Paediatric Musculoskeletal Development: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Robin Tacchetti|Robin Tacchetti]] based on the course by [https://members.physio-pedia.com/course_tutor/krista-eskay/ Krista Eskay]<br> | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
== Introduction == | |||
The musculoskeletal system is influenced by many different factors as infants and children grow. It can adapt to the demands, or lack of demands, that are placed on it. The major load on bone comes from muscle forces. When muscle pull is altered due to genetic or neuromuscular conditions, alignment may be impacted. Atypical alignment can directly affect functional activities and an individual's participation.<ref name=":0">Eskay K. Paediatric Musculoskeletal Development Course. Plus. 2023.</ref> | |||
The following sections highlight key stages and changes that occur during musculoskeletal development. | |||
== Rib Cage == | |||
* Initially, the rib cage in infants is barrel-shaped and rigid; ribs are elevated and perpendicular to the spine | |||
* By 2 years, the rib cage is oblong-shaped; the ribs depress and develop an angulation in relation to their attachment with the spine - this is due to the diaphragm pull and forces from sitting/standing/walking; there is also lateral expansion of ribs (caused by breathing, the action of intercostal muscles, gravity) | |||
* Atypical = persistence of the barrel shape | |||
== Trunk == | |||
* Initially, infants have a [[Kyphosis|kyphotic]] spine | |||
* Overtime this transitions to a more "neutral" spine (as seen in adults) | |||
* Specific activities which encourage this transition: | |||
** Prone push-ups and sitting activate the posterior chain musculature (i.e. the infant is pushing into thoracic extension) | |||
** Crawling creates co-contraction of the anterior and posterior muscles (for stability)<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Changes in Alignment to Consider === | |||
===== Increased Curvature of the Spine ===== | |||
Increased curvature of the spine (i.e. [[scoliosis]]) can affect:<ref name=":0" /> | |||
* breathing | |||
* lung positioning | |||
* heart location | |||
* visceral function | |||
== Pelvis == | |||
[[File:Anterior and posterior pelvic tilt shutterstock 1952124109.jpg|thumb]] | |||
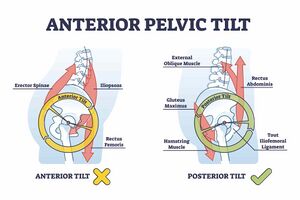
* Initially, infants have a rounded pelvis with a posterior tilt | |||
* Sitting and standing activate core muscles, which leads to the development of an anterior pelvic tilt | |||
** At 12 months old: an infant has 12 degrees of anterior pelvic tilt | |||
** At 30 months old: a child has 15 degrees of anterior tilt | |||
** Anterior tilt decreases to around adult angles (i.e. around 10 degrees) by age 8<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Lower Extremities == | |||
Typical joint patterns in infants are as follows: | |||
* Hip: flexion, abduction and lateral rotation | |||
* Knee: flexion, genu varum, medial rotation of tibia | |||
* Ankle: dorsiflexion, slight pronation<ref name=":0" /> | |||
These joints are discussed in more detail below. | |||
=== Hip === | |||
Infants are born with: | |||
* increased hip external rotation which decreases over time | |||
* hip adduction limitation | |||
* 34 degrees of hip extension limitation | |||
** as infants spend more time in prone, their anterior capsule stretches, decreasing the hip extension limitation | |||
*** [[File:Coxa.png|thumb]]at 6 weeks old infants have a 19 degree hip extension limitation | |||
*** toddlers have a 7 degree hip extension limitation | |||
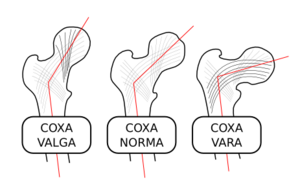
* increased coxa valga - 140-160 degrees | |||
** as become more ambulatory, femoral neck angle decreases | |||
** decreases over time to 126 degrees in adults | |||
* anteversion of the femur - 40 degrees | |||
** this decreases to 16 degrees in adults | |||
==== Changes in Alignment to Consider (Hip and Pelvis) ==== | |||
===== Hip ===== | |||
hip | * Femoral neck angle remains high - high femoral anteversion: increased risk of posterior hip dislocation | ||
* Please note that it is especially important to consider the hips in children who are non-ambulatory at the age of 30 months<ref name=":0" /> | |||
