Semispinalis Cervicis: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (deleted pubmed) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Maintains head posture.<ref name="pt">ptcentral.com/muscles/muscletrunk.html</ref> <br> | Maintains head posture.<ref name="pt">ptcentral.com/muscles/muscletrunk.html</ref> <br><div class="researchbox"> </div> | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | |||
</div> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 6 June 2018
Original Editor Oyemi Sillo
Lead Editors - Lucinda hampton, Oyemi Sillo, Vanessa Rhule, Kim Jackson, Ahmed Nasr, 127.0.0.1, Tarina van der Stockt and WikiSysop
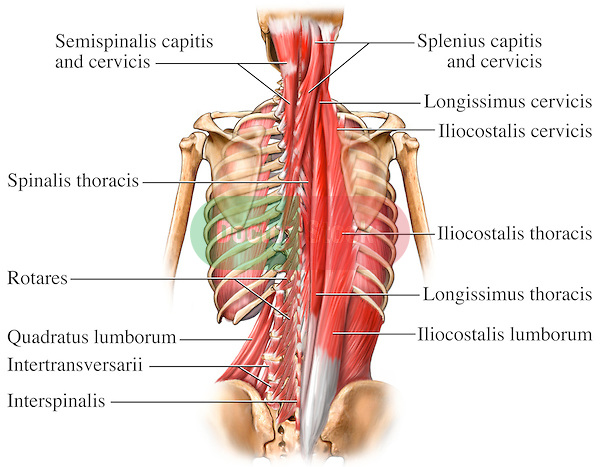
Description[edit | edit source]
Semispinalis Cervicis belongs to the Transversospinal group of muscles.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Transverse processes of T1 to T6[2][3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Spinous processes of C2 to C5[2]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves[2][3]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Deep cervical artery[3]
Action[edit | edit source]
Acting bilaterally: extension of the cervical spine
Acting unilaterally: lateral flexion of the neck and rotation to the opposite side.[2]
Function[edit | edit source]
Maintains head posture.[4]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/semispinalis_cervicis_1
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5221/
- ↑ ptcentral.com/muscles/muscletrunk.html