Module 7: Play: Difference between revisions
(vision box) |
(table) |
||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
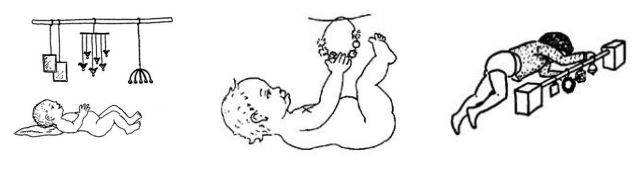
'''Vision-box''' | '''Vision-box''' | ||
Making it: | Making it: | ||
*Cardboard box | *Cardboard box | ||
*Mobiles – placed above her waist; not more than 3 objects. These can be shiny things (like an old CD or pieces of foil), brightly coloured beads, or light pieces of material that will move with a gentle breeze or blowing. | *Mobiles – placed above her waist; not more than 3 objects. These can be shiny things (like an old CD or pieces of foil), brightly coloured beads, or light pieces of material that will move with a gentle breeze or blowing. | ||
<u>Using it:</u> | <u>Using it:</u> | ||
*The child lies on her back with her head and upper body inside the box. | *The child lies on her back with her head and upper body inside the box. | ||
*This can be used for a child who cannot see well. The dark box with the shiny or brightly coloured mobiles may help her begin to use and train her eyes. | *This can be used for a child who cannot see well. The dark box with the shiny or brightly coloured mobiles may help her begin to use and train her eyes. | ||
*She will enjoy looking at the bright or shiny colours, or watching the light material blow in the wind. | *She will enjoy looking at the bright or shiny colours, or watching the light material blow in the wind. | ||
| [[Image: | | [[Image:Vision box.JPG]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| | '''Texture bag/box''' | ||
<u>Making it:</u> | |||
*Material of different textures – soft; silky; corduroy; woolly; embroidered; netting | |||
*Piece of steel wool or plastic hair curler (scratchy feeling) | |||
*Something hard – marbles, steel teaspoon, glass bottle<br> | |||
*Soft toy – teddy bear | |||
*Clothes peg | |||
*Plastic packet or noisy paper | |||
*Seeds or pods of different textures – smooth, rough etc. | |||
<u>Using it:</u> | |||
*This is especially good for children who have problems seeing well, and for those who do not move easily by themselves. | |||
*Help the child to feel the different textures on the outside and inside of her hand. First work on the outside of her hand – then open her hand and let her feel it on the inside of, or put it in her hand. | |||
*A child who can move her hands can practice taking and giving the objects. | |||
| [[Image:Texture_bag.JPG]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| | '''Drum''' | ||
<u>Making it:</u> | |||
*Can or plastic container or pot | |||
*Stick or wooden spoon or metal spoon | |||
<u>Using it:</u> | |||
*Help the child to hold the stick and to play the drum (involve the family and get others to sing with her. Involve the child in family or church gatherings where there is music or singing) | |||
*Encourage the child to hold the sticks by herself if possible | |||
*Encourage her to move her arm by herself to hit the drum | |||
| [[Image:Drum_plating_with_CP.JPG]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
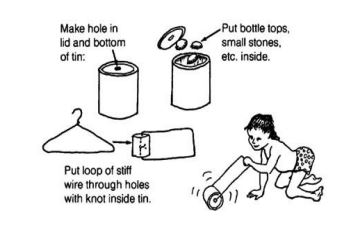
| | '''Push/pull rattle''' | ||
<u>Making it:</u> | |||
*Use a tin or plastic container that has a lid | |||
*Make a tiny hole in the lid and bottom of the tin | |||
*Put some small stones or seeds into the tin | |||
*Use a wire hanger to make a rectangular loop through the holes | |||
<u>Using it:</u> | |||
*Help / encourage the child to hold the wire and push the toy away and pull it back towards her | |||
*Encourage her to walk / crawl while pushing the toy | |||
| [[Image:Push_pull_CP.JPG]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
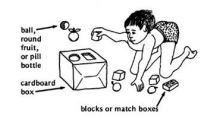
| | | | ||
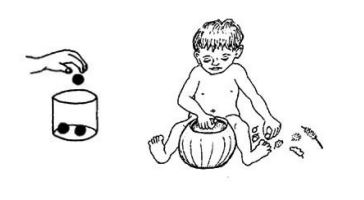
| | *'''Putting in/out<br>''' | ||
<u>Making it:<br></u> | |||
*<u></u>Large tin or plastic container | |||
*Small items (seeds, bolts, match boxes, stones, small plastic cups, scrunched newspaper balls, bottle tops or lids). | |||
<u>Using it:</u> | |||
*Encourage the child to pick up the small objects one by one | |||
*She can take them out of the container, and put them back in | |||
*Encourage her to talk about what she is doing – “in” and “out”. | |||
| [[Image:Putting_in_out_CP.JPG]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
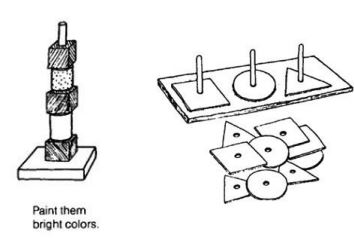
| | '''Stacking poles''' | ||
<u style="font-size: 13.28px;">Making it:</u> | |||
