Facial Schwannoma: Difference between revisions
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | ||
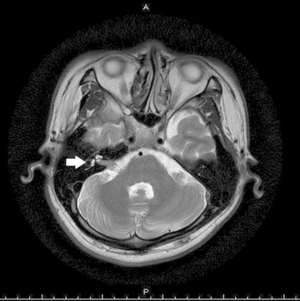
[[File:Facial nerve schwannoma.png|thumb|Contrast-enhanced T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging reveals an intracanalicular tumor in the region of the cerebellopontine angle (shown by the arrow).]] | |||
For details of the path of the Cranial Nerve 7, please see the [[Facial Nerve]] page. | For details of the path of the Cranial Nerve 7, please see the [[Facial Nerve]] page. | ||
=== Location of Tumour === | === Location of Tumour === | ||
The majority of tumours are found on the segment of the nerve within the internal auditory canal, with one UK study<ref>Doshi J, Heyes R, Freeman SR, Potter G, Ward C, Rutherford S, King A, Ramsden R, Lloyd SK. | The majority of tumours are found on the segment of the nerve within the internal auditory canal, with one UK study<ref>Doshi J, Heyes R, Freeman SR, Potter G, Ward C, Rutherford S, King A, Ramsden R, Lloyd SK. | ||
Clinical and Radiological Guidance in Managing Facial Nerve Schwannomas | Clinical and Radiological Guidance in Managing Facial Nerve Schwannomas | ||
Otology & Neurotology. 36(5):892–895, JUNE 2015 | Otology & Neurotology. 36(5):892–895, JUNE 2015 | ||
</ref> of a cohort of 28 Facial Schwannoma patients reporting 68% incidence in this section of the nerve. | </ref> of a cohort of 28 Facial Schwannoma patients reporting 68% incidence in this section of the nerve. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 36: | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
The presentation frequently comprises hearing loss and facial weakness or paralysis.<br> | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
Revision as of 21:47, 28 November 2019
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (28/11/2019)
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Facial Schwannoma is a very rare tumour which grows on the 7th Cranial Nerve, the Facial Nerve.
It is also known as a Facial Neuroma.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
For details of the path of the Cranial Nerve 7, please see the Facial Nerve page.
Location of Tumour[edit | edit source]
The majority of tumours are found on the segment of the nerve within the internal auditory canal, with one UK study[1] of a cohort of 28 Facial Schwannoma patients reporting 68% incidence in this section of the nerve.
The same study also found multi-segmental lesions in 46% of the patients.
Facial weakness was most commonly associated with involvement of the labyrinthine segment (89%).
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
Schwannomas are extremely slow growing tumours, the majority of which are benign[2].
They originate from the Schwann cell sheath of the facial nerve.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The presentation frequently comprises hearing loss and facial weakness or paralysis.
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Doshi J, Heyes R, Freeman SR, Potter G, Ward C, Rutherford S, King A, Ramsden R, Lloyd SK. Clinical and Radiological Guidance in Managing Facial Nerve Schwannomas Otology & Neurotology. 36(5):892–895, JUNE 2015
- ↑ Jayashankar N, Sankhla S. Facial schwannomas: Diagnosis and surgical perspectives. Neurol India [serial online] 2018 [cited 2019 Nov 28];66:144-6. Available from: http://www.neurologyindia.com/text.asp?2018/66/1/144/222821