===== Increased Anterior Pelvic Tilt ===== | |||
* Abdominals and hip extensors are long | |||
* Hip flexors and lumbar extensors are short | |||
*'''Leads to''' difficulty activating abdominals and [[Gluteal Muscles|gluteus]] muscles, which can make it difficult for children to engage in functional play / activities<ref name=":0" /> | |||
===== Decreased Anterior Pelvic Tilt ===== | |||
*[[Iliopsoas]] and anterior hip capsule are long / stretched out | |||
*[[Gluteus Maximus|Gluteus maximus]] is shortened | |||
*'''Leads to''' anterior hip laxity and hip instability<ref name=":0" /> | |||
===== Pelvic Obliquity ===== | |||
* Common in individuals with [[hemiplegia]] and diplegia | |||
* Depressed hip side (shorter side): | |||
** shorter, lower extremity or increased pronation on this side | |||
** reduced stance time | |||
** reduced loading, resulting in less bony deposition, so the [[Bone|long bones]] of this leg tend to grow at a slower rate | |||
** sometimes functional ankle plantarflexion (i.e. so can reach the ground with this foot) | |||
* Longer side: | |||
** often have compensatory foot pronation | |||
** there may be medial rotation of the lower extremity and knee flexion to compensate | |||
*'''Leads to''' gait asymmetry, pelvic rotation on the shorter side<ref name=":0" /> | |||
*'''Significant increase in pelvic obliquity''' might contribute to:<ref name=":1">Karkenny AJ, Magee LC, Landrum MR, Anari JB, Spiegel D, Baldwin K. [https://journals.lww.com/jbjsoa/Fulltext/2021/03000/The_Variability_of_Pelvic_Obliquity_Measurements.13.aspx The Variability of Pelvic Obliquity Measurements in Patients with Neuromuscular Scoliosis]. JBJS Open Access. 2021 Jan;6(1).</ref> | |||
**imbalances in sitting | |||
**pain due to "impingement of the pelvis on the ribs"<ref name=":1" /> | |||
**ischial [[Pressure Ulcers|decubitus / pressure ulcers]] | |||
=== Knee === | |||
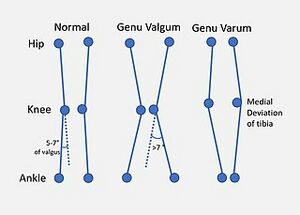
* Genu varum<ref>A El-Hak AH, Shehata EM, Zanfaly AI, Soudy ES. Genu Varum in Children; [https://ejhm.journals.ekb.eg/article_231636_f5bc851645db9d787fadaa87cf381506.pdf Various Treatment Modalities for Bowleg's Correction.] The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine. 2022 Apr 1;87(1):1858-63.</ref> | |||
** infants born in genu varum (i.e. bow-legged position) | |||
** by toddlerhood, knees are in genu valgum (i.e. knock-knee position) - genu valgum peaks around 2 1/2 years old and then decreases over time<ref name=":0" /><ref>Ganeb SS, Egaila SE, Younis AA, El-Aziz AM, Hashaad NI. [https://erar.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43166-021-00082-1 Prevalence of lower limb deformities among primary school students]. Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation. 2021 Dec;48:1-7.</ref> | |||
** by adulthood, knee should be in neutral[[File:Genuvarus.jpg|thumb]] | |||
* Knee flexion | |||
** infants born with 30 degree knee flexion contracture | |||
** resolves in the first few months of life | |||
* Infants are born with medial rotation of the tibia | |||
** this resolves by 12 months<ref name=":0" /> | |||
==== Changes in Alignment to Consider ==== | |||
===== Increased Medial Tibial Torsion ===== | |||
* Internal rotation of the tibia | |||
* Not common | |||
* Toeing in | |||
* Most likely associated with medial rotation occurring higher up in the chain<ref name=":0" /> | |||
===== Increased Lateral Tibial Torsion ===== | |||
* External rotation of the tibia | |||
* Individuals present with crouched posture<ref name=":0" /> | |||
===== Increased Genu Valgum ===== | |||
Possible impairments: | |||
* pain in calf, thigh and/or knee | |||
* increased fatigue with activities | |||
* less efficient gait | |||
** decreased gait velocity | |||
** decreased balance | |||
* increased Q-angle | |||
**[[Quadratus Femoris|quadriceps]] less efficient secondary to abnormal muscle pull<ref name=":0" /><ref>Çankaya T, Dursun Ö, Davazlı B, Toprak H, Çankaya H, Alkan B. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7344134/ Assessment of quadriceps angle in children aged between 2 and 8 years]. Turkish Archives of Pediatrics/Türk Pediatri Arşivi. 2020;55(2):124.</ref> | |||
* lateral subluxation of the [[patella]] | |||
