Fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Image:Bone_fractures.gif|center]] | [[Image:Bone_fractures.gif|center]] | ||
= <br><br><br> | = When is fracture healed ? = | ||
The answer to this question depends upon many factors, including :<br>• The type of bone fractured<br>• The type of fracture sustained<br>• The age of the person<br>• The treatment undergone <br>• The nutritional status of the person. <br> A fracture is considered to be clinically healed based upon the combination of physical findings and symptoms over time. | |||
And the following suggest complete healing :<br>• absence of pain on weight-bearing, lifting or movement<br>• no tenderness on palpation at the fracture site<br>• blurring or disappearance of the fracture line on X-ray<br>• full or near full functional ability .<br>To understand more about fracture healing watch this :<br>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VZF3xicLtTw | |||
= Fracture management : = | |||
Once a fracture has been diagnosed, the most suitable treatment must be decided upon. This should be the minimum possible intervention that will safely and effectively provide the right environment for healing of the fracture.<br> | |||
Revision as of 00:34, 22 February 2017
Definition :[edit | edit source]
A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone.
Causes of fracture :[edit | edit source]
Most fractures are a result of some form of injury. This might be a direct blow, a fall from a height or a weight falling onto a part of the body.
Other fractures may be caused by indirect trauma, such as falling on an outstretched hand leading to the transmission of force up the arm causing a fracture of the clavicle.
Twisting forces may result in fractures of the tibia and fibula, for example during soccer or skiing when the weight of the body rotates on a fixed foot.
Stress or fatigue fractures are caused by repeated minor trauma, which can occur after walking or running long distances, and often affect the foot metatarsals.
Pathological fractures :
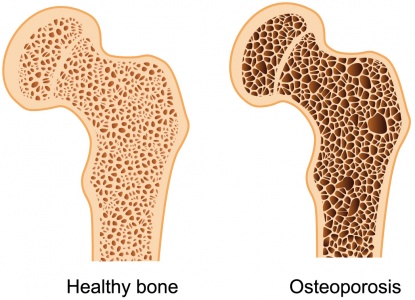
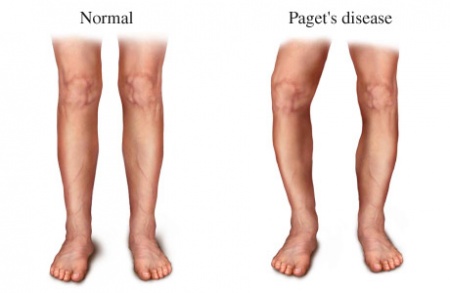
These occur as the result of a disease that weakens the composition of the bone itself such as diseases osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, carcinoma, osteomyelitis .
Clinical Features Of Fracture :[edit | edit source]
Clinical features vary depending on the cause and nature of the injury, and range from unconsciousness to the patient being able to use the limb, although complaining of pain .
And these features are :
• Pain
• Deformity
• Edema
• Loss of function
• Muscle spasm
• Muscle atrophy
• Abnormal movement
• limitation of joint motion
• shock
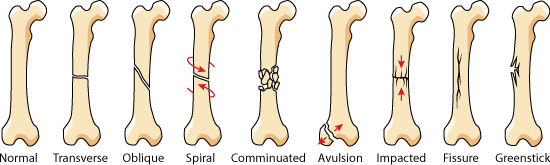
Types of fracture :[edit | edit source]
When is fracture healed ?[edit | edit source]
The answer to this question depends upon many factors, including :
• The type of bone fractured
• The type of fracture sustained
• The age of the person
• The treatment undergone
• The nutritional status of the person.
A fracture is considered to be clinically healed based upon the combination of physical findings and symptoms over time.
And the following suggest complete healing :
• absence of pain on weight-bearing, lifting or movement
• no tenderness on palpation at the fracture site
• blurring or disappearance of the fracture line on X-ray
• full or near full functional ability .
To understand more about fracture healing watch this :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VZF3xicLtTw
Fracture management :[edit | edit source]
Once a fracture has been diagnosed, the most suitable treatment must be decided upon. This should be the minimum possible intervention that will safely and effectively provide the right environment for healing of the fracture.