Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
== Case Reports/ Case Studies == | == Case Reports/ Case Studies == | ||
[http:// | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12425126 Stevens L. Chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease and its effect on laryngeal visualization and intubation: a case report. AANA Journal [serial on the Internet]. (2002, Oct), [cited March 17, 2011]; 70(5): 373-375. Available from: MEDLINE.] | ||
<br> A Randomized Study Comparing the Shaker Exercise with Traditional Therapy: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2895999/?tool=pubmed A Preliminary Study] | <br>A Randomized Study Comparing the Shaker Exercise with Traditional Therapy: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2895999/?tool=pubmed A Preliminary Study] | ||
== Resources <br> == | == Resources <br> == | ||
Revision as of 20:56, 31 March 2011
Original Editors - Tessa Puckett from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Lead Editors - Your name will be added here if you are a lead editor on this page. Read more.
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
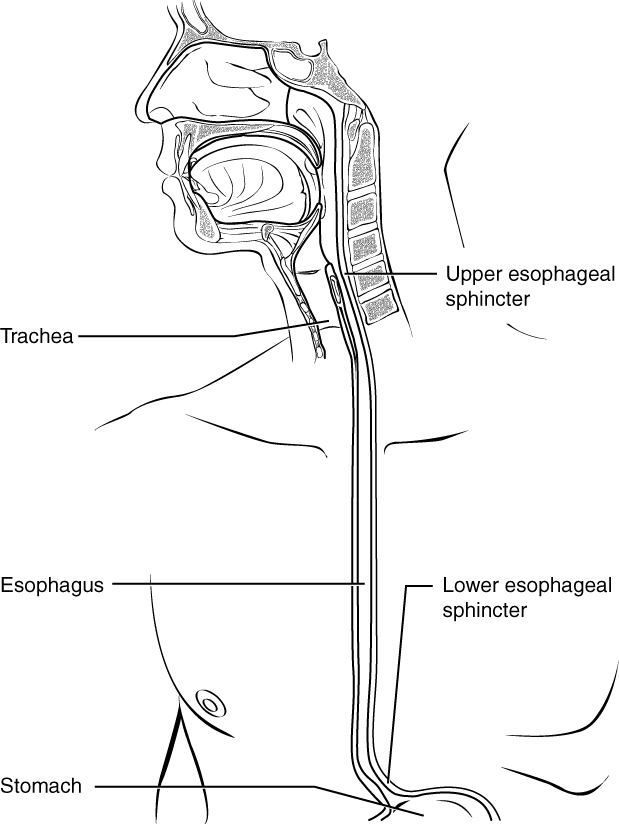
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), sometimes referred to as esophagitis, is a condition that results from reflux (backward flow) of the stomach contents into the esophagus. Reflux of infectious agents, chemical irritants, physical agents such as radiation and nasogastric intubation can cause GERD and can irritate and inflame the esophagus causing heartburn, belching, sore throat and other symptoms. Heartburn and indigestion are not other words for GERD, but are common symptoms of the condition. [1][2][3]
[Photo courtesy of the National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001311/figure/d19e2114/?report=objectonly.]
Prevalence[edit | edit source]
add text here
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here
Associated Co-morbidities[edit | edit source]
add text here
Medications[edit | edit source]
H2 Receptor Blockers
File:Pepcid.jpgFile:Zantac.jpg
Proton Pump Inihibitors
File:Prilosec.jpgFile:Nexium.jpg
Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values[edit | edit source]
add text here
Etiology/Causes[edit | edit source]
add text here
Systemic Involvement[edit | edit source]
add text here
Medical Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
add text here
Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
Shakers Head Lift Exercise PDF Handout from The Ohio State University Medical Center Department of Rehabilitation Services - Dodd Hall[4]
Alternative/Holistic Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
add text here
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here
Case Reports/ Case Studies[edit | edit source]
Stevens L. Chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease and its effect on laryngeal visualization and intubation: a case report. AANA Journal [serial on the Internet. (2002, Oct), [cited March 17, 2011]; 70(5): 373-375. Available from: MEDLINE.]
A Randomized Study Comparing the Shaker Exercise with Traditional Therapy: A Preliminary Study
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
see tutorial on Adding PubMed Feed
Failed to load RSS feed from http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1PW-O5V9EIraHx6Utb0JkY5qObdTZAlZCEHZnz9rPDhn_kksht|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: Implications for the Physical Therapist. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier; 2009.
- ↑ Goodman, Snyder. Differential Diagnosis for Physical Therapists: Screening for Referral. 4th Ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2003.
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001311/ (accessed 17 March 2011).
- ↑ The Ohio State University Medical Center Department of Rehabilitation Services - Dodd Hall. Exercises to Improve Swallowing. http://medicalcenter.osu.edu/PatientEd/Materials/PDFDocs/dis-cond/general/exercises-swallowing.pdf (accessed 31 March 2011).