Hypertonicity vs spasticity: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Hypertonicity or spastic dystonia = | |||
1-hypertonicity or spastic dystonia is a continues increase in the muscle tension without regarding to the movement and is dependent upon afferent information from feedback following movements of stretch , decorticat and decerbrate rigidity are a form of spastic dystonia, spastic dystonia is considered to be a form of sustained efferent muscular hyperactivity , dependent on continues supraspinal derive to the alpha motor neuron [[Image:Decorticate.jpg]]<br> | 1-hypertonicity or spastic dystonia is a continues increase in the muscle tension without regarding to the movement and is dependent upon afferent information from feedback following movements of stretch , decorticat and decerbrate rigidity are a form of spastic dystonia, spastic dystonia is considered to be a form of sustained efferent muscular hyperactivity , dependent on continues supraspinal derive to the alpha motor neuron [[Image:Decorticate.jpg]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 19:12, 19 March 2014
Hypertonicity or spastic dystonia[edit | edit source]
1-hypertonicity or spastic dystonia is a continues increase in the muscle tension without regarding to the movement and is dependent upon afferent information from feedback following movements of stretch , decorticat and decerbrate rigidity are a form of spastic dystonia, spastic dystonia is considered to be a form of sustained efferent muscular hyperactivity , dependent on continues supraspinal derive to the alpha motor neuron 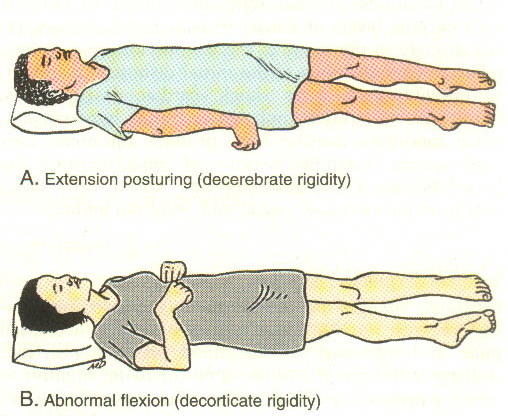
[edit | edit source]
Spasticity[edit | edit source]
- spasticity is a velocity dependent increase in muscle tone in regarding to passive movement
pyramidal tract lesions
-pyramidal tract injury doesn't give raise to spasticity the main symptoms are weakness and loss of dexterity which is greater in distal than in the proximal muscles
- pyramidal tract is the system which balance the muscle tone.
neural component of spasticity: [edit | edit source]
1-Dorsoreticulospinal tract (DRT) : Has inhibitory effect on MRT &VST
2-medial reticulospinal tract (MRT) &
3-vestibulospinal tract ( VST ):
-they have facilitatory effect on the extensor tone,
- all the three systems are though to inhibit flexor reflex afferents responsible for flexor spasm






