Humerus: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Humerus.gif|thumb|<ref>http://www.bartleby.com/107/illus207.html</ref>]] | [[File:Humerus.gif|thumb|<ref>http://www.bartleby.com/107/illus207.html</ref>]] | ||
=== Upper | === Upper Extremity Features === | ||
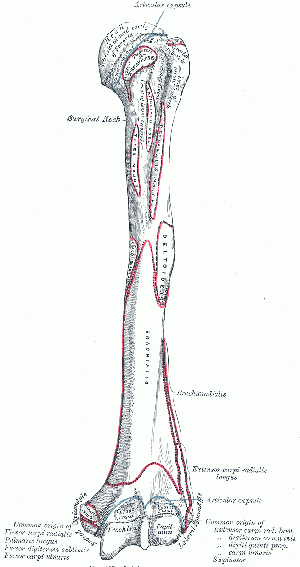
The head (caput humeri) is the articular surface of the upper extremity, which is an irregular hemisphere. | |||
=== Body | The anatomical neck is the part between the head and the tuberosities. | ||
The surgical neck is the part between the tuberosities and the shaft. | |||
The greater tuberosity it is located lateral to the head. | |||
The lesser tuberosity is located inferior to the head, on the anterior part of the humerus, Its very prominent and palpable. | |||
Bicipital (intertubercular) groove is located between the two tuberosities. The Biceps tendon is placed here. | |||
=== Body Features === | |||
The body of the humerus has three borders and three surfaces. | The body of the humerus has three borders and three surfaces. | ||
Borders | ==== Borders ==== | ||
# Anterior | |||
# Lateral | |||
# Medial | |||
Surfaces | |||
==== Surfaces ==== | |||
# Antero-lateral | |||
# Antero-medial | |||
# Posterior | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Humerus | The Humerus serves as an attachment to 13 Muscles and 3 very important Nerves, which control the functions of hand and elbow, pass through the humerus.<ref>https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-function-of-the-humerus-bone-in-the-human-arm</ref> | ||
== Articulations == | == Articulations == | ||
Articulatio Humeri | |||
Articulatio Cubiti | |||
== Muscle | == Muscle Attachments == | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!Muscle | |||
!Attachment | |||
|- | |||
|Supraspinatus | |||
|Greater Tubercle | |||
|- | |||
|Infraspinatus | |||
|Greater Tubercle | |||
|- | |||
|Teres Minor | |||
|Greater Tubercle | |||
Upper Part of the Lateral Border | |||
|- | |||
|Subscapularis | |||
|Lesser Tubercle | |||
|- | |||
|Pectoralis Major | |||
|Upper Part of the Anterior Border | |||
|- | |||
|Triceps Brachii | |||
|Lower Part of the Lateral Border | |||
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge | |||
|- | |||
|Brachioradialis | |||
|Lateral Supracondylar Ridge | |||
|- | |||
|Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus | |||
|Lateral Supracondylar Ridge | |||
|- | |||
|Teres Major | |||
|Crest of the Lesser Tubercle | |||
|- | |||
|Coracobrachialis | |||
|Crest of the Lesser Tubercle | |||
|- | |||
|Brachialis | |||
|Medial Supracondylar Ridge | |||
|- | |||
|Pronator Teres | |||
|Medial Supracondylar Ridge | |||
|- | |||
|Latissimus Dorsi | |||
|Bicipital Groove | |||
|} | |||
= References = | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Gray H., 2000, Anatomy of Human Body, Twentieth Edition, New York, Bartleby.com | Gray H., 2000, Anatomy of Human Body, Twentieth Edition, New York, Bartleby.com | ||
[[User:Liridona Dervishi|Liridona Dervishi]] | [[User:Liridona Dervishi|Liridona Dervishi]] | ||
Revision as of 00:55, 29 December 2017
Description[edit | edit source]
Humerus is a long bone which consists of a shaft (diaphysis) and two extremities (epiphysis). It is the longest bone of the upper extremity. It's name comes from the word "humorous" because when hitting it at the ulnar nerve it gives a strange "kind of funny" feeling.
Structure[edit | edit source]
Upper Extremity Features[edit | edit source]
The head (caput humeri) is the articular surface of the upper extremity, which is an irregular hemisphere.
The anatomical neck is the part between the head and the tuberosities.
The surgical neck is the part between the tuberosities and the shaft.
The greater tuberosity it is located lateral to the head.
The lesser tuberosity is located inferior to the head, on the anterior part of the humerus, Its very prominent and palpable.
Bicipital (intertubercular) groove is located between the two tuberosities. The Biceps tendon is placed here.
Body Features[edit | edit source]
The body of the humerus has three borders and three surfaces.
Borders[edit | edit source]
- Anterior
- Lateral
- Medial
Surfaces[edit | edit source]
- Antero-lateral
- Antero-medial
- Posterior
Function[edit | edit source]
The Humerus serves as an attachment to 13 Muscles and 3 very important Nerves, which control the functions of hand and elbow, pass through the humerus.[2]
Articulations[edit | edit source]
Articulatio Humeri
Articulatio Cubiti
Muscle Attachments[edit | edit source]
| Muscle | Attachment |
|---|---|
| Supraspinatus | Greater Tubercle |
| Infraspinatus | Greater Tubercle |
| Teres Minor | Greater Tubercle
Upper Part of the Lateral Border |
| Subscapularis | Lesser Tubercle |
| Pectoralis Major | Upper Part of the Anterior Border |
| Triceps Brachii | Lower Part of the Lateral Border
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge |
| Brachioradialis | Lateral Supracondylar Ridge |
| Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus | Lateral Supracondylar Ridge |
| Teres Major | Crest of the Lesser Tubercle |
| Coracobrachialis | Crest of the Lesser Tubercle |
| Brachialis | Medial Supracondylar Ridge |
| Pronator Teres | Medial Supracondylar Ridge |
| Latissimus Dorsi | Bicipital Groove |
References[edit | edit source]
Gray H., 2000, Anatomy of Human Body, Twentieth Edition, New York, Bartleby.com