Moving and Handling: Difference between revisions
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | |||
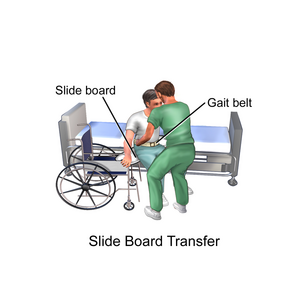
[[File:Slide board.png|right|frameless]] | |||
Moving and handling forms a key part of most occupations.<ref name=":2">Health and Safety Executive. Moving and handling in health and social care. Available from: https://www.hse.gov.uk/healthservices/moving-handling.htm (accessed 28/06/2020).</ref> Safe moving and handling requires physiotherapists to know the correct procedures for moving adults and children without causing injury to either themselves or the person they are supporting. This includes learning to use hoists and other aids. | |||
= | |||
Moving and handling forms a key part of most occupations | |||
This page will look into the [[ergonomics]] behind the safe moving and handling practices relating to physiotherapy. See also [[Transfer Aids]] and [[Bed Mobility and Transfers in Spinal Cord Injury]] | |||
== | === Techniques === | ||
'''Preparation'''<ref name=":0">Bridger R. [https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=Jr4FIRQnVqQC&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=introduction+to+ergonomics+bridger&ots=QoFb9eA9-T&sig=_yetZo2fiM9yHEnptI_KZGORQRI&redir_esc=y Introduction to ergonomics.] Crc Press; 2008.</ref> | |||
* Check physician’s order to ambulate and any restrictions related to ambulation due to medical treatment or surgical procedure. | |||
* Gather any supplies for ambulation required | |||
* Introduce yourself to and confirm patient ID with two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth) | |||
* Perform an assessment of patient’s strength and abilities. | |||
* Ensure clothing (including footwear) are appropriate | |||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
* Ensure clothing (including footwear) are appropriate | |||
* Ensure all participants are aware of the task, including the order of specific task and end position of the patient | * Ensure all participants are aware of the task, including the order of specific task and end position of the patient | ||
* Get the equipment ready and in order, with required accessories | * Get the equipment ready and in order, with required accessories | ||
| Line 104: | Line 29: | ||
* Ask how they felt after the transfer | * Ask how they felt after the transfer | ||
== Sitting == | |||
'''Preparation''' | |||
# Check a patients [[Weight bearing|weight-bearing]] status with colleagues, medical notes, the client and family if needed | |||
# Check a patients weight-bearing status with colleagues, medical notes, the client and family if needed | |||
# Consider hoisting if non-weight bearing, never put weight through a patients non-weight bearing leg | # Consider hoisting if non-weight bearing, never put weight through a patients non-weight bearing leg | ||
# Make sure the patient knows what to expect during the transfer | # Make sure the patient knows what to expect during the transfer | ||
'''Supervising sitting repositioning''' | |||
# Patient places feet flat of the floor and slightly under the chair | # Patient places feet flat of the floor and slightly under the chair | ||
# Patient leans forwards so weight is over their knees | # Patient leans forwards so weight is over their knees | ||
# Patient stands, moves as far back into the seat as possible OR pushes back on armrests and their feet to slide back into the seat | # Patient stands, moves as far back into the seat as possible OR pushes back on armrests and their feet to slide back into the seat | ||
'''Assistance Sitting''' | |||
# Ask client to feel for chair on back of legs, reach for armrests and slowly lower themselves | |||
# Encourage client to bend at the hips<ref name=":3">Turner A, Foster M, Johnson SE, editors. [https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=NpHhq8VZI-0C&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=occupational+therapy+and+physical+dysfunction&ots=1xSPu-N4q7&sig=IxaZs2pJ2dzD6OMdDOqbHWnd-aU&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=occupational%20therapy%20and%20physical%20dysfunction&f=false Occupational therapy and physical dysfunction: principles, skills and practice.] Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 2002.</ref> | |||
== Standing == | |||
'''Supervising standing''' | |||
# Patient places hands on armrests, feet flat of the floor and slightly under the chair | # Patient places hands on armrests, feet flat of the floor and slightly under the chair | ||
# Pt moves slightly closer to the edge of the seat | # Pt moves slightly closer to the edge of the seat | ||
# Pt sits forwards, "nose over toes" | # Pt sits forwards, "nose over toes" | ||
# If needed, the patient rocks backwards and forwards | # If needed, the patient rocks backwards and forwards | ||
# Patient leans forwards so weight is over their knees | # Patient leans forwards so weight is over their knees | ||
# Carer counts down "ready, steady, stand". On stand, the patient pushes up into a standing position | # Carer counts down "ready, steady, stand". On stand, the patient pushes up into a standing position<ref name=":3" /> | ||
'''Assistance Standing''' | |||
# Caregiver adopts the lunge position, beside the patient | # Caregiver adopts the lunge position, beside the patient | ||
# Outside hand is flat on the front of patients shoulder, inside arm across lower back | # Outside hand is flat on the front of patients shoulder, inside arm across lower back | ||
# With weight starting on the back foot, carer rocks forward with the client | # With weight starting on the back foot, carer rocks forward with the client | ||
# Check clients arms are free and in front | # Check clients arms are free and in front | ||
''' | == '''Rolling in Bed''' == | ||
'''Supervised'''<ref name=":3" /> | |||
'''Supervised''' | |||
# Patient turns head in direction of roll | # Patient turns head in direction of roll | ||
# Patient flexes knee further from the direction of roll | # Patient flexes knee further from the direction of roll | ||
| Line 181: | Line 62: | ||
# Client rolls over, pushing with outside of foot and reaching across body | # Client rolls over, pushing with outside of foot and reaching across body | ||
# Client completes roll | # Client completes roll | ||
'''Assistance''' | '''Assistance'''<ref name=":3" /> | ||
# Patient turns head in direction of roll | # Patient turns head in direction of roll | ||
# Patient flexes knee further from the direction of roll | # Patient flexes knee further from the direction of roll | ||
| Line 188: | Line 69: | ||
# Client is rolled onto their side | # Client is rolled onto their side | ||
== Moving in Bed == | |||
'''Supervised bridge:''' | |||
* Teach the patient to do a bridge to move up and down in the bed | * Teach the patient to do a bridge to move up and down in the bed | ||
* Patient to hold on to head of bed with arms and pull themselves up. This can be done in combination with a bridge, and works well in patients with an increased BMI, or that have specific lower limb weight bearing limitations/pain, preventing them to do an optimal bridge. | * Patient to hold on to head of bed with arms and pull themselves up. This can be done in combination with a bridge, and works well in patients with an increased BMI, or that have specific lower limb weight bearing limitations/pain, preventing them to do an optimal bridge. | ||
1 x assistance: | '''Supervised hip hitch:''' | ||
''Ask the client to:'' | |||
# Sit up in bed ''(1. Raise head 2. Put both hands on bed & raise upper body c arms 3. Pushup from bed c arms)'' | |||
# Make their hands into closed fists and put their fists just behind their hips | |||
# Bend their knees and dig their heels into the bed, ready to push themselves up the bed | |||
# Push themselves up by pushing through their heels and fists at the same time, to lift and move their bottom up the bed. | |||
'''1 x assistance:''' | |||
* Assist to lift pelvis | * Assist to lift pelvis | ||
* Place patient in crook lying | * Place patient in crook lying | ||
* Put one around patient's shoulders and the other at the back of the scapula | * Put one around patient's shoulders and the other at the back of the scapula | ||
* Assist with pulling upwards when the patient does a bridge | * Assist with pulling upwards when the patient does a bridge<ref name=":3" /> | ||
