Expanded Disability Status Scale: Difference between revisions
Memoona Awan (talk | contribs) (image added) |
Memoona Awan (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Memoona Awan|Memoona Awan]]<br> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Memoona Awan|Memoona Awan]]<br> | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
A neurologist John Kurtzke in 1983 designed a scale called Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) as an advance from his previous 10 step Disability Status Scale (DSS). It is used to evaluate disability in [[Multiple Sclerosis (MS)|multiple sclerosis]] and | A neurologist John Kurtzke in 1983 designed a scale called Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) as an advance from his previous 10-step Disability Status Scale (DSS). It is used to evaluate disability in [[Multiple Sclerosis (MS)|multiple sclerosis]] and monitor changes in the level of disability over time<ref>[https://mstrust.org.uk/a-z/expanded-disability-status-scale-edss Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS)] [Internet]. multiple sclerosis trust. 2020 [cited 2024 Feb 29].</ref>. | ||
== Technique == | == Technique == | ||
[[File:Edss_image.jpg|thumb|400x400px|Expanded disability scale]] | [[File:Edss_image.jpg|thumb|400x400px|Expanded disability scale]] | ||
The EDSS quantify disability of MS | The EDSS quantify disability of MS patients based on neurological assessment by categorizing signs and symptoms in eight functional systems (FS). Furthermore, it comprises the ability to execute [[Activities of Daily Living|activities of daily living (ADL)]] and ambulatory function. | ||
# Visual functions: visual field, visual acuity, scotoma and disc pallor. | # Visual functions: visual field, visual acuity, scotoma and disc pallor. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
# [[Cerebral Cortex|Cerebral]] functions: problems with thinking and memory | # [[Cerebral Cortex|Cerebral]] functions: problems with thinking and memory | ||
# Ambulation score. | # Ambulation score. | ||
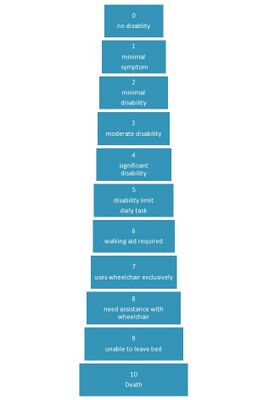
Scores from 0 to 4.0 are determined by FS scores, which means that in this range the EDSS is essentially a measure of impairment. Scores | Scores from 0 to 4.0 are determined by FS scores, which means that in this range the EDSS is essentially a measure of impairment. Scores of 4.0 higher basically address disability. Ambulatory function and the use of walking aids heavily determine the range of 4.0–7.0, and scores between 7.0 and 9.5 are largely determined by the ability to carry out ADL. Each step is defined by the functional system score.<ref>van Munster, C. E., & Uitdehaag, B. M. (2017). [https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-017-0412-5 Outcome Measures in Clinical Trials for Multiple Sclerosis.] ''CNS drugs'', ''31''(3), 217–236. </ref> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Evidence == | == Evidence == | ||
Studies have found that Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) has good reliability and validity in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. | Studies have found that the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) has good reliability and validity in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. It has been found that EDSS is strongly correlated to a Turkish version of the self-reported disability status scale (SRDSS) which indicates good concurrent validity<ref>Ecem, Yeliz, Ayla Fil, Gülşah, Tuncer, K Salcı, Balkan, Sütçü, Aslı. [https://www.msard-journal.com/article/S2211-0348(23)00026-3/abstract#seccesectitle0001 Reliability and validity of the incremental shuttle walk test in patients with fully ambulatory multiple sclerosis.] Multiple sclerosis and related disorders [Internet]. 2023 Jan [cited 2024 Feb 29];70.</ref>. Another study have found showing good accuracy and weighted kappa when self-reported gait measure, the SRDSS, was developed and validated against clinical EDSS<ref>John Robert Ciotti Noah Sanders Amber Salter Joseph R. Berger Anne Haney Cross Salim Chahin. [https://www.msard-journal.com/article/S2211-0348(19)30955-1/fulltext#%20 Clinical instruments to retrospectively capture levels of EDSS.] Multiple sclerosis and related disorders [Internet]. 2019 Dec [cited 2024 Feb 29];39. </ref>.Additionally, an algorithm was developed to derive EDSS scores from previous neurological clinical documentation, and it was found to have substantial agreement with formal EDSS scores and high inter-rater agreement<ref>BİLEK, F., & DEMİR, C. F. . [https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/balikesirsbd/issue/71251/1022783#article_cite Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Version of the Self-Reported Disability Status Scale in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis.] Balıkesir Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi, [Internet]. 2022 Jul [cited 2024 Feb 29];11(2):288–294. </ref>. | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 15:13, 1 March 2024
Purpose[edit | edit source]
A neurologist John Kurtzke in 1983 designed a scale called Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) as an advance from his previous 10-step Disability Status Scale (DSS). It is used to evaluate disability in multiple sclerosis and monitor changes in the level of disability over time[1].