* collapse of the medial foot arch | |||
* protective in-toeing<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Ankles/Feet === | |||
Infants are born with: | |||
* hindfoot varus | |||
** with weight bearing, transitions to valgus | |||
* feet straight forward or slight pointing in | |||
** toeing out increases in adults | |||
* high arch<ref name=":0" /><ref>Sanpera I, Villafranca-Solano S, Muñoz-Lopez C, Sanpera-Iglesias J. [https://eor.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/eor/6/6/2058-5241.6.210021.xml How to manage pes cavus in children and adolescents?]. EFORT Open Reviews. 2021 Jun;6(6):510.</ref> | |||
** adults tend to transition to flatter feet<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Role of Paediatric Physiotherapy == | |||
Physiotherapists can help facilitate correct movement patterns to improve biomechanical alignment. Early intervention is associated with better functional outcomes. Some interventions that paediatric physiotherapists use are listed below: | |||
* weight shifts | |||
* loading | |||
* static positioning devices | |||
* [[splinting]] | |||
* [[Bracing for Clubfoot|bracing]]<ref name=":0" /> | |||
The video below by Pathways demonstrates a 2-month-old typical vs. atypical development side by side: | |||
{{#ev:youtube| _0cErYu3A8Q}} | |||
== Resources == | |||
* [[Biomechanics]] | |||
* [[Infant Development]] | |||
* [[Coxa Vara / Coxa Valga]] | |||
* [[Valgus Knee]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Paediatrics]] | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
[[Category:Course Pages]] | |||
[[Category:Plus Content]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:54, 14 January 2024
Top Contributors - Robin Tacchetti, Jess Bell and Naomi O'Reilly
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The musculoskeletal system is influenced by many different factors as infants and children grow. It can adapt to the demands, or lack of demands, that are placed on it. The major load on bone comes from muscle forces. When muscle pull is altered due to genetic or neuromuscular conditions, alignment may be impacted. Atypical alignment can directly affect functional activities and an individual's participation.[1]
The following sections highlight key stages and changes that occur during musculoskeletal development.
Rib Cage[edit | edit source]
- Initially, the rib cage in infants is barrel-shaped and rigid; ribs are elevated and perpendicular to the spine
- By 2 years, the rib cage is oblong-shaped; the ribs depress and develop an angulation in relation to their attachment with the spine - this is due to the diaphragm pull and forces from sitting/standing/walking; there is also lateral expansion of ribs (caused by breathing, the action of intercostal muscles, gravity)
- Atypical = persistence of the barrel shape
Trunk[edit | edit source]
- Initially, infants have a kyphotic spine
- Overtime this transitions to a more "neutral" spine (as seen in adults)
- Specific activities which encourage this transition:
- Prone push-ups and sitting activate the posterior chain musculature (i.e. the infant is pushing into thoracic extension)
- Crawling creates co-contraction of the anterior and posterior muscles (for stability)[1]
Changes in Alignment to Consider[edit | edit source]
Increased Curvature of the Spine[edit | edit source]
Increased curvature of the spine (i.e. scoliosis) can affect:[1]
- breathing
- lung positioning
- heart location
- visceral function
Pelvis[edit | edit source]
- Initially, infants have a rounded pelvis with a posterior tilt
- Sitting and standing activate core muscles, which leads to the development of an anterior pelvic tilt
- At 12 months old: an infant has 12 degrees of anterior pelvic tilt
- At 30 months old: a child has 15 degrees of anterior tilt
- Anterior tilt decreases to around adult angles (i.e. around 10 degrees) by age 8[1]
Lower Extremities[edit | edit source]
Typical joint patterns in infants are as follows:
- Hip: flexion, abduction and lateral rotation
- Knee: flexion, genu varum, medial rotation of tibia
- Ankle: dorsiflexion, slight pronation[1]
These joints are discussed in more detail below.
