Hamate: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) (Corrected editor code) |
(Added links and reference. Updated function section) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
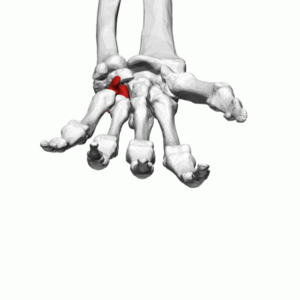
[[File:Hamate bone (left hand) - animation.gif|thumb|[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hamate_bone_(left_hand)_-_animation02.gif Hamate bone (left hand) animation]]]The hamate bone is one of eight carpal bones that forms part of the wrist joint. The word hamate is derived from the Latin word ''hamulus'' which means “a little hook”. It is a wedge-shaped bone with a hook-like process that can be found in the medial side of the wrist.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF. ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy.'' Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006</ref> Sometimes it is also called unciform bone. | [[File:Hamate bone (left hand) - animation.gif|thumb|[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hamate_bone_(left_hand)_-_animation02.gif Hamate bone (left hand) animation]]]The hamate bone is one of eight [[Wrist and Hand|carpal]] bones that forms part of the wrist joint. The word hamate is derived from the Latin word ''hamulus'' which means “a little hook”. It is a wedge-shaped bone with a hook-like process that can be found in the medial side of the wrist.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF. ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy.'' Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006</ref> Sometimes it is also called unciform bone. | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
The hamate has a wedge-like shape with a distinct bony process called hook of hamate that extends from the palmar surface | The hamate sits on the medial side of the distal row of carpal bones. The hamate has a wedge-like shape with a distinct bony process called hook of hamate that extends from the palmar surface.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The hamate is one of the carpal bones that form the carpal arch, wherein the carpal tunnel is situated. It | The hamate is one of the carpal bones that form the carpal arch, wherein the [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome|carpal tunnel]] is situated. The hamate creates the medial border of the carpal tunnel<ref name=":1">Davis DL. Hook of the Hamate: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5892414/ The Spectrum of Often Missed Pathologic Findings]. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017 Nov;209(5):1110-1118.</ref>. | ||
The hook of hamate can be palpated on the medial side of the wrist inferior and laterally to the [[pisiform]].<ref name=":0" />It creates the medial border of the [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome|carpal tunnel]] and the lateral border of the [[Guyon Canal|Guyon canal]]<ref name=":1" />. | |||
It also serves as an attachment for multiple structures such as the transverse carpal ligament ([[flexor retinaculum]]). The pisohamate ligament connects the pisiform to the hamate and this forms an osseofibrous tunnel that is called the ulnar canal ([[Guyon Canal|Guyon canal]]). The [[Ulnar Nerve|ulnar nerve]] passes through this canal between the [[pisiform]] and hook of hamate.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
The hook of the hamate is a tendon attachment point to create a pully for the flexor tendons of the 4th and 5th digits<ref name=":1" />. | |||
== Articulations == | == Articulations == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 22: | ||
== Muscle attachments == | == Muscle attachments == | ||
* Flexor carpi ulnaris - This is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It attaches distally to the [[pisiform]], hook of [[hamate]] and 5th metacarpal. It allows wrist flexion and | * [[Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle|Flexor carpi ulnaris]] - This is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It attaches distally to the [[pisiform]], hook of [[hamate]] and 5th metacarpal. It allows wrist flexion and ulnar deviation. | ||
* Flexor digiti minimi brevis - This is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It attaches proximally to the [[Hamate|hook of hamate]] and flexor retinaculum. It allows flexion of the proximal phalanx of the 5th finger. | * [[Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis|Flexor digiti minimi brevis]] - This is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It attaches proximally to the [[Hamate|hook of hamate]] and flexor retinaculum. It allows flexion of the proximal phalanx of the 5th finger. | ||
* Opponens digiti minimi - This is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It attaches proximally to the [[Hamate|hook of hamate]] and flexor retinaculum. It draws the 5th metacarpal anterior and rotates it to get opposition with the thumb. | * [[Opponens Digiti Minimi|Opponens digiti minimi]] - This is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It attaches proximally to the [[Hamate|hook of hamate]] and flexor retinaculum. It draws the 5th metacarpal anterior and rotates it to get opposition with the thumb. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
Latest revision as of 15:38, 18 May 2022
Top Contributors - Kim Jackson, Nina Myburg and Patti Cavaleri
Description[edit | edit source]
The hamate bone is one of eight carpal bones that forms part of the wrist joint. The word hamate is derived from the Latin word hamulus which means “a little hook”. It is a wedge-shaped bone with a hook-like process that can be found in the medial side of the wrist.[1] Sometimes it is also called unciform bone.
Structure[edit | edit source]
The hamate sits on the medial side of the distal row of carpal bones. The hamate has a wedge-like shape with a distinct bony process called hook of hamate that extends from the palmar surface.[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
The hamate is one of the carpal bones that form the carpal arch, wherein the carpal tunnel is situated. The hamate creates the medial border of the carpal tunnel[2].
The hook of hamate can be palpated on the medial side of the wrist inferior and laterally to the pisiform.[1]It creates the medial border of the carpal tunnel and the lateral border of the Guyon canal[2].
It also serves as an attachment for multiple structures such as the transverse carpal ligament (flexor retinaculum). The pisohamate ligament connects the pisiform to the hamate and this forms an osseofibrous tunnel that is called the ulnar canal (Guyon canal). The ulnar nerve passes through this canal between the pisiform and hook of hamate.[1]
The hook of the hamate is a tendon attachment point to create a pully for the flexor tendons of the 4th and 5th digits[2].
Articulations[edit | edit source]
The hamate articulates with the 4th and 5th metacarpals, lunate, triquetrum and capitate. [3]
Muscle attachments[edit | edit source]
- Flexor carpi ulnaris - This is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It attaches distally to the pisiform, hook of hamate and 5th metacarpal. It allows wrist flexion and ulnar deviation.
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis - This is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It attaches proximally to the hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum. It allows flexion of the proximal phalanx of the 5th finger.
- Opponens digiti minimi - This is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It attaches proximally to the hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum. It draws the 5th metacarpal anterior and rotates it to get opposition with the thumb.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Davis DL. Hook of the Hamate: The Spectrum of Often Missed Pathologic Findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017 Nov;209(5):1110-1118.
- ↑ Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. Twentieth edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 Available from: https://www.bartleby.com/107/ [Accessed 30 April 2019]