Anticipatory Adjustments: Balance Intervention Strategies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
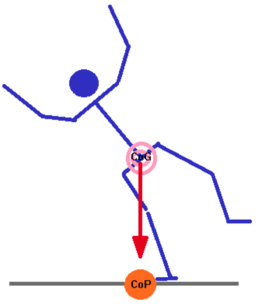
[[File:Center of pressure in relation to center of gravity while off balance.png|left|thumb|Poor Control of Center of Mass]] | [[File:Center of pressure in relation to center of gravity while off balance.png|left|thumb|Poor Control of Center of Mass]] | ||
When working with individuals to improve their ability to maintain their [[Base of support|center of gravity]], you initially think of static and dynamic [[balance]]. The first level of intervention for your patients who demonstrate instability due to lack of ability to control their center of mass is anticipatory adjustments. An activity that qualifies as being an anticipatory adjustment is when a patient is | When working with individuals to improve their ability to maintain their [[Base of support|center of gravity]], you initially think of static and dynamic [[balance]]. The first level of intervention for your patients who demonstrate instability due to lack of ability to control their center of mass is anticipatory adjustments. An activity that qualifies as being an anticipatory adjustment is when a patient is made aware of a task to perform and the patient has to then perform the task. The patient is able to think and know the desired movement pattern for the defined situation. The patient is able to practice both physically and mentally the physical response and movement pattern.<br> | ||
== Indication == | == Indication == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
An example of a patient who would need to master anticipatory adjustments would be a patient who is not able to easily move to perform an activity like the [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Star_Excursion_Balance_Test star excursion balance test]. When patients are not able to successfully weight shift and move their center of mass in a controlled manner (like movement patterns in the star excursion balance test), the patient is unstable and is at high risk of falling. Providing activities that focus on anticipatory adjustments will help the patient learn center of mass and how to control center of mass. The video shares how a person can be directed to perform various movement patterns and how the center of mass can be controlled. The video also shares what failing to control the center of mass would look like.<br> | An example of a patient who would need to master anticipatory adjustments would be a patient who is not able to easily move to perform an activity like the [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Star_Excursion_Balance_Test star excursion balance test]. When patients are not able to successfully weight shift and move their center of mass in a controlled manner (like movement patterns in the star excursion balance test), the patient is unstable and is at high risk of falling. Providing activities that focus on anticipatory adjustments will help the patient learn center of mass and how to control center of mass. The video shares how a person can be directed to perform various movement patterns and how the center of mass can be controlled. The video also shares what failing to control the center of mass would look like.<br> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|PlRs6pnucgE}}<ref>Shahin Rabbani. Anticipatory Balance Control - MIG 2014. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PlRs6pnucgE</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|PlRs6pnucgE}}<ref>Shahin Rabbani. Anticipatory Balance Control - MIG 2014. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PlRs6pnucgE</ref> | ||
This video demonstrates activities defined as anticipatory adjustments that can be performed in the clinic. | |||
{{#ev:youtube|7FxPix0TABw}}<ref>Dr. Tamara Hefferon. Anticipatory Balance. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7FxPix0TABw</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|7FxPix0TABw}}<ref>Dr. Tamara Hefferon. Anticipatory Balance. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7FxPix0TABw</ref> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Clinical presentation includes information you receive from the patient. If you consider patient reported outcome measures, then you will appreciate learning the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale.<ref>Powell LE, Myers AM. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7814786 The activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale.] The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 1995 Jan 1;50(1):M28-34.</ref> Confidence in balance and fear of falling are predictive of future falls.<ref>Merrill R. Landers, Sarrie Oscar, Jessica Sasaoka, Kyle Vaughn; [https://academic.oup.com/ptj/article/96/4/433/2686463 Balance Confidence and Fear of Falling Avoidance Behavior Are Most Predictive of Falling in Older Adults: Prospective Analysis], ''Physical Therapy'', Volume 96, Issue 4, 1 April 2016, Pages 433–442</ref><ref>Cleary K, Skornyakov E. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28633057 Predicting falls in community dwelling older adults using the Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale.] Archives of gerontology and geriatrics. 2017 Sep 1;72:142-5.</ref> A score < 67% indicates an increased risk of falling.<ref>Raad, Jason et al. [https://www.archives-pmr.org/article/S0003-9993(13)00366-3/fulltext A Brief Review of the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale in Older Adults.] Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Volume 94, Issue 7, 1426 - 1427.<footer></footer></ref> | |||
A patient who needs interventions that require anticipatory adjustments will share stories of having difficulty feeling safe walking outdoors. Will report holding onto furniture or walls while walking. Will mention feeling unsteady. | |||