*Wooden base with stick or small poles or long paper towel rolls | |||
*Rings (cut holes into plastic lids, make ring out of foil, soft branches, woven grass, cut up toilet rolls) | |||
*Blocks (out of cardboard from empty boxes or scrap wood) – make a hole in the centre. | |||
*<u>Using it:<br></u> | |||
*<u></u>Help the child to take a ring or block and place it on one of the rings | |||
*If there are different types of rings, help the child to match the ones that look the same | |||
*Encourage the child to count the rings as she puts them on. | |||
| [[Image:Satcking_poles_2.JPG]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
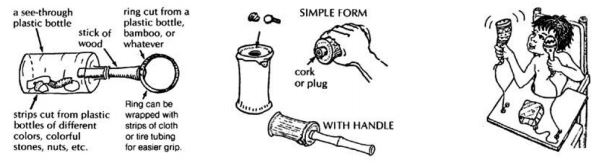
| | '''Posting''' | ||
<u>Making it:</u><br> | |||
*<u></u>Plastic container or tin with plastic lid and shaped holes cut out | |||
*Find small objects, and cut the holes in the lid to the same size & shape – use bottle tops, match boxes, small lids, pieces of wood. | |||
*Simple toy – objects and holes are all one shape | |||
*Complex toy – objects and holes are a variety of shapes | |||
<u>Using it:<br></u> | |||
*Encourage the child to post the object into the correct shape and size hole. | |||
*Help her to pick up and let go of the objects (if she has difficulty using her hands). Let her guide the object into the hole she wants to put it in. Talk to her about the size and shape of the different objects as she plays. | |||
| [[Image:Posting_CP.JPG]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 14 May 2017
Page Outcomes [edit | edit source]
When you have finished this workshop, you should be able to:
- Understand and explain to other caregivers the importance of play for a child’s development.
- Help your child with cerebral palsy to enjoy times of play that promotes her communication, movements, social and emotional skills, and learning.
Play[edit | edit source]
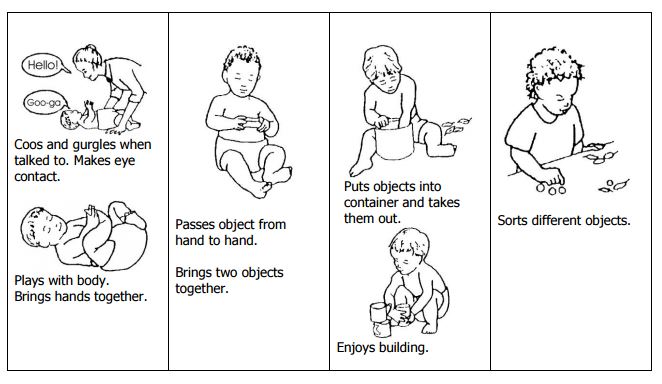
Play is any activity that a child CHOOSES to do, and has FUN whilst doing. Through play, a child uses her SENSES to explore and learn.
Senses:
- Seeing
- Hearing
- Touching / Feeling
- Smelling
- Tasting
Something else that works very closely with our senses, and is involved in play, is movement.
Examples of play:
- Enjoying the sound of a rattle/music (hearing)
- Looking at something that is shiny or colourful or pretty, or mom’s face (seeing)
- A baby kicking her legs and laughing (movement)
- Handling different objects – soft, hard, prickly etc (touching / feeling)
- Playing “peek-a-boo” (seeing)
- Splashing in water (feeling and movement)
- Hide and seek (hiding an object under a lid or box and getting the child to try and lift the box to find the object, or hiding yourself from them and seeing if they can move or look for you (seeing)
- Pretending to make food out of mud (touching or feeling)
- Swimming or spinning around in circles (movement)
- Singing & clapping games (sight, movement, hearing)
- Running around (movement)
- Playing soccer or other sports (sight, movement, feeling)
This child is playing and learning:
Why play is important[edit | edit source]
- It gives her opportunities to explore and therefore learn about things in her environment.
- It gives her opportunities to use and develop her senses.
- It gives her a reason to practice moving (when she is having fun she will be motivated to move).
- It gives her opportunities to interact with other people and learn social skills.
- It gives her opportunities to think and learn.
Remember:
- A child in a poor position, and without play and communication, will not develop and learn.
- A child who is not enjoying the activity because she can’t do it, will not develop and learn.
Children need help to play[edit | edit source]
To learn to play, all children need the encouragement of their parents, siblings and other people.
Children with cerebral palsy also need encouragement, and may need special help and attention.The caregivers of a child with cerebral palsy need to encourage her to be active in play situations, and they need to help her to learn.
Play is more important than toys. Almost anything can be used as a toy, if it is used in play.
Simple toys that you can make at home[edit | edit source]
Let’s look at a variety of simple toys that you can make at home for your child. For each toy, we will briefly discuss how you can make it, and then think about which children would benefit from such a toy, and how you can use it to play with them.