Technique[edit | edit source]
The EDSS quantify disability of MS patients based on neurological assessment by categorizing signs and symptoms in eight functional systems (FS). Furthermore, it comprises the ability to execute activities of daily living (ADL) and ambulatory function.
- Visual functions: visual field, visual acuity, scotoma and disc pallor.
- Brainstem functions: problems with speech, swallowing and nystagmus.
- Pyramidal functions: muscle weakness or difficulty moving limbs
- Cerebellar functions: ataxia, loss of balance, coordination or tremor.
- Sensory functions: numbness or loss of function.
- Bowel and bladder functions: urinary retention, urgency and bowel dysfunction
- Cerebral functions: problems with thinking and memory
- Ambulation score.
Scores from 0 to 4.0 are determined by FS scores, which means that in this range the EDSS is essentially a measure of impairment. Scores of 4.0 higher basically address disability. Ambulatory function and the use of walking aids heavily determine the range of 4.0–7.0, and scores between 7.0 and 9.5 are largely determined by the ability to carry out ADL. Each step is defined by the functional system score.[2]
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Studies have found that the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) has good reliability and validity in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. It has been found that EDSS is strongly correlated to a Turkish version of the self-reported disability status scale (SRDSS) which indicates good concurrent validity[4]. Another study have found showing good accuracy and weighted kappa when self-reported gait measure, the SRDSS, was developed and validated against clinical EDSS[5].Additionally, an algorithm was developed to derive EDSS scores from previous neurological clinical documentation, and it was found to have substantial agreement with formal EDSS scores and high inter-rater agreement[6].
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) [Internet]. multiple sclerosis trust. 2020 [cited 2024 Feb 29].
- ↑ van Munster, C. E., & Uitdehaag, B. M. (2017). Outcome Measures in Clinical Trials for Multiple Sclerosis. CNS drugs, 31(3), 217–236.
- ↑ Dr. Brandon Beaber. Neurologist Explains EDSS for Multiple Sclerosis. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v9sFiM_lkJ4 [last accessed 29/02/2024]
- ↑ Ecem, Yeliz, Ayla Fil, Gülşah, Tuncer, K Salcı, Balkan, Sütçü, Aslı. Reliability and validity of the incremental shuttle walk test in patients with fully ambulatory multiple sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis and related disorders [Internet]. 2023 Jan [cited 2024 Feb 29];70.
- ↑ John Robert Ciotti Noah Sanders Amber Salter Joseph R. Berger Anne Haney Cross Salim Chahin. Clinical instruments to retrospectively capture levels of EDSS. Multiple sclerosis and related disorders [Internet]. 2019 Dec [cited 2024 Feb 29];39.
- ↑ BİLEK, F., & DEMİR, C. F. . Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Version of the Self-Reported Disability Status Scale in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis. Balıkesir Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi, [Internet]. 2022 Jul [cited 2024 Feb 29];11(2):288–294.
\