Activities of Daily Living in Cerebral Palsy: Difference between revisions
Michelle Lee (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michelle Lee (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Definition == | == Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Definition == | ||
The Activities of Daily Living are a series of basic activities performed by individuals on a daily basis necessary for independent living at home or in the community. There are many variations on the definition of the activities of daily living but most organizations agree there are 5 basic categories. | The Activities of Daily Living are a series of basic activities performed by individuals on a daily basis necessary for independent living at home or in the community. There are many variations on the definition of the activities of daily living but most organizations agree there are 5 basic categories. | ||
*Personal hygiene such bathing, grooming and oral care | *Personal hygiene such bathing, grooming and oral care | ||
*Dressing including the ability to make appropriate clothing decisions | *Dressing including the ability to make appropriate clothing decisions | ||
*Eating, the ability to feed oneself though not necessarily prepare food | *Eating, the ability to feed oneself though not necessarily prepare food | ||
*Maintaining continence or the ability to use a restroom | *Maintaining continence or the ability to use a restroom | ||
*Transferring oneself from seated to standing and get in and out of bed | *Transferring oneself from seated to standing and get in and out of bed | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
IADLs are actions that are important to being able to live independently but are not necessarily required activities on a daily basis. The instrumental activities are more subtle and can help more finely determine the level of assistance required by the elderly or disabled. The IADLs include: | IADLs are actions that are important to being able to live independently but are not necessarily required activities on a daily basis. The instrumental activities are more subtle and can help more finely determine the level of assistance required by the elderly or disabled. The IADLs include: | ||
*Basic communication such as using a telephone | *Basic communication such as using a telephone | ||
*Transportation, either by driving, arranging rides or the ability to use public transportation | *Transportation, either by driving, arranging rides or the ability to use public transportation | ||
*Meal preparation and the ability to safely use kitchen equipment | *Meal preparation and the ability to safely use kitchen equipment | ||
*Shopping and the ability to make appropriate food and clothing purchase decisions | *Shopping and the ability to make appropriate food and clothing purchase decisions | ||
*Housework such as doing laundry and cleaning dishes | *Housework such as doing laundry and cleaning dishes | ||
*Managing medications such as taking accurate dosages at appropriate times and managing re-fills | *Managing medications such as taking accurate dosages at appropriate times and managing re-fills | ||
*Managing personal finances, operating within a budget, writing checks and paying bills | *Managing personal finances, operating within a budget, writing checks and paying bills | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
=== ADL Skill === | === ADL Skill === | ||
ADL (sometimes also called Self Care Skills) play a major role in a child's overall functional growth, confidence and independence. These essential skills include the child's ability to feed themselves using utensils appropriately and to perform toileting, bathing and grooming activities. Problems in this area may be due to an underlying problem. This may include impaired Sensory Integration or diminished Fine Motor / Upper Body Coordination. Children may also exhibit poor motor planning which affects their ability to sequence, time and grade motor activities. | ADL (sometimes also called Self Care Skills) play a major role in a child's overall functional growth, confidence and independence. These essential skills include the child's ability to feed themselves using utensils appropriately and to perform toileting, bathing and grooming activities. Problems in this area may be due to an underlying problem. This may include impaired Sensory Integration or diminished Fine Motor / Upper Body Coordination. Children may also exhibit poor motor planning which affects their ability to sequence, time and grade motor activities. | ||
=== Eating and drinking === | === Eating and drinking === | ||
Eating and drinking: everyday it is done a few times. For most children with cerebral palsy is does not give challenges. <br>But for a few children with cerebral palsy it can be a difficult time. Difficult because of the way they are being fed; or difficult because they do not like it; and have difficulty eating. For the parents it can be a difficult time, as it is can be very dificult and can take a long time to feed a child one proper meal. | Eating and drinking: everyday it is done a few times. For most children with cerebral palsy is does not give challenges. <br>But for a few children with cerebral palsy it can be a difficult time. Difficult because of the way they are being fed; or difficult because they do not like it; and have difficulty eating. For the parents it can be a difficult time, as it is can be very dificult and can take a long time to feed a child one proper meal. | ||
Eating and drinking adequatley is important to prevent abnormal development of eating and drinking habits, which can become worse if we do not do anything it is also an important preparation for learning to speak. | Eating and drinking adequatley is important to prevent abnormal development of eating and drinking habits, which can become worse if we do not do anything it is also an important preparation for learning to speak. | ||
=== Development of feeding skills according to age === | === Development of feeding skills according to age === | ||