== Sitting over the Edge of a Bed == | |||
'''Supervised'''<ref>Pedretti LW, Early MB, editors. [https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=CoFUDgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=%5BBOOK%5D+Occupational+therapy:+Practice+skills+for+physical+dysfunction&ots=4Rsnz3g2Dr&sig=TksFKrg1YlFHPHYWgRsjkGyMUS8&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=%5BBOOK%5D%20Occupational%20therap Occupational therapy: Practice skills for physical dysfunction.] St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 2001 Feb.</ref> | '''Supervised'''<ref>Pedretti LW, Early MB, editors. [https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=CoFUDgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=%5BBOOK%5D+Occupational+therapy:+Practice+skills+for+physical+dysfunction&ots=4Rsnz3g2Dr&sig=TksFKrg1YlFHPHYWgRsjkGyMUS8&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=%5BBOOK%5D%20Occupational%20therap Occupational therapy: Practice skills for physical dysfunction.] St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 2001 Feb.</ref> | ||
| Line 205: | Line 96: | ||
# Uses hands and elbow to push up whilst lowering legs to floor | # Uses hands and elbow to push up whilst lowering legs to floor | ||
{{#ev:youtube|watch?v=G4YMmodurWY}} | {{#ev:youtube|watch?v=G4YMmodurWY}} | ||
== Slide Sheets == | |||
{{#ev:youtube|watch?v=O_0pglA201U}} | {{#ev:youtube|watch?v=O_0pglA201U}} | ||
'''Applying''' | '''Applying'''<ref name=":3" /> | ||
# Place slide sheets underneath a bed sheet | # Place slide sheets underneath a bed sheet | ||
# Keep edges of slide sheet to edge of the bed | # Keep edges of slide sheet to edge of the bed | ||
# Push slide sheet under the patient, pushing down on the mattress | # Push slide sheet under the patient, pushing down on the mattress | ||
# Roll patient to the side and pull through the slide sheets | # Roll patient to the side and pull through the slide sheets | ||
'''Pushing client up the bed with slide sheets''' | '''Pushing client up the bed with slide sheets'''<ref name=":3" /> | ||
# Apply slide sheets | # Apply slide sheets | ||
# Place extra pillow at head of the bed | # Place extra pillow at head of the bed | ||
# Enter a lung position | # Enter a lung position | ||
# Patient pushes up the bed with their feet, whilst carers slide up the bed | # Patient pushes up the bed with their feet, whilst carers slide up the bed | ||
'''Removing slide sheets''' | '''Removing slide sheets'''<ref name=":3" /> | ||
# Tuck in both sheets on one side | # Tuck in both sheets on one side | ||
# In a lunge position, a therapist pulls out diagonally from the other side | # In a lunge position, a therapist pulls out diagonally from the other side | ||
# Place sheets neatly for next use | # Place sheets neatly for next use | ||
== Sitting to sitting == | |||
'''Supervision'''<ref name=":3" /> | |||
'''Supervision''' | |||
# Patient leans forward and slides to the front of the chair | # Patient leans forward and slides to the front of the chair | ||
# Client places leading foot in the direction they're going | # Client places leading foot in the direction they're going | ||
| Line 234: | Line 123: | ||
Therapist stays close by throughout | Therapist stays close by throughout | ||
'''Assistance without an aid''' | '''Assistance without an aid'''<ref name=":3" /> | ||
# Assisted sit to stand (as above) | # Assisted sit to stand (as above) | ||
# Patient instructed to walk or step to another chair | # Patient instructed to walk or step to another chair | ||
| Line 240: | Line 129: | ||
# Patient sits down | # Patient sits down | ||
== Transfer Board and Slide Sheets == | |||
{{#ev:youtube|watch?v=2rpWBTcTr_g}} | |||
# Beds moved together | # Beds moved together | ||
# Side sheets positioned on transfer board | # Side sheets positioned on transfer board | ||
| Line 249: | Line 139: | ||
# Transfer board and slide sheets removed | # Transfer board and slide sheets removed | ||
== Hoisting == | |||
[[File:Hoist.jpg|thumb|Hoist]] | |||
'''Applying a sling in bed''' | |||
Therapist one: | Therapist one: | ||
# folds the sling with labels and handles on the outside | # folds the sling with labels and handles on the outside | ||
| Line 261: | Line 152: | ||
