. In order to isolate the rectus abdominis, do the exercise while bending the knees to minimize the engagement of hip flexors. (For rectus abdominis, raising the trunk should be performed straightly)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Sevensma KE, Leavitt L, Pihl KD. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Rectus Sheath.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537153/ (accessed 19.12.2021)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Helen J.Hislop Jacqueline Montgomery,Muscle Testing,2007,8th edition.
- ↑ Rectus Abdominis,https://www.mananatomy.com/body-systems/muscular-system/rectus-abdominis, (accessed 23 April 2017)
- ↑ Diastasis recti abdominis, https://www.coreconcepts.com.sg/condition/diastasis-recti-abdominis/ (accessed 14 April 2017)
- ↑ Abdominal separation (diastasis recti), http://www.webmd.com/baby/guide/abdominal-separation-diastasis-recti (accessed 14 April 2017)
- ↑ Diastasis recti, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001602.htm (accessed 14 April 2017)