Introduction to Quadruped Anatomical Terminology
Terminology[edit | edit source]
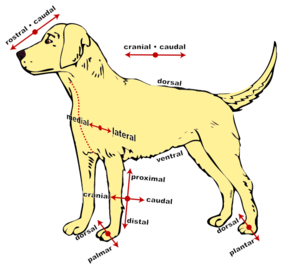
Many veterinary anatomical terms are similar to those used in human anatomy, but there are some important terms to know if you are working with animals.
Animals stand on all fours:[1]
- Anterior in humans = ventral in aminals (i.e. directed towards the ground)
- Posterior in humans = dorsal in animals
- Humans – palms face anterior
- Animals – palms face posterior, thus the radius and the first digit are medial
Animals are quadripedal – i.e. their vertebral column is parallel to the ground:[1]
- Head is cranial
- Tail is caudal
- Within the head, rostral refers to structures closer to the nose
Terminology relevant to the limbs:[1]
- Proximal - the parts of the limbs that are nearest to the body
- Distal - the part of a structure that is furthest away from the main mass of tissue
- Front limb - the thoracic or pectoral limb
- Hind limb - the pelvic limb
Terminology referring to the thoracic or forelimb:[1]
- Dorsal – cranial face of the distal part of the forelimb or dorsum of the manus (i.e. the section from the carpus down)
- Palmar (volar) - opposite to the dorsal surface
- Radial – the part of the forearm where the radius is located (medial)
- Ulnar – the part of the forearm in which the ulna is located (lateral)
- Brachium – specifically the region from the shoulder to the elbow
- Axilla – the space between thoracic limb and the thoracic wall
Terminology referring to the pelvic or hind limb:[1]
- Dorsal – anterior face of the distal part of the pelvic limb or dorsum of pes
- Plantar – opposite of the dorsal surface
- Crus – the section of the hindlimb between the knee and the tarsus
- Pes – the section of the hindlimb from the tarsus down
- Tibial – the side of the leg where the tibia is located (medial)
- Fibular – the side of the leg where the fibula is located (lateral)
Terminology to indicate relative distance from the centre of the limb:[1]
- Axis – the centre line of the body or any part of it
- Axial and abaxial refers to, or being relative to the axis (e.g. the axial surface of a digit faces the axis while the abaxial surface faces away from the axis)
Terminology to indicate the relative distance from the surface of the body:[1]
- Superficial – relatively near to the surface of the body or the surface of a solid organ
- Deep – relatively near to the centre of the body or the centre of a solid organ
- External or outer – away from the centre of a hollow organ
- Internal or inner – close to or in the direction of the centre of a hollow organ
Terminology to describe the basic movement of the parts of the body:[1]
- Protraction – limb forwards
- Retraction – limb backwards
- Extension – angle increased
- Flexion –angle reduced
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named:1 - ↑ atdove.org. Directional Terms in Veterinary Medicine. 2017. Available from: https://youtu.be/nKYmpzmiwzI
- ↑ Rod Allrich. Directional Terms Used in Animal Anatomy. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T8pCS4rdm38 [last accessed 4/1/20201]