Management of Ankle Osteochondral Lesions: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Ewa Jaraczewska|Ewa Jaraczewska]] based on the course by [https://members.physio-pedia.com/instructor/helene-simpson/ Helene Simpson] | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Ewa Jaraczewska|Ewa Jaraczewska]] based on the course by [https://members.physio-pedia.com/instructor/helene-simpson/ Helene Simpson] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
== | == Definitions == | ||
Cartilage is a connective tissue characterised by three components: polysaccharides ( a cellular component composed of ground substance), fibrous proteins, and interstitial fluid with water as a main component.<ref name=":3">Armiento AR, Alini M, Stoddart MJ. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169409X18303193?via%3Dihub Articular fibrocartilage - Why does hyaline cartilage fail to repair?] Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Jun;146:289-305.</ref> It gets its nutrition via diffusion from surrounding tissues as it has no direct blood supply, lymphatics and nerves.<ref name=":3" /> There are three types of cartilaginous tissues, each with different composition and function: hyaline, | Cartilage is a connective tissue characterised by three components: polysaccharides ( a cellular component composed of ground substance), fibrous proteins, and interstitial fluid with water as a main component.<ref name=":3">Armiento AR, Alini M, Stoddart MJ. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169409X18303193?via%3Dihub Articular fibrocartilage - Why does hyaline cartilage fail to repair?] Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Jun;146:289-305.</ref> It gets its nutrition via diffusion from surrounding tissues as it has no direct blood supply, lymphatics and nerves.<ref name=":3" /> There are three types of cartilaginous tissues, each with different composition and function: hyaline, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage. | ||
* Hyaline cartilage: connective tissue located at the ends of bones. Its primary cells are chondrocytes. Their role is to maintain the cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) which is responsible for biological and mechanical function of the cartilage. Hyaline cartilage ECM contains:<ref>Lakin BA, Snyder BD, Grinstaff MW. [https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044525 Assessing cartilage biomechanical properties: techniques for evