Principles of Amputation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
*Maintains muscle length and strength | *Maintains muscle length and strength | ||
*Preserves growth plates in children | *Preserves growth plates in children | ||
*Candidates for end bearing prosthesis | *Candidates for end bearing prosthesis | ||
*Proprioception | |||
Risks | Risks | ||
Revision as of 13:50, 16 March 2015
Original Editor - Lucy Coughlan as part of the WCPT Network for Amputee Rehabilitation Project
Top Contributors - Admin, Aicha Benyaich, Tarina van der Stockt, Rachael Lowe, Shaimaa Eldib, Tony Lowe, Kim Jackson, Rucha Gadgil, Lauren Lopez, Sheik Abdul Khadir, Amrita Patro, Wanda van Niekerk, Jess Bell and Simisola Ajeyalemi
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Amputation is the removal of a body extremity by trauma, prolonged constriction or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb such as a malignancy, infection or gangrene. In some cases an amputation is carried out on individuals as a preventative surgery for such problems and other people are born with amputations due to congenital disorders (link to paediatric limb deficiency page Physiopedia).
A decision to amputate a limb should be made through discussion with the multidisciplinary team - including the patient - wherever possible; in an emergency situation the decision should made based on medical need. There are a number of different investigations that can be carried out to assess the need for an amputation; these examinations assess the bones and soft tissues to establish limb viability.
- X-ray – images of bones to view fractures or disease
- Computerised Tomography (CT) scan – detailed images of bone, tissue and blood vessels
- Angiogram – outlines blood vessels
- Doppler ultrasound – occlusion of blood vessels
- Venogram and arteriogram – detailed imaging of blood vessels
These tests will help the surgeons to find out if the blood supply to the limb is intact, the lower limb is supplied by the popliteal artery which subdivides into the:
- Posterior tibial artery
- Anterior tibial artery
- Fibular artery
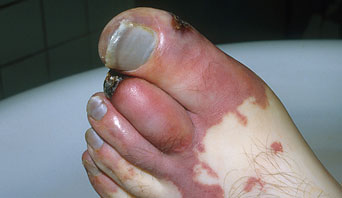
In vascular disease these arteries can become blocked or narrowed over time which reduces the circulation to the legs; this can cause pain, ulceration and blackened areas. If left untreated this can lead to gangrene or infection and an amputation is needed to avoid this becoming life threatening.
In trauma one or more of these blood vessels may be ruptured beyond repair due to the nature of the injuries sustained – e.g. in a car accident, gunshot wound or blast. In this situation an amputation is performed as the limb does not have any blood supply beyond the level of injury and is therefore deemed non-viable.
There are a number of injury severity scores that may be used in conjunction with clinical investigations to establish the likelihood of limb salvage. Examples of this include:
- Mangled Extremity Severity Score (MESS) Johansen et al. J Trauma, 1990.30: 568-73
- Nerve Injury, Ischemia, Soft-Tissue Injury, Skeletal Injury, Shock, and Age of Patient Score (NISSA) McNamara et al. J Orthop Trauma, 1994.8: 81-7
- Limb salvage index (LSI) Russell et al. Ann Surg, 1991.213: 473-81
Once a decision has been made to remove part of a limb the level of amputation needs to be decided; this can have significant consequences so there are a number of factors to take into account when planning the surgery: •
- Boundary of dead or diseased tissue - if the infection or disease is not completely eradicated the patient may need to undergo further operations or treatment so it is important that the amputation is done at a level where this can be achieved
- Suitability for prosthesis - if the patient is likely to be a candidate for prosthetic rehab the level of amputation needs to be carefully considered
- Mobility and function - it is useful to consider the patients’ pre-morbid level of mobility and function
- Cosmesis - length and shape of stump affect the aesthetic appearance
Lower Limb Amputations[edit | edit source]
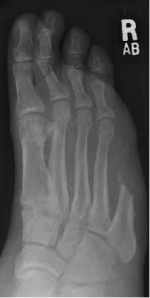
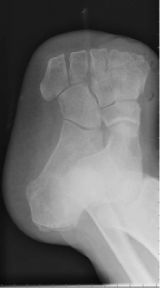
Amputations of the foot[edit | edit source]
- Toe - amputation through phalanges or disarticulation of metatarsal-phalangeal joint
- Ray - amputation of phalanges and some or all of corresponding metatarsal
- Transmetatarsal - partial foot amputation through metatarsals
- Ankle disarticulation – amputation through the ankle joint
Benefits
