Peroneus Tertius: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
(Added links and function) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
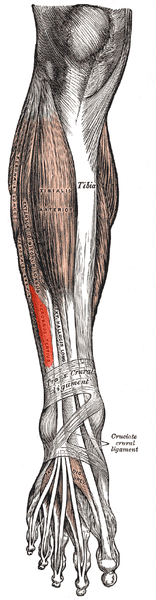
[[File:Peroneus tertius.png|thumb|Peroneus tertius muscle]] | [[File:Peroneus tertius.png|thumb|Peroneus tertius muscle]] | ||
The Peroneus Tertius muscle also called | The Peroneus Tertius muscle, also called Fibularis Tertius, is one of the 3 peroneal muscles ([[Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus Muscle|peroneus longus]], [[Peroneus Brevis]]).<ref name=":0">Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.</ref> It is the most superficial muscle in the anterior compartment of leg. Other muscles in the anterior compartment include [[Tibialis Anterior|tibialis anterior]], [[Extensor Hallucis Longus|extensor hallucis longus]] and [[extensor digitorum longus]]<ref name=":3">Chaurasia BD. [https://www.pdfdrive.com/bd-chaurasia-books.html Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical.] Vol 2. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010</ref> This muscle is absent in 5% to 17% of the human white population.<ref name=":1">Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.</ref> | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
Distal half or third of the [[fibula]] | Distal half or third of the [[fibula]]<ref name=":2">Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5449999/ The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine.] 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.</ref> | ||
Intermuscular septum<ref name=":4">Olewnik Ł. Fibularis Tertius: Anatomical Study and Review of the Literature. Clin Anat. 2019 Nov;32(8):1082-1093.</ref> | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
Before reaching it's insertion, the tendon passes under the extensor retinaculum of the foot with the [[extensor digitorum longus]] tendon<ref name=":4" />. | |||
Dorsal surface of the base of the [[Metatarsals|5th metatarsal]]<ref name=":2" /> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|n6XWHKJg2OY}}<ref>Nabil Ebraheim. Peroneus Tertius Muscle- Everything You Need To Know-Dr.Nabil Ebraheim Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n6XWHKJg2OY [last accessed 11/05/2020]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|n6XWHKJg2OY}}<ref>Nabil Ebraheim. Peroneus Tertius Muscle- Everything You Need To Know-Dr.Nabil Ebraheim Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n6XWHKJg2OY [last accessed 11/05/2020]</ref> | ||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
Deep peroneal nerve | Deep peroneal nerve<ref name=":0" /> | ||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
Anterior | Anterior tibial artery<ref name=":3" /> | ||
=== Function === | === Function === | ||
* Assists with foot dorsiflexion and eversion<ref name=":2" /> | |||
* Works with extensor digitorum longus during swing phase of gait<ref name=":4" /> | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Revision as of 21:28, 23 March 2022
Top Contributors - Sai Kripa, Kim Jackson, Patti Cavaleri, Claire Testa, Lilian Ashraf and Oyemi Sillo
Description[edit | edit source]
The Peroneus Tertius muscle, also called Fibularis Tertius, is one of the 3 peroneal muscles (peroneus longus, Peroneus Brevis).[1] It is the most superficial muscle in the anterior compartment of leg. Other muscles in the anterior compartment include tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus[2] This muscle is absent in 5% to 17% of the human white population.[3]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Distal half or third of the fibula[4]
Intermuscular septum[5]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Before reaching it's insertion, the tendon passes under the extensor retinaculum of the foot with the extensor digitorum longus tendon[5].
Dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal[4]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Deep peroneal nerve[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Anterior tibial artery[2]
Function[edit | edit source]
- Assists with foot dorsiflexion and eversion[4]
- Works with extensor digitorum longus during swing phase of gait[5]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
The strength of eversion and dorsiflexion is not compromised in people who lack the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.[3]
Peroneus Tertius Syndrome is a condition characterized by catching, clicking, locking or popping of peroneus tertius tendon over ankle during walking. It is a rare condition of anterolateral ankle pain or rear foot pain. This muscle deeply pass through the inferior extensor retinaculum and literature believe that this syndrome could be secondary to impingement and constriction of peroneus tertius.[2]
When a person gets indulge in too much of exercise, the anterior compartment muscles become painful or tender to touch leading to anterior compartment syndrome or fresher's syndrome.[2]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lippert, Lynn S. Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F A Davis Company; 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Chaurasia BD. Human Anatomy Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical. Vol 2. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, 2010
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Witvrouw E, Vanden Borre K, Willems TM, Huysmans J, Broos E, De Clercq D. The significance of peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a prospective study. The American journal of sports medicine. 2006 Jul;34(7):1159-63.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Olewnik Ł. Fibularis Tertius: Anatomical Study and Review of the Literature. Clin Anat. 2019 Nov;32(8):1082-1093.
- ↑ Nabil Ebraheim. Peroneus Tertius Muscle- Everything You Need To Know-Dr.Nabil Ebraheim Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n6XWHKJg2OY [last accessed 11/05/2020]