Peroneus Tertius: Difference between revisions
(Added links and function) |
(updated description section) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:Peroneus tertius.png|thumb|Peroneus tertius muscle]] | [[File:Peroneus tertius.png|thumb|Peroneus tertius muscle]] | ||
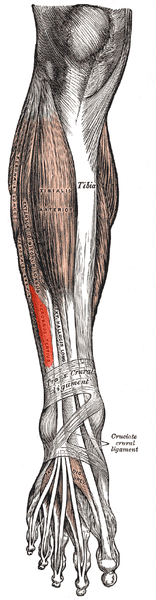
The Peroneus Tertius muscle, also called Fibularis Tertius, is one of the 3 peroneal muscles ([[Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus Muscle|peroneus longus]], [[Peroneus Brevis]]).<ref name=":0">Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.</ref> It is the most superficial muscle in the anterior compartment of leg. Other muscles in the anterior compartment include [[Tibialis Anterior|tibialis anterior]], [[Extensor Hallucis Longus|extensor hallucis longus]] and [[extensor digitorum longus]]<ref name=":3">Chaurasia BD. [https://www.pdfdrive.com/bd-chaurasia-books.html Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical.] Vol 2. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010</ref> | The Peroneus Tertius muscle, also called Fibularis Tertius, is one of the 3 peroneal muscles ([[Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus Muscle|peroneus longus]], [[Peroneus Brevis]]).<ref name=":0">Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.</ref> It is the most superficial muscle in the anterior compartment of leg. Other muscles in the anterior compartment include [[Tibialis Anterior|tibialis anterior]], [[Extensor Hallucis Longus|extensor hallucis longus]] and [[extensor digitorum longus]]<ref name=":3">Chaurasia BD. [https://www.pdfdrive.com/bd-chaurasia-books.html Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical.] Vol 2. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010</ref> | ||
The muscle's presence varies depending on the population studied. Prevalence in different populations has been reported to be the following<ref name=":4" />: | |||
* Asian populations: 38.5%-95.5% | |||
* West Asian populations: 38.5%-42% | |||
* India: 87-90% | |||
* China: 89.3% | |||
* Japan: 95.5% | |||
* Egypt: 52.8% | |||
* Tunisia: 67.7% | |||
* Chile: 49.1% | |||
* Brazil: 93.8% | |||
* Bolivia: 100% | |||
* Spain: 38.2% | |||
* Belgium: 81.5% | |||
* Britain: 92.7% | |||
* France: 90.9% | |||
* Austria: 92.9% | |||
* Poland: 85.8% | |||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
| Line 30: | Line 49: | ||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
The strength of eversion and dorsiflexion is not compromised in people who lack the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.<ref name=":1" /> | The strength of eversion and dorsiflexion is not compromised in people who lack the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.<ref name=":1">Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.</ref> | ||
Peroneus Tertius Syndrome is a condition characterized by catching, clicking, locking or popping of peroneus tertius tendon over ankle during walking. It is a rare condition of anterolateral ankle pain or rear foot pain. This could be secondary to impingement and constriction of peroneus tertius in the extensor retinaculum.<ref name=":3" /> | |||
[[ | Peroneus tertius may be affected when a person has [[Compartment Syndrome of the Lower Leg|anterior compartment syndrome]].<ref name=":3" /> | ||
The tendon may be used by surgeons as a donor for tendon transfer or tendoplasty procedures<ref name=":4" />. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 21:50, 23 March 2022
Top Contributors - Sai Kripa, Kim Jackson, Patti Cavaleri, Claire Testa, Lilian Ashraf and Oyemi Sillo
Description[edit | edit source]
The Peroneus Tertius muscle, also called Fibularis Tertius, is one of the 3 peroneal muscles (peroneus longus, Peroneus Brevis).[1] It is the most superficial muscle in the anterior compartment of leg. Other muscles in the anterior compartment include tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus[2]
The muscle's presence varies depending on the population studied. Prevalence in different populations has been reported to be the following[3]:
- Asian populations: 38.5%-95.5%
- West Asian populations: 38.5%-42%
- India: 87-90%
- China: 89.3%
- Japan: 95.5%
- Egypt: 52.8%
- Tunisia: 67.7%
- Chile: 49.1%
- Brazil: 93.8%
- Bolivia: 100%
- Spain: 38.2%
- Belgium: 81.5%
- Britain: 92.7%
- France: 90.9%
- Austria: 92.9%
- Poland: 85.8%
Origin[edit | edit source]
Distal half or third of the fibula[4]
Intermuscular septum[3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Before reaching it's insertion, the tendon passes under the extensor retinaculum of the foot with the extensor digitorum longus tendon[3].
Dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal[4]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Deep peroneal nerve[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Anterior tibial artery[2]
Function[edit | edit source]
- Assists with foot dorsiflexion and eversion[4]
- Works with extensor digitorum longus during swing phase of gait[3]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
The strength of eversion and dorsiflexion is not compromised in people who lack the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.[6]
Peroneus Tertius Syndrome is a condition characterized by catching, clicking, locking or popping of peroneus tertius tendon over ankle during walking. It is a rare condition of anterolateral ankle pain or rear foot pain. This could be secondary to impingement and constriction of peroneus tertius in the extensor retinaculum.[2]
Peroneus tertius may be affected when a person has anterior compartment syndrome.[2]
The tendon may be used by surgeons as a donor for tendon transfer or tendoplasty procedures[3].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Chaurasia BD. Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical. Vol 2. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Olewnik Ł. Fibularis Tertius: Anatomical Study and Review of the Literature. Clin Anat. 2019 Nov;32(8):1082-1093.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.
- ↑ Nabil Ebraheim. Peroneus Tertius Muscle- Everything You Need To Know-Dr.Nabil Ebraheim Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n6XWHKJg2OY [last accessed 11/05/2020]
- ↑ Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.