The Bath Indices
Intoduction[edit | edit source]
The Bath Indices is a functional and disease activity indices used to aid diagnosis and monitor disease activity in people with Ankylosis Spondilitis (AS). It is made up of four indices which are the Bath Ankylosis Spondylitis Metrology Index(BASMI), the Bath Ankylosis Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI), the Bath Ankylosis Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), and the Bath Ankylosis Spondylitis Patient Global Score (BAS-G). All indices produce a score out of 10, giving a clear numerical outcome each time the indices are used. Also, the four indices have been studied for reliability, speed, variability, reproducibility, and sensitivity to change.
The Bath Ankylosis Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI)[edit | edit source]
Objective[edit | edit source]
The Bath Ankylosis Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI), is a set of 10 questions designed to determine the degree of functional limitation in patients with Ankylosis Spondylitis (AS). The 10 questions were chosen with a major input from patients with AS. The first 8 questions are pertaining to everyday tasks and dependent on functional anatomy (bending, reaching, changing position, standing, turning, and climbing steps with or without rail) while the final 2 questions assess the patients’ ability to cope with everyday life. (Calin et al, 1994). Each item is scored on the scale of 0-10.
A 10 cm visual analog scale (VAS) was used to answer the questions but it is now being replaced by a numerical pain rating scale (NRS) in many centers (4).
Intended Population[edit | edit source]
It is a patient self-report questionnaire for patient with Ankylosis Spondylitis.
Method of Use[edit | edit source]
BASFI is made up of 10 questions which are related to activities of daily living and are scored with a rating scale from 0 (no functional impairments) to 10 (maximal impairment). Each question is answered on a 10 cm horizontal VAS or a numeric respone scale (NRS). A score of 0 indicates the activity was easy and a score of 10 indicates the activity was impossible for the person to accomplish.
All scores from the questions 1-10 are added and then divided by 10. The mean of the individual scores is calculated to give the overall index score. A higher score indicates a higher degree of functional limitations.
The BASFI Items and Scoring[edit | edit source]
Difficulty on a ten point scale (1 is easy and 10 is impossible)
Please indicate your level of ability with each of the following activities during the past week.
1) Putting on your socks or tights without help or aids (e.g sock aid).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2) Bending from the waist to pick up a pen from the floor without aid.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
3) Reaching up to a high shelf without help or aids (e.g helping hand).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
4) Getting up from an armless chair without your hands or any other help.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
5) Getting up off the floor without help from lying on your back.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
6 ) Standing unsupported for 10 minutes without discomfort.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
7) Climbing 12-15 steps without using a handrail or walking aid.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
8) Looking over your shoulder without turning your body.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
9) Doing physically demanding activities (e.g physiotherapy exercises, gardening or sports).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
10) Doing a full days activities whether it be at home or at work.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Evidence[edit | edit source]
The BASFI satisfies the criteria required of a functional index: it is quick and easy to complete, is reliable and is sensitive to change across the whole spectrum of disease. Furthermore, over the 3 week period of inpatient treatment, the BASFI revealed a significant improvement in function (20%, p = 0.004) while there was a less impressive change in the Dougados functional index (6%, p = 0.03). This demonstrates the superior sensitivity of the BASFI: Consistency was good for both indices (p < 0.001), as was the relationship between patient perception of function and function as assessed by an external observer (p < 0.001).[1]
Reliability[edit | edit source]
When patients were assessed on their actual performance of eight items from the BASFI representing activities of daily life, adequate to excellent test-retest reproducibility was shown (van Weely et al, 2009). A significant association between the BASMI and BASFI has also been demonstrated (Sieper et al, 2009) indicating the importance of spinal mobility on an individual’s functional status.
Validity[edit | edit source]
Calin et al. (1994) compared BASFI with Dougados functional index, it was found that the BASFI demonstrates a significant improvement in function while there was less change in the Dougados score (Calin et el,1994).
