Fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Most fractures are a result of some form of injury. This might be a direct blow, a fall from a height or a weight falling onto a part of the body. <br>Other fractures may be caused by indirect trauma, such as falling on an outstretched hand leading to the transmission of force up the arm causing a fracture of the clavicle. <br>Twisting forces may result in fractures of the tibia and fibula, for example during soccer or skiing when the weight of the body rotates on a fixed foot.<br> Stress or fatigue fractures are caused by repeated minor trauma, which can occur after walking or running long distances, and often affect the foot metatarsals. | Most fractures are a result of some form of injury. This might be a direct blow, a fall from a height or a weight falling onto a part of the body. <br>Other fractures may be caused by indirect trauma, such as falling on an outstretched hand leading to the transmission of force up the arm causing a fracture of the clavicle. <br>Twisting forces may result in fractures of the tibia and fibula, for example during soccer or skiing when the weight of the body rotates on a fixed foot.<br> Stress or fatigue fractures are caused by repeated minor trauma, which can occur after walking or running long distances, and often affect the foot metatarsals. | ||
Pathological fractures :<br>These occur as the result of a disease that weakens the composition of the bone itself such as diseases osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, carcinoma, osteomyelitis .<br>[[Image:Osteoporosis.jpg|450x300px]][[Image:1034771399pagets1.jpg|450x300px]]<br><br><br> | = Pathological fractures :<br>These occur as the result of a disease that weakens the composition of the bone itself such as diseases osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, carcinoma, osteomyelitis .<br>[[Image:Osteoporosis.jpg|450x300px]][[Image:1034771399pagets1.jpg|450x300px]]<br><br><br><br>Clinical Features Of Fracture : = | ||
Clinical features vary depending on the cause and nature of the injury, and range from unconsciousness to the patient being able to use the limb, although complaining of pain .<br>And these features are :<br>• Pain <br>• Deformity<br>• Edema<br>• Loss of function<br>• Muscle spasm<br>• Muscle atrophy<br>• Abnormal movement<br>• limitation of joint motion<br>• shock | |||
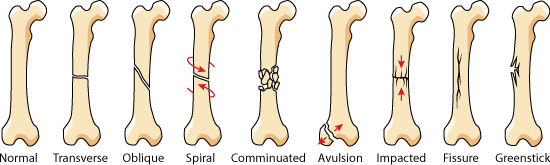
= Types of fracture : = | |||
[[Image:Bone_fractures.gif|center]] | |||
= <br><br><br> = | |||
Revision as of 00:31, 22 February 2017
Definition :[edit | edit source]
A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone.
Causes of fracture :[edit | edit source]
Most fractures are a result of some form of injury. This might be a direct blow, a fall from a height or a weight falling onto a part of the body.
Other fractures may be caused by indirect trauma, such as falling on an outstretched hand leading to the transmission of force up the arm causing a fracture of the clavicle.
Twisting forces may result in fractures of the tibia and fibula, for example during soccer or skiing when the weight of the body rotates on a fixed foot.
Stress or fatigue fractures are caused by repeated minor trauma, which can occur after walking or running long distances, and often affect the foot metatarsals.
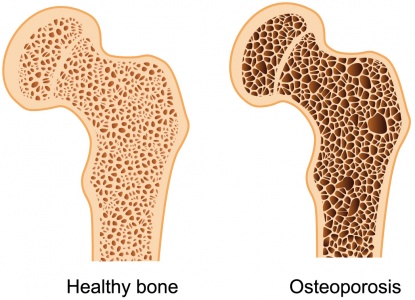
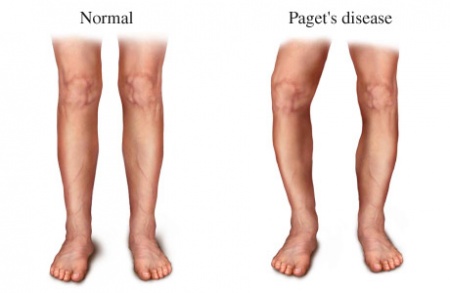
Pathological fractures :
These occur as the result of a disease that weakens the composition of the bone itself such as diseases osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, carcinoma, osteomyelitis .
Clinical Features Of Fracture :[edit | edit source]
Clinical features vary depending on the cause and nature of the injury, and range from unconsciousness to the patient being able to use the limb, although complaining of pain .
And these features are :
• Pain
• Deformity
• Edema
• Loss of function
• Muscle spasm
• Muscle atrophy
• Abnormal movement
• limitation of joint motion
• shock