Both therapists: | Both therapists: | ||
# Pull slings towards themselves, removing creases | # Pull slings towards themselves, removing creases | ||
# Complete the sling positioning, crossing leg loops between legs | # Complete the sling positioning, crossing leg loops between legs<ref name=":3" /> | ||
'''Applying a sling to a client in a chair''' | |||
# Ask the client to lean forward in the chair | # Ask the client to lean forward in the chair | ||
# Place the sling behind the client | # Place the sling behind the client | ||
# Ensure the bottom of the sling reaches the base of the spine and that the sling is positioned correctly | # Ensure the bottom of the sling reaches the base of the spine and that the sling is positioned correctly | ||
# Put the leg straps under each leg one at a time | # Put the leg straps under each leg one at a time<ref name=":3" /> | ||
'''Hoisting from bed to chair''' | |||
# Lower the sling bar above the client's chest | |||
# Attach the sling to the bar | |||
# Slowly raise the patient off the mattress | |||
# Move hoist so the client is over the chair, one person in-front & closely securing the patient, another behind & securing | |||
# Place a hand on the sling bar whilst lowering the patient | |||
# Remove the sling from the bar, hand still on the bar, and move the hoist away | |||
# Remove sling<ref name=":3" /> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|watch?v=3GOgp_HX4JQ}} | |||
=== Supervising a fallen client who is conscious and uninjured === | |||
''Talk to the client and explain what you are doing throughout'' | |||
# Run through DR ABC with patient ''(If conscious and airway intact, continue. If patient is not breathing, commence CPR)'' | |||
# | # Do they remember falling? | ||
# | # Place a pillow under their head for comfort | ||
# | # Cover them if required. | ||
# | # Ask if they think they could stand themselves up with instruction, if they can, continue | ||
# | # Ask client to roll on to their side then get on to hands and knees . ''(When they have done this, ask if they are dizzy or feeling worse – if they are, get the client to lie down and hoist them instead)'' . | ||
# | # Once they are on their hands and knees, place a chair as close as possible to the client’s hip. | ||
# | # Ask them to use the chair to lean on with their closest hand, and using their nearest leg get them to put their foot flat on the floor then push up into a sitting position using their leg and arm. ''(If the client cannot get onto the chair, get them to lie down again and hoist them)'' | ||
# Alternatively, the client may prefer to use their furthest leg and foot to provide extra balance, particularly if the client is large . | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
| Line 287: | Line 190: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Assistive Technology]] | |||
[[Category:Acute Care]] | |||
[[Category:Older People/Geriatrics]] | |||
[[Category:Health Promotion]] | |||
[[Category:Health and Well-being]] | |||
[[Category:Occupational Health]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:16, 27 May 2023
Original Editors - Samuel Winter
Top Contributors - Leana Louw, Samuel Winter and Lucinda hampton
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Moving and handling forms a key part of most occupations.[1] Safe moving and handling requires physiotherapists to know the correct procedures for moving adults and children without causing injury to either themselves or the person they are supporting. This includes learning to use hoists and other aids.
This page will look into the ergonomics behind the safe moving and handling practices relating to physiotherapy. See also Transfer Aids and Bed Mobility and Transfers in Spinal Cord Injury
Techniques[edit | edit source]
Preparation[2]
- Check physician’s order to ambulate and any restrictions related to ambulation due to medical treatment or surgical procedure.
- Gather any supplies for ambulation required
- Introduce yourself to and confirm patient ID with two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth)
- Perform an assessment of patient’s strength and abilities.
