Morton's Neuroma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
Microscopically, the affected nerve is markedly distorted, with extensive concentric perineural fibrosis. The arterioles are thickened and occlusion by thrombi are occasionally present.[8][9] | Microscopically, the affected nerve is markedly distorted, with extensive concentric perineural fibrosis. The arterioles are thickened and occlusion by thrombi are occasionally present.[8][9] | ||
=== === | === '''Imaging:''' === | ||
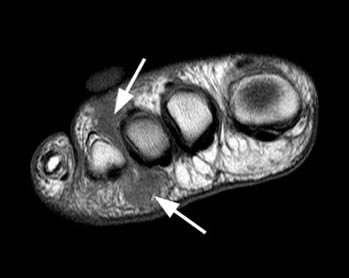
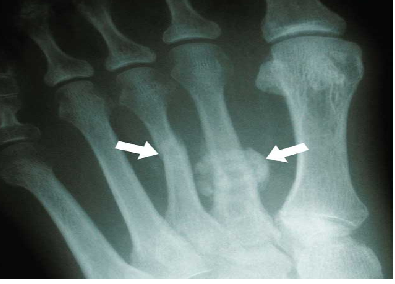
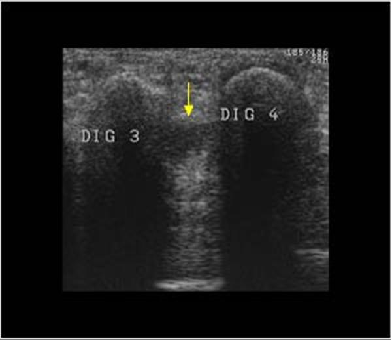
Though a neuroma is a soft tissue abnormality and will not be visualized on standard radiographs, the first step in the assessment of forefoot pain is an X-ray in order to evaluate for the presence of arthritis and exclude stress fractures/reactions and focal bone lesions, which may mimic the symptoms of a neuroma. Ultrasound (sonography) accurately demonstrates thickening of the interdigital nerve within the web space of greater than 3mm, diagnostic of a Morton’s neuroma. This typically occurs at the level of the intermetatarsal ligament. Frequently, intermetatarsal bursitis coexists with the diagnosis. Other conditions that may also be visualized with ultrasound and can be clinically confused with a neuroma include synovitis/capsulitis from the adjacent metatarsophalangeal joint, stress fractures/reaction, and plantar plate disruption.[10][11] MRI can similarly demonstrate the above conditions; however, in the setting where more than one abnormality coexists, ultrasound has the added advantage of determining which may be the source of the patient’s pain by applying direct pressure with the probe. Further to this, ultrasound can be used to guide treatment such as cortisone injections into the webspace, as well as alcohol ablation of the nerve. | |||
Though a neuroma is a soft tissue abnormality and will not be visualized on standard radiographs, the first step in the assessment of forefoot pain is an X-ray in order to evaluate for the presence of arthritis and exclude stress fractures/reactions and focal bone lesions, which may mimic the symptoms of a neuroma. Ultrasound (sonography) accurately demonstrates thickening of the interdigital nerve within the web space of greater than 3mm, diagnostic of a Morton’s neuroma. This typically occurs at the level of the intermetatarsal ligament. Frequently, intermetatarsal bursitis coexists with the diagnosis. Other conditions that may also be visualized with ultrasound and can be clinically confused with a neuroma include synovitis/capsulitis from the adjacent metatarsophalangeal joint, stress fractures/reaction, and plantar plate disruption.[10][11] MRI can similarly demonstrate the above conditions; however, in the setting where more than one abnormality coexists, ultrasound has the added advantage of determining which may be the source of the patient’s pain by applying direct pressure with the probe. Further to this, ultrasound can be used to guide treatment such as cortisone injections into the webspace, as well as alcohol ablation of the nerve. | |||
[[Image:Morton's-Xray.png]][[Image:Morton's-US.png]] | [[Image:Morton's-Xray.png]][[Image:Morton's-US.png]] | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 6 January 2017
Original Editor - Venugopal Pawar
Lead Editors
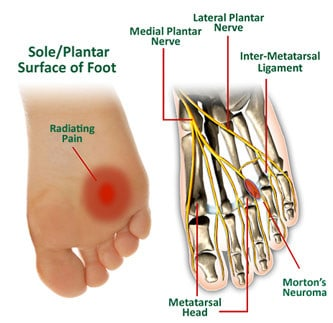
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
[edit | edit source]
Morton's neuroma (also known as Morton neuroma, Morton's metatarsalgia, Intermetatarsal neuroma and Intermetatarsal space neuroma.[1]) is a benign neuroma of an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the second and third intermetatarsal spaces (between 2nd−3rd and 3rd−4th metatarsal heads), which results in the entrapment of the affected nerve. The main symptoms are pain and/or numbness, sometimes relieved by removing footwear.