Milestones for feeding development: | Milestones for feeding development: | ||
*Newborn: locates nipples as soon as it touches lips and sucks well. | *Newborn: locates nipples as soon as it touches lips and sucks well. | ||
*6-7 months: begins to chew soft solid food and begins to drink from cup | *6-7 months: begins to chew soft solid food and begins to drink from cup | ||
*1 year: begins to hold and use spoon and holds cup; can bit of pieces from biscuits; tongue moves from side to side when chewing | *1 year: begins to hold and use spoon and holds cup; can bit of pieces from biscuits; tongue moves from side to side when chewing | ||
*2 years: drinks from cup; eats and chews very well | *2 years: drinks from cup; eats and chews very well | ||
*3 years: eats independently | *3 years: eats independently | ||
=== Difficulties eating and drinking experienced in cerebral palsy === | === Difficulties eating and drinking experienced in cerebral palsy === | ||
Depending on the age of the child difficulties can include:: | Depending on the age of the child difficulties can include:: | ||
*Sucking the mothers breast | *Sucking the mothers breast | ||
*Eating from a spoon | *Eating from a spoon | ||
*Chewing and/or swallowing | *Chewing and/or swallowing | ||
*Closing mouth and lips | *Closing mouth and lips | ||
*Drinking from a cup | *Drinking from a cup | ||
*Drooling | *Drooling | ||
*Holding objects and taking them to the mouth | *Holding objects and taking them to the mouth | ||
*Biting | *Biting | ||
*Hand mouth coordination | *Hand mouth coordination | ||
=== Activities to help with eating and drinking === | === Activities to help with eating and drinking === | ||
Here are some things to consider to aid with the eating and drinking process: | Here are some things to consider to aid with the eating and drinking process: | ||
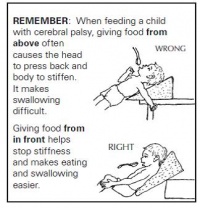
*The body and the head of the child should be in the right position. | *The body and the head of the child should be in the right position. | ||
*When feeding the child: maybe sit in front of him or on the side of the child which relaxes him/her most. | *When feeding the child: maybe sit in front of him or on the side of the child which relaxes him/her most. | ||
*If you put pieces of e.g. biscuit in the mouth of the child: put it at the side of her mouth and not on the tongue. Change side after each piece. | *If you put pieces of e.g. biscuit in the mouth of the child: put it at the side of her mouth and not on the tongue. Change side after each piece. | ||
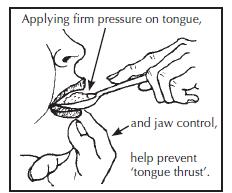
*When feeding with a spoon: push the spoon downwards on the middle of the tongue and wait till the child closes the mouth and takes the food form the spoon. If the child needs help with this: put a little pressure upwards under the chin (jaw control). Take the spoon out in a straight line. | *When feeding with a spoon: push the spoon downwards on the middle of the tongue and wait till the child closes the mouth and takes the food form the spoon. If the child needs help with this: put a little pressure upwards under the chin (jaw control). Take the spoon out in a straight line. | ||
*If the child cannot close the mouth when drinking help the child | *If the child cannot close the mouth when drinking help the child | ||
*Use a straw, which can be easier for the child | *Use a straw, which can be easier for the child | ||
*Cut out a piece of the cup (because of the nose), so the child does not need to tilt the head backwards.<br> | *Cut out a piece of the cup (because of the nose), so the child does not need to tilt the head backwards.<br> | ||
{| width="200" border="1" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| width="200" border="1" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image: | | [[Image:Feeding position 1.jpg|thumb|center|200x250px]] | ||
| [[Image:Cup Cp.jpg|thumb|center|400x250px]] | | [[Image:Cup Cp.jpg|thumb|center|400x250px]] | ||
| [[Image: | | [[Image:Drinking CP .jpg|thumb|center|250x200px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br> | === Eating and drinking as a learning activity === | ||
The process of eating and drinking is a learning activity. Here are some of the ways the child can learn during this activity: | |||
'''Preparing for eating/drinking:<br>''' | |||
Understanding and learning words (mother is telling what she is preparing, name of food, utensils, colours, asking where the plate or spoon is), talking (asking the child to tell what the mother is doing, the name of the food, tell where to find plate). Sitting, pointing, picking up the plate etc. | |||
'''Eating and drinking:''' | |||
*Sitting (head and trunk control, balance); opening mouth, chewing, muscle control and muscle strength of mouth muscles, eye hand coordination, taste of different kind of food; names of food and names of tast etc. | |||
'''Cleaning up''': | |||
*Telling what needs to be done, helping with cleaning up (either by physical helping or by telling what needs to be done); sequence and planning of activities, balance. | |||
'''Eating with others:''' | |||
*Waiting for turn, listening to others. | |||
=== Assistive devices for eating and drinking === | |||
Assistive devices can help the child to learn to eat by himself or to make it easier for him to eat and drink. When there are problems with eating and drinking parents often do not think about teaching the child to learn to do it by himself. Therapist often do not see the child during ADL and sometimes forget to use these times as practice time. | |||
[[Category:Cerebral_Palsy]] | |||
Revision as of 11:41, 20 August 2016
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Definition[edit | edit source]
The Activities of Daily Living are a series of basic activities performed by individuals on a daily basis necessary for independent living at home or in the community. There are many variations on the definition of the activities of daily living but most organizations agree there are 5 basic categories.
