Limbic System
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Stacy Schiurring, Kim Jackson and Rucha Gadgil
Introduction[edit | edit source]
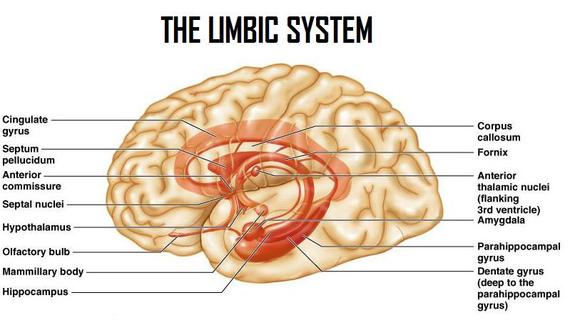
The limbic system is a set of structures of the brain. These structures cover both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system, but a collection of structures from the cerebrum, diencephalon, and midbrain. It supports many different functions, including emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction.[1]
It combines higher mental functions and primitive emotion into a single system often referred to as the emotional nervous system. It is not only responsible for our emotional lives but also our higher mental functions, such as learning and formation of memories. The limbic system is the reason that some physical things such as eating seem so pleasurable to us, and the reason why some medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, are caused by mental stress. There are several important structures within the limbic system: the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus.[2]
The limbic system is among the oldest parts of the brain in evolutionary terms: it can be found in fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals.
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Kiddle Limbic system facts for kids Available from: https://kids.kiddle.co/Limbic_system (accessed 28.12.2020)
- ↑ Lumen learning Structure and function of the brain Available from:https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-psychology/chapter/structure-and-function-of-the-brain/ (accessed 28.12.2020)