- Range of prosthetic options such as insoles, toe fillers or ankle-foot orthosis (exeption for ankle disarticulation)
Risks
- May need further surgery in future
- Can lead to skin breakdown and joint pain
- Cosmesis might be not accepted by the patient
|
|

|
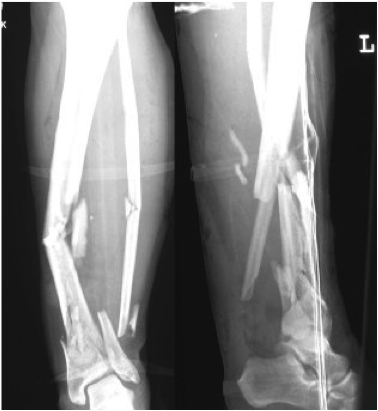
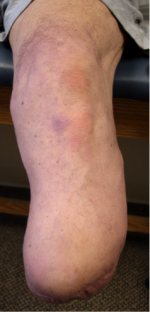
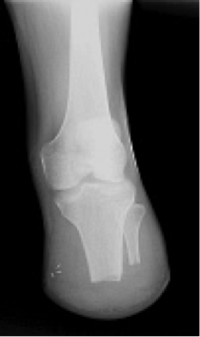
Transtibial / below knee amputation[edit | edit source]
This amputation is done through the tibia and fibula, measurements are taken and flap lines marked out. The surgeon dissects through the skin to then isolate and ligate the nerves and blood vessels. In order to minimise the risk of neuropathic pain (see complications) the nerves are dissected on tension so the end will retract back into the tissues where they can heal away from the stump end. The tibia is dissected using an oscillating saw – optimum length of residual bone is approximately 14-16cm; the tibia should be bevelled at approximately 45° to remove sharp anterior edge, the fibula should ideally be approx. 1-2 cm shorter than the tibia on a perpendicular axis. Preferred flap technique of surgeon is then used to close the wound and create functional stump - options include skew flap, long posterior flap, sagittal flap or medial flap.
This video shows one example of how a transtibial amputation can be performed.
Benefits
- Preservation of the knee joint
- Candidates for patella tendon bearing prosthesis
Risks
- At risk of knee flexion contractures (see complications)
- May need ‘bone bridge’ surgery due to distal fibula pain (see complications)
|
|
Knee disarticulation amputation[edit | edit source]
Amputation through the knee joint
Benefits
- Long lever prevents contractures
- Maintains muscle length and strength
- Preserves growth plates in children
- Candidates for end bearing prosthesis
- Proprioception
Risks
- Bulky prosthesis (see complications)
- Poor cosmesis as knee mechanism is distal to knee joint (see complications)
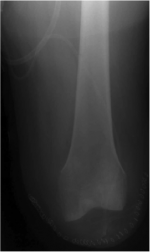
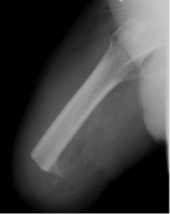
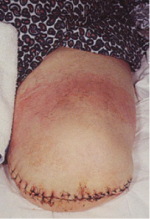
Transfemoral / above knee amputation[edit | edit source]
This amputation is done through the femur, measurements are taken and flap lines marked out. The surgeon dissects through the skin to then isolate and ligate the nerves and blood vessels. In order to minimise the risk of neuropathic pain (see complications) the nerves are dissected on tension so the end will retract back into the tissues where they can heal away from the stump end. The femur is dissected on its perpendicular axis using an oscillating saw – optimum length of residual bone is approximately 10cm proximal to the superior border of patella.
With a transfemoral amputation the distal attachments of the thigh muscles is lost, in order to preserve their function and length a myodesis may be performed to anchor the adductor (and sometimes hamstring) muscles to bone. The hamstrings and quadriceps may then be sutured together over the distal end of the femur – a technique called a myoplasty to help pad the end of the stump.
This video shows one example of how a transfemoral amputation can be performed
Benefits
- Candidate for ischial tuberosity bearing prosthesis
Risks
- Contractures (see complications)
- Prosthesis can be heavy (see complications)
|
|
Other types of amputation in the lower limb[edit | edit source]
Hip disarticulation[edit | edit source]
- Amputation of the whole lower limb through the hip joint
- Many are wheelchair users but can be considered for ischial tuberosity bearing prosthesis
Hemi-pelvectomy (hindquarter)[edit | edit source]
Amputation of the whole lower limb and ipsilateral hemi-pelvis
Likely to be a wheelchair user
Some are considered for a trunk and contralateral ischial tuberosity weight bearing prosthesis
Upper Limb Amputations[edit | edit source]
54% of all upper limb amputations are as a result of trauma; in comparison only 3% of lower limb amputations are as a result of trauma. Upper limb amputations are seen more rarely than lower limb amputations (www.limbless-statitics.org 2005/2006).
Levels of upper limb amputations:
- Fingers
- Partial hand
- Wrist disarticulation
- Transradial
- Elbow disarticulation
- Transhumeral
- Shoulder disarticulation
- Scapulo-thoracic dissociation (forequarter)
There are a range of different prosthetics available for the upper limb; these range from hooks to passive orthotics that might mainly serve an aesthetic purpose to fully mechanical and functional limbs.
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.