Internal consistency reliability and construct validity of BASFI was deemed acceptable by the authors, but they also mentioned that random measurement error of BASFI was not negligible.[2]
Haywood et al. (2005) reported that BASFI is one of three AS assessment instruments with the most extensive evidence for validity through comparison with instruments that measure similar or related constructs, and/or with measures of mobility.[3]
Responsiveness[edit | edit source]
There was 20% (P = 0.004) improvement in function over 3 weeks versus 6% (P = 0.03) improvement demonstrated by the Dougados functional index during the physiotherapy treatment over the same 3-week period.
Miscellaneous[edit | edit source]
One of the benefits of the scale in the way it is administered resides in the visual analogue scale which is a lot easier and quicker to use for patients, although it requires a bit of interpretation from the clinician.
The Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)[edit | edit source]
Objective[edit | edit source]
The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) is the gold standard for measuring and following disease activity and thus functional status in the person with Ankylosing Spondylitis[4].
Like the BASFI, the BASDAI consists of six 10-cm horizontal visual analog scales to measure severity of fatigue, spinal and peripheral joint pain, localized tenderness, and morning stiffness (both qualitative and quantitative)[4]. This VAS has now been replaced by a numerical rating scale (NRS) in many centres (4).
The questions are answered on a 10 cm VAS, anchored with the labels “none” and “very severe” at either end of the first five questions, and with "0 hours” and “two hours” at either end of the question on duration of morning stiffness. The mean of the two scores for morning stiffness counts as one variable. The final score is defined by calculating the mean of the five items. Final scores range from 0 (best) to 10 (worst).
Intended Population[edit | edit source]
Persons with Ankylosis Spindylitis.
Method of Use[edit | edit source]
BASDAI is a quick and simple index (taking between 30 secs and 2 mins to complete). It is a self-reported questionnaire that is made up of 6 questions related to 5 major symptoms: fatigue, spinal pain, joint pain/swelling, areas of localized tenderness, morning stiffness. Each question is answered on a ten centimeter visual analog scales. A score of 0 = none (no symptoms), and a score of 10 = very severe symptoms. A mean score is calculated across all 6 items and higher score reflects greater degree of disease activity. To give each symptom equal weighting, the mean of the two scores relating to morning stiffness is taken. The resulting 0 to 50 score is divided by 5 to give a final 0 – 10 BASDAI score.
The higher the BASDAI score, the more severe the patient’s disability due to their AS.[4][5]
The BASDAI Item and Scoring[edit | edit source]
Please tick the box which represents your answer.
All questions refer to last week. (i.e. )
1. How would you describe the overall level of fatigue/tiredness you have experienced?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none very severe
2. How would you describe the overall level of AS neck, back or hip pain you have had
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none very severe
3. How would you describe the overall level of pain/swelling in joints other than neck, back or hips you have had?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none very severe
4. How would you describe the overall level of discomfort you have had from any areas tender to touch or pressure?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none very severe
5. How would you describe the overall level of morning stiffness you have had from the time you wake up?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none very severe
0 1 2 or more
hr hr hrs
6. How long does your morning stiffness last from the time you wake up?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none very severe
0 1 2 or more
hr hr hrs
Scoring the BASDAI:
Mean score of 5 & 6:
The total of 1 to 4 added to the mean of 5 &6:
Total out of 5 (BASDAI):
The mean measurement (score) of questions 5 and 6 is added to the scores from questions 1 to 4. This total is then divided by 5 to give the average. This is the BASDAI score. The higher the BASDAI score, the more severe the patients disability due to their AS.
Reference[edit | edit source]
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Reliability[edit | edit source]
BASDAI demonstrated statistically significant (p<0.001) reliability.
Test-retest reliability across the scale responses where said to be good (who said that it is good)[4].
Validity[edit | edit source]
When compared to a previous disease activity index it is felt that BASDAI is superior in terms of symptoms considered and their weighting. This may be due to the input from patients with AS when the index was developed. The BASDAI was also found to be superior in all aspects to the Newcastle Enthesis Index[4].