Hip[edit | edit source]
Infants are born with:
- increased hip external rotation which decreases over time
- hip adduction limitation
- 34 degrees of hip extension limitation
- as infants spend more time in prone, their anterior capsule stretches, decreasing the hip extension limitation
- at 6 weeks old infants have a 19 degree hip extension limitation
- toddlers have a 7 degree hip extension limitation
- as infants spend more time in prone, their anterior capsule stretches, decreasing the hip extension limitation
- increased coxa valga - 140-160 degrees
- as become more ambulatory, femoral neck angle decreases
- decreases over time to 126 degrees in adults
- anteversion of the femur - 40 degrees
- this decreases to 16 degrees in adults
Changes in Alignment to Consider (Hip and Pelvis)[edit | edit source]
Hip[edit | edit source]
- Femoral neck angle remains high - high femoral anteversion: increased risk of posterior hip dislocation
- Please note that it is especially important to consider the hips in children who are non-ambulatory at the age of 30 months[1]
Increased Anterior Pelvic Tilt[edit | edit source]
- Abdominals and hip extensors are long
- Hip flexors and lumbar extensors are short
- Leads to difficulty activating abdominals and gluteus muscles, which can make it difficult for children to engage in functional play / activities[1]
Decreased Anterior Pelvic Tilt[edit | edit source]
- Iliopsoas and anterior hip capsule are long / stretched out
- Gluteus maximus is shortened
- Leads to anterior hip laxity and hip instability[1]
Pelvic Obliquity[edit | edit source]
- Common in individuals with hemiplegia and diplegia
- Depressed hip side (shorter side):
- shorter, lower extremity or increased pronation on this side
- reduced stance time
- reduced loading, resulting in less bony deposition, so the long bones of this leg tend to grow at a slower rate
- sometimes functional ankle plantarflexion (i.e. so can reach the ground with this foot)
- Longer side:
- often have compensatory foot pronation
- there may be medial rotation of the lower extremity and knee flexion to compensate
- Leads to gait asymmetry, pelvic rotation on the shorter side[1]
- Significant increase in pelvic obliquity might contribute to:[2]
- imbalances in sitting
- pain due to "impingement of the pelvis on the ribs"[2]
- ischial decubitus / pressure ulcers
Knee[edit | edit source]
- Genu varum[3]
- Knee flexion
- infants born with 30 degree knee flexion contracture
- resolves in the first few months of life
- Infants are born with medial rotation of the tibia
- this resolves by 12 months[1]
Changes in Alignment to Consider[edit | edit source]
Increased Medial Tibial Torsion[edit | edit source]
- Internal rotation of the tibia
- Not common
- Toeing in
- Most likely associated with medial rotation occurring higher up in the chain[1]
Increased Lateral Tibial Torsion[edit | edit source]
- External rotation of the tibia
- Individuals present with crouched posture[1]
Increased Genu Valgum[edit | edit source]
Possible impairments:
- pain in calf, thigh and/or knee
- increased fatigue with activities
- less efficient gait
- decreased gait velocity
- decreased balance
- increased Q-angle
- quadriceps less efficient secondary to abnormal muscle pull[1][5]
- lateral subluxation of the patella
- collapse of the medial foot arch
- protective in-toeing[1]
Ankles/Feet[edit | edit source]
Infants are born with:
- hindfoot varus
- with weight bearing, transitions to valgus
- feet straight forward or slight pointing in
- toeing out increases in adults
- high arch[1][6]
- adults tend to transition to flatter feet[1]
Role of Paediatric Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapists can help facilitate correct movement patterns to improve biomechanical alignment. Early intervention is associated with better functional outcomes. Some interventions that paediatric physiotherapists use are listed below:
The video below by Pathways demonstrates a 2-month-old typical vs. atypical development side by side:
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Eskay K. Paediatric Musculoskeletal Development Course. Plus. 2023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Karkenny AJ, Magee LC, Landrum MR, Anari JB, Spiegel D, Baldwin K. The Variability of Pelvic Obliquity Measurements in Patients with Neuromuscular Scoliosis. JBJS Open Access. 2021 Jan;6(1).
- ↑ A El-Hak AH, Shehata EM, Zanfaly AI, Soudy ES. Genu Varum in Children; Various Treatment Modalities for Bowleg's Correction. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine. 2022 Apr 1;87(1):1858-63.
- ↑ Ganeb SS, Egaila SE, Younis AA, El-Aziz AM, Hashaad NI. Prevalence of lower limb deformities among primary school students. Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation. 2021 Dec;48:1-7.
- ↑ Çankaya T, Dursun Ö, Davazlı B, Toprak H, Çankaya H, Alkan B. Assessment of quadriceps angle in children aged between 2 and 8 years. Turkish Archives of Pediatrics/Türk Pediatri Arşivi. 2020;55(2):124.
- ↑ Sanpera I, Villafranca-Solano S, Muñoz-Lopez C, Sanpera-Iglesias J. How to manage pes cavus in children and adolescents?. EFORT Open Reviews. 2021 Jun;6(6):510.