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process
[edit | edit source]
Some sources claim that entrapment of the plantar nerve because of compression between the metatarsal heads, as originally proposed by Morton, is highly unlikely, because the plantar nerve is on the plantar side of the transverse metatarsal ligament and thus does not come in contact with the metatarsal heads. It is more likely that the transverse metatarsal ligament is the cause of the entrapment.[2][3]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Symptoms include: pain on weight bearing, frequently after only a short time. The nature of the pain varies widely among individuals. Some people experience shooting pain affecting the contiguous halves of two toes. Others describe a feeling like having a pebble in their shoe or walking on razor blades. Burning, numbness, and paresthesia may also be experienced.[5] The symptoms progress over time, often beginning as a tingling sensation in the ball of the foot.[6]
Morton's neuroma lesions have been found using MRI in patients without symptoms.[7]
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Negative signs include no obvious deformities, erythema, signs of inflammation, or limitation of movement. Direct pressure between the metatarsal heads will replicate the symptoms, as will compression of the forefoot between the finger and thumb so as to compress the transverse arch of the foot.
There are other causes of pain in the forefoot. Too often all forefoot pain is categorized as neuroma. Other conditions to consider are capsulitis, which is an inflammation of ligaments that surrounds two bones, at the level of the joint. In this case, it would be the ligaments that attach the phalanx (bone of the toe) to the metatarsal bone. Inflammation from this condition will put pressure on an otherwise healthy nerve and give neuroma-type symptoms. Additionally, an intermetatarsal bursitis between the third and fourth metatarsal bones will also give neuroma-type symptoms because it too puts pressure on the nerve. Freiberg's disease, which is an osteochondritis of the metatarsal head, causes pain on weight bearing or compression.[citation needed]
Histopathology:[edit | edit source]
Microscopically, the affected nerve is markedly distorted, with extensive concentric perineural fibrosis. The arterioles are thickened and occlusion by thrombi are occasionally present.[8][9]
Imaging:[edit | edit source]
Though a neuroma is a soft tissue abnormality and will not be visualized on standard radiographs, the first step in the assessment of forefoot pain is an X-ray in order to evaluate for the presence of arthritis and exclude stress fractures/reactions and focal bone lesions, which may mimic the symptoms of a neuroma. Ultrasound (sonography) accurately demonstrates thickening of the interdigital nerve within the web space of greater than 3mm, diagnostic of a Morton’s neuroma. This typically occurs at the level of the intermetatarsal ligament. Frequently, intermetatarsal bursitis coexists with the diagnosis. Other conditions that may also be visualized with ultrasound and can be clinically confused with a neuroma include synovitis/capsulitis from the adjacent metatarsophalangeal joint, stress fractures/reaction, and plantar plate disruption.[10][11] MRI can similarly demonstrate the above conditions; however, in the setting where more than one abnormality coexists, ultrasound has the added advantage of determining which may be the source of the patient’s pain by applying direct pressure with the probe. Further to this, ultrasound can be used to guide treatment such as cortisone injections into the webspace, as well as alcohol ablation of the nerve.
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Key Evidence[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to key evidence with regards to any of the above headings
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Case Studies[edit | edit source]
add links to case studies here (case studies should be added on new pages using the case study template)
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.