- Personal hygiene such bathing, grooming and oral care
- Dressing including the ability to make appropriate clothing decisions
- Eating, the ability to feed oneself though not necessarily prepare food
- Maintaining continence or the ability to use a restroom
- Transferring oneself from seated to standing and get in and out of bed
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs) Definition
[edit | edit source]
IADLs are actions that are important to being able to live independently but are not necessarily required activities on a daily basis. The instrumental activities are more subtle and can help more finely determine the level of assistance required by the elderly or disabled. The IADLs include:
- Basic communication such as using a telephone
- Transportation, either by driving, arranging rides or the ability to use public transportation
- Meal preparation and the ability to safely use kitchen equipment
- Shopping and the ability to make appropriate food and clothing purchase decisions
- Housework such as doing laundry and cleaning dishes
- Managing medications such as taking accurate dosages at appropriate times and managing re-fills
- Managing personal finances, operating within a budget, writing checks and paying bills
ADLs are defined as "the things we normally do...such as feeding ourselves, bathing, dressing, grooming, work, homemaking, and leisure.
Instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) are not necessary for fundamental functioning, but they let an individual live independently in a community. The rest of this page will focus on the ADL's of children with CP.
Using Daily Routine[edit | edit source]
Often parents do not have time to do all kind of extra activities with their child. The most effective way to work with the parents is to help them choose activities of daily life on which to focus. And to choose those activities that are at that time the most important for them.
Some activities come back every day or even a few times a day. To focus on doing these activities in a proper way (good positioning) and in an active way (so the child is learning) will give many opportunities for the child to learn.
ADL Skill[edit | edit source]
ADL (sometimes also called Self Care Skills) play a major role in a child's overall functional growth, confidence and independence. These essential skills include the child's ability to feed themselves using utensils appropriately and to perform toileting, bathing and grooming activities. Problems in this area may be due to an underlying problem. This may include impaired Sensory Integration or diminished Fine Motor / Upper Body Coordination. Children may also exhibit poor motor planning which affects their ability to sequence, time and grade motor activities.
Eating and drinking[edit | edit source]
Eating and drinking: everyday it is done a few times. For most children with cerebral palsy is does not give challenges.
But for a few children with cerebral palsy it can be a difficult time. Difficult because of the way they are being fed; or difficult because they do not like it; and have difficulty eating. For the parents it can be a difficult time, as it is can be very dificult and can take a long time to feed a child one proper meal.
Eating and drinking adequatley is important to prevent abnormal development of eating and drinking habits, which can become worse if we do not do anything it is also an important preparation for learning to speak.
Development of feeding skills according to age[edit | edit source]
Milestones for feeding development:
- Newborn: locates nipples as soon as it touches lips and sucks well.
- 6-7 months: begins to chew soft solid food and begins to drink from cup
- 1 year: begins to hold and use spoon and holds cup; can bit of pieces from biscuits; tongue moves from side to side when chewing
- 2 years: drinks from cup; eats and chews very well
- 3 years: eats independently
Difficulties eating and drinking experienced in cerebral palsy[edit | edit source]
Depending on the age of the child difficulties can include::
- Sucking the mothers breast
- Eating from a spoon
- Chewing and/or swallowing
- Closing mouth and lips
- Drinking from a cup
- Drooling
- Holding objects and taking them to the mouth
- Biting
- Hand mouth coordination
Activities to help with eating and drinking[edit | edit source]
Here are some things to consider to aid with the eating and drinking process:
- The body and the head of the child should be in the right position.
- When feeding the child: maybe sit in front of him or on the side of the child which relaxes him/her most.
- If you put pieces of e.g. biscuit in the mouth of the child: put it at the side of her mouth and not on the tongue. Change side after each piece.
- When feeding with a spoon: push the spoon downwards on the middle of the tongue and wait till the child closes the mouth and takes the food form the spoon. If the child needs help with this: put a little pressure upwards under the chin (jaw control). Take the spoon out in a straight line.
- If the child cannot close the mouth when drinking help the child
- Use a straw, which can be easier for the child
- Cut out a piece of the cup (because of the nose), so the child does not need to tilt the head backwards.
Eating and drinking as a learning activity[edit | edit source]
The process of eating and drinking is a learning activity. Here are some of the ways the child can learn during this activity:
Preparing for eating/drinking:
Understanding and learning words (mother is telling what she is preparing, name of food, utensils, colours, asking where the plate or spoon is), talking (asking the child to tell what the mother is doing, the name of the food, tell where to find plate). Sitting, pointing, picking up the plate etc.
Eating and drinking:
- Sitting (head and trunk control, balance); opening mouth, chewing, muscle control and muscle strength of mouth muscles, eye hand coordination, taste of different kind of food; names of food and names of tast etc.
Cleaning up:
- Telling what needs to be done, helping with cleaning up (either by physical helping or by telling what needs to be done); sequence and planning of activities, balance.
Eating with others:
- Waiting for turn, listening to others.
Assistive devices for eating and drinking[edit | edit source]
Assistive devices can help the child to learn to eat by himself or to make it easier for him to eat and drink. When there are problems with eating and drinking parents often do not think about teaching the child to learn to do it by himself. Therapist often do not see the child during ADL and sometimes forget to use these times as practice time.