Quadratus Femoris: Difference between revisions
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) (Created page with "<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- Leana Louw '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} </div> <div class="noeditb...") |
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
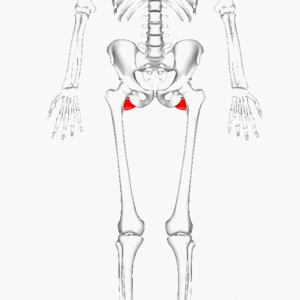
Quadratus femoris is a short, flat and rectangular muscle. It is situated inferior to the obturator internus and gemelli.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref> | |||
[[File:Quadratus femoris.gif|none|thumb]] | |||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
Lateral border of the ischial tuberosity.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
Quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest of the femur and area inferior to it.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1).<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
* External rotates the thigh | |||
* Assists in adduction of the thigh | |||
* Stabilise the femur head in the acetabulum<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
| Line 31: | Line 39: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
Revision as of 17:07, 1 February 2020
Original Editor - Leana Louw
Top Contributors - Leana Louw, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson and Wendy Snyders
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (1/02/2020)
Description[edit | edit source]
Quadratus femoris is a short, flat and rectangular muscle. It is situated inferior to the obturator internus and gemelli.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Lateral border of the ischial tuberosity.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest of the femur and area inferior to it.[1]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1).[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Function[edit | edit source]
- External rotates the thigh
- Assists in adduction of the thigh
- Stabilise the femur head in the acetabulum[1]