The validity of BASDAI was further assessed by Calin et al (1999) have further. They concluded that the BASDAI has excellent content validity[6].
Responsiveness[edit | edit source]
Following a 3 week physiotherapy course, the BASDAI showed a significant (p=0.009) 16.4% score improvement, therefore demonstrating a sensitivity to change[4].
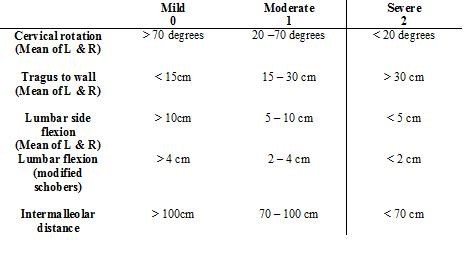
BASMI: Bath AS Metrology Index[edit | edit source]
To accurately assess axial status (cervical, dorsal and lumbar spine, hips and pelvic soft tissue) of individuals with AS and from these derive a metrology index to define clinically significant changes in spinal mobility.
Five clinical measurements were included in the index:
1. Cervical rotation (degrees of motion)
2. Tragus to wall distance (centimetre tape measure)
3. Lumbar side flexion (centimetre tape measure)
4. Modified Schober Test centimetre tape measure)
5. Intermalleolar distance (centimetre tape measure)
A BASMI score from between 0 to 10 is calculated after the clinical exam is performed and each of the 5 measurements is obtained. The range of severity 0-10 reflects mild to moderate disease activity and functional ability in the spinal column. The higher the BASMI score the more severe the patient’s limitation of movement due to their AS.
BAS-G: Bath AS Patient Global score[edit | edit source]
The impact of AS from the patients’ perspective encompasses all aspects of disease including activity, function and structural damage, in one summary measure. The patient global assessment is useful in clinical practice, and may be the single most responsive measure in this setting.
The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Global score (BAS-G) is consistent with the other measures in the core set, utilizing the ‘in the last week’ approach to obtain a snapshot of current patient status but also it also refers to the patient’s average well-being over the last 6 months, which can be helpful to describe longer-term disease progression.
The BAS-G consists of two questions which ask patients’ to indicate, on a 10cm VAS, the effect the disease has had on their well-being over the
- last week
- last six months.
The mean of the two scores gives a BAS-G score of 0 – 10. The higher the score, the greater the perceived effect of the disease on the patient’s well-being.
1) How have you been over the last week?
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Very Good Bad
2) How have you been over the last six months?
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Very Good Bad
Scoring the BAS-G:
Total Score out of 20:
BAS-G Score, Total Sore/2:
The total figure is divided by 2 to obtain an average, this is the BAS-G score. The higher the BAS-G score, the more severe the effect of AS on the patient’s life
- ↑ Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O’Hea J, Mallorie P, et al A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2281–5.
- ↑ Madsen OR, Rytter A, Hansen LB, Suetta C, Egsmose C. Reproducibility of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Indices of disease activity (BASDAI), functional status. (BASFI) and overall well-being (BAS-G) in anti-tumour necrosis factor-treated spondyloarthropathy patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2010 Aug;29(8):849-54. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20306214/
- ↑ Haywood KL, Garratt AM, Dawes PT. Patient-assessed health in ankylosing spondylitis: a structured review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 May;44(5):577–86. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15695297/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Garret S et al. A new approach to defining disease status in Ankylosing Spondylitis: The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI). Journal of Rheumatology. 1994;2286-91.
- ↑ Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Braun J, Burgos-Vargas R, Dougados M, Hermann K-G, Landewé R, Maksymowych W and Van der Heijde D. (2009) The assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloathritis. Ann Rheum Dis (2009): 68 (Suppl 11).
- ↑ Calin A, et al. Defining disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis: is a combination of variables (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index) an appropriate instrument? Rheumatology (Oxford).1999;Vol(9),878-82.