Kim test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subst:specialtest}} | |||
Test Description: | Test Description: | ||
| Line 7: | Line 11: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | |||
[[Image:Kim test.jpg|Image:Kim_test.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:Kim_test.jpg]] | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
The sensitivity of the Kim test was 80%, specificity was 94%. The interexaminer reliability between 2 examiners was 0.91. | The sensitivity of the Kim test was 80%, specificity was 94%. The interexaminer reliability between 2 examiners was 0.91. | ||
| | ||
The accuracy of the jerk test in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion was the following: sensitivity, 73%; specificity, 98%. | The accuracy of the jerk test in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion was the following: sensitivity, 73%; specificity, 98%. | ||
| | ||
The Kim test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly inferior labral lesion, whereas the jerk test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly posterior labral lesion. The sensitivity in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion increased to 97% when the 2 tests were combined. | |||
<br> | |||
| | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 20 November 2009
{{subst:specialtest}}
Test Description:
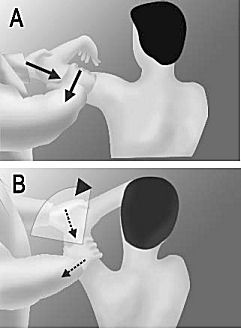
A - With the patient in a sitting position with the arm 90 degrees of abduction, the examiner holds the elbow and lateral aspect of the proximal arm, and a strong axial loading force is applied.
B - while the arm is elevated 45 degrees diagonally upward, downward and backward force is applied to the proximal arm. A sudden onset of posterior shoulder pain indicates a positive test result, regardless of accompanying posterior clunk of the humeral head.
The sensitivity of the Kim test was 80%, specificity was 94%. The interexaminer reliability between 2 examiners was 0.91.
The accuracy of the jerk test in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion was the following: sensitivity, 73%; specificity, 98%.
The Kim test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly inferior labral lesion, whereas the jerk test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly posterior labral lesion. The sensitivity in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion increased to 97% when the 2 tests were combined.