- Ensure clothing (including footwear) are appropriate
- Ensure all participants are aware of the task, including the order of specific task and end position of the patient
- Get the equipment ready and in order, with required accessories
- Prepare the environment, clear route and access ways are clear, move objects, and the destination is ready
- Prepare client, explain what will happen and what they are expected to do. Ensure clothes, including footwear, are appropriate, ensure they have any aids they need
- Choose a lead caregiver
- Count down "ready, steady, move" prior to the task
Communication between caregiver and patient[2]
- Talk through the steps prior
- Ask if OK as being moved
- Ask how they felt after the transfer
Sitting[edit | edit source]
Preparation
- Check a patients weight-bearing status with colleagues, medical notes, the client and family if needed
- Consider hoisting if non-weight bearing, never put weight through a patients non-weight bearing leg
- Make sure the patient knows what to expect during the transfer
Supervising sitting repositioning
- Patient places feet flat of the floor and slightly under the chair
- Patient leans forwards so weight is over their knees
- Patient stands, moves as far back into the seat as possible OR pushes back on armrests and their feet to slide back into the seat
Assistance Sitting
- Ask client to feel for chair on back of legs, reach for armrests and slowly lower themselves
- Encourage client to bend at the hips[3]
Standing[edit | edit source]
Supervising standing
- Patient places hands on armrests, feet flat of the floor and slightly under the chair
- Pt moves slightly closer to the edge of the seat
- Pt sits forwards, "nose over toes"
- If needed, the patient rocks backwards and forwards
- Patient leans forwards so weight is over their knees
- Carer counts down "ready, steady, stand". On stand, the patient pushes up into a standing position[3]
Assistance Standing
- Caregiver adopts the lunge position, beside the patient
- Outside hand is flat on the front of patients shoulder, inside arm across lower back
- With weight starting on the back foot, carer rocks forward with the client
- Check clients arms are free and in front
Rolling in Bed[edit | edit source]
Supervised[3]
- Patient turns head in direction of roll
- Patient flexes knee further from the direction of roll
- Places arm across their chest in direction of roll
- Client rolls over, pushing with outside of foot and reaching across body
- Client completes roll
Assistance[3]
- Patient turns head in direction of roll
- Patient flexes knee further from the direction of roll
- Patient crosses arms against chest
- Therapist stands in direction of roll and places one hand on furthest shoulder, other on the furthest hip
- Client is rolled onto their side
Moving in Bed[edit | edit source]
Supervised bridge:
- Teach the patient to do a bridge to move up and down in the bed
- Patient to hold on to head of bed with arms and pull themselves up. This can be done in combination with a bridge, and works well in patients with an increased BMI, or that have specific lower limb weight bearing limitations/pain, preventing them to do an optimal bridge.
Supervised hip hitch:
Ask the client to:
- Sit up in bed (1. Raise head 2. Put both hands on bed & raise upper body c arms 3. Pushup from bed c arms)
- Make their hands into closed fists and put their fists just behind their hips
- Bend their knees and dig their heels into the bed, ready to push themselves up the bed
- Push themselves up by pushing through their heels and fists at the same time, to lift and move their bottom up the bed.