The [[Berg Balance Scale]] is a performance measurement tool that can be used to determine if a patient is at risk of falls. | |||
As you observe your patient, you may notice that they demonstrate some gait characteristics that could be interpreted as compensating for unsteadiness. Patients will demonstrate a slower gait speed. Patients will decrease their step length. Patients will have an increased step width.<ref>Yiou E, Caderby T, Delafontaine A, Fourcade P, Honeine JL. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29184756 Balance control during gait initiation: State-of-the-art and research perspectives. World journal of orthopedics.] 2017 Nov 18;8(11):815.</ref> | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
[https://www.cdc.gov/steadi/index.html Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries] (STEADI) for screening ideas. | |||
Activities like ball throwing help with providing a perturbation along with an anticipatory adjustment to maintain balance.<ref>Aruin AS. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4913780/ Enhancing Anticipatory Postural Adjustments: A Novel Approach to Balance Rehabilitation.] ''J Nov Physiother''. 2016;6(2):e144.</ref> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 23:10, 11 February 2019
Original Editor - Selena Horner
Top Contributors - Selena Horner, Kim Jackson and Rucha Gadgil
Description[edit | edit source]
When working with individuals to improve their ability to maintain their center of gravity, you initially think of static and dynamic balance. The first level of intervention for your patients who demonstrate instability due to lack of ability to control their center of mass is anticipatory adjustments. An activity that qualifies as being an anticipatory adjustment is when a patient is made aware of a task to perform and the patient has to then perform the task. The patient is able to think and know the desired movement pattern for the defined situation. The patient is able to practice both physically and mentally the physical response and movement pattern.
Indication[edit | edit source]
An example of a patient who would need to master anticipatory adjustments would be a patient who is not able to easily move to perform an activity like the star excursion balance test. When patients are not able to successfully weight shift and move their center of mass in a controlled manner (like movement patterns in the star excursion balance test), the patient is unstable and is at high risk of falling. Providing activities that focus on anticipatory adjustments will help the patient learn center of mass and how to control center of mass. The video shares how a person can be directed to perform various movement patterns and how the center of mass can be controlled. The video also shares what failing to control the center of mass would look like.
This video demonstrates activities defined as anticipatory adjustments that can be performed in the clinic.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Clinical presentation includes information you receive from the patient. If you consider patient reported outcome measures, then you will appreciate learning the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale.[3] Confidence in balance and fear of falling are predictive of future falls.[4][5] A score < 67% indicates an increased risk of falling.[6]
A patient who needs interventions that require anticipatory adjustments will share stories of having difficulty feeling safe walking outdoors. Will report holding onto furniture or walls while walking. Will mention feeling unsteady.
The Berg Balance Scale is a performance measurement tool that can be used to determine if a patient is at risk of falls.
As you observe your patient, you may notice that they demonstrate some gait characteristics that could be interpreted as compensating for unsteadiness. Patients will demonstrate a slower gait speed. Patients will decrease their step length. Patients will have an increased step width.[7]
Resources[edit | edit source]
Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries (STEADI) for screening ideas.
Activities like ball throwing help with providing a perturbation along with an anticipatory adjustment to maintain balance.[8]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Shahin Rabbani. Anticipatory Balance Control - MIG 2014. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PlRs6pnucgE
- ↑ Dr. Tamara Hefferon. Anticipatory Balance. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7FxPix0TABw
- ↑ Powell LE, Myers AM. The activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 1995 Jan 1;50(1):M28-34.
- ↑ Merrill R. Landers, Sarrie Oscar, Jessica Sasaoka, Kyle Vaughn; Balance Confidence and Fear of Falling Avoidance Behavior Are Most Predictive of Falling in Older Adults: Prospective Analysis, Physical Therapy, Volume 96, Issue 4, 1 April 2016, Pages 433–442
- ↑ Cleary K, Skornyakov E. Predicting falls in community dwelling older adults using the Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale. Archives of gerontology and geriatrics. 2017 Sep 1;72:142-5.
- ↑ Raad, Jason et al. A Brief Review of the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale in Older Adults. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Volume 94, Issue 7, 1426 - 1427.<footer></footer>
- ↑ Yiou E, Caderby T, Delafontaine A, Fourcade P, Honeine JL. Balance control during gait initiation: State-of-the-art and research perspectives. World journal of orthopedics. 2017 Nov 18;8(11):815.
- ↑ Aruin AS. Enhancing Anticipatory Postural Adjustments: A Novel Approach to Balance Rehabilitation. J Nov Physiother. 2016;6(2):e144.