1 x assistance:
- Assist to lift pelvis
- Place patient in crook lying
- Put one around patient's shoulders and the other at the back of the scapula
- Assist with pulling upwards when the patient does a bridge[3]
Sitting over the Edge of a Bed[edit | edit source]
Supervised[4]
- Patient turns to their side, facing the carer
- Patient places outside hand and inside elbow flat on the bed
- Client puts legs over the edge of the bed
- Uses hands and elbow to push up whilst lowering legs to floor
Slide Sheets[edit | edit source]
Applying[3]
- Place slide sheets underneath a bed sheet
- Keep edges of slide sheet to edge of the bed
- Push slide sheet under the patient, pushing down on the mattress
- Roll patient to the side and pull through the slide sheets
Pushing client up the bed with slide sheets[3]
- Apply slide sheets
- Place extra pillow at head of the bed
- Enter a lung position
- Patient pushes up the bed with their feet, whilst carers slide up the bed
Removing slide sheets[3]
- Tuck in both sheets on one side
- In a lunge position, a therapist pulls out diagonally from the other side
- Place sheets neatly for next use
Sitting to sitting[edit | edit source]
Supervision[3]
- Patient leans forward and slides to the front of the chair
- Client places leading foot in the direction they're going
- Patient reaches forwards to take the far arm of the chair
- The client pushes through their arms and legs
- Client transfers to the other chair
- Client lowers into chair
Therapist stays close by throughout
Assistance without an aid[3]
- Assisted sit to stand (as above)
- Patient instructed to walk or step to another chair
- Patient instructed to reach for the armrests
- Patient sits down
Transfer Board and Slide Sheets[edit | edit source]
- Beds moved together
- Side sheets positioned on transfer board
- Assistance to roll onto the side away from the direction of transfer
- Transfer board placed underneath the patient
- Patient rolled back to neutral
- Patient slide to target bed
- Transfer board and slide sheets removed
Hoisting[edit | edit source]
Applying a sling in bed
Therapist one:
- folds the sling with labels and handles on the outside
- Position the sling from the base of the spine upwards
- Feed the upper strap under the client's neck
- Fold the upper shoulder loop into sling and roll the upper portion of the sling into the space behind the client's back
Therapist two:
- Locate the loop from under the patient's neck and pull towards you
Both therapists:
- Pull slings towards themselves, removing creases
- Complete the sling positioning, crossing leg loops between legs[3]
Applying a sling to a client in a chair
- Ask the client to lean forward in the chair
- Place the sling behind the client
- Ensure the bottom of the sling reaches the base of the spine and that the sling is positioned correctly
- Put the leg straps under each leg one at a time[3]
Hoisting from bed to chair
- Lower the sling bar above the client's chest
- Attach the sling to the bar
- Slowly raise the patient off the mattress
- Move hoist so the client is over the chair, one person in-front & closely securing the patient, another behind & securing
- Place a hand on the sling bar whilst lowering the patient
- Remove the sling from the bar, hand still on the bar, and move the hoist away
- Remove sling[3]
Supervising a fallen client who is conscious and uninjured[edit | edit source]
Talk to the client and explain what you are doing throughout
- Run through DR ABC with patient (If conscious and airway intact, continue. If patient is not breathing, commence CPR)
- Do they remember falling?
- Place a pillow under their head for comfort
- Cover them if required.
- Ask if they think they could stand themselves up with instruction, if they can, continue
- Ask client to roll on to their side then get on to hands and knees . (When they have done this, ask if they are dizzy or feeling worse – if they are, get the client to lie down and hoist them instead) .
- Once they are on their hands and knees, place a chair as close as possible to the client’s hip.
- Ask them to use the chair to lean on with their closest hand, and using their nearest leg get them to put their foot flat on the floor then push up into a sitting position using their leg and arm. (If the client cannot get onto the chair, get them to lie down again and hoist them)
- Alternatively, the client may prefer to use their furthest leg and foot to provide extra balance, particularly if the client is large .
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Manual Handling Assessment Charts
- Risk Assessment Tool for Pushing and Pulling
- Manual handling at work: A brief guide
- Getting to grips with hoisting people == A brief guide ==
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Health and Safety Executive. Moving and handling in health and social care. Available from: https://www.hse.gov.uk/healthservices/moving-handling.htm (accessed 28/06/2020).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bridger R. Introduction to ergonomics. Crc Press; 2008.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 Turner A, Foster M, Johnson SE, editors. Occupational therapy and physical dysfunction: principles, skills and practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 2002.
- ↑ Pedretti LW, Early MB, editors. Occupational therapy: Practice skills for physical dysfunction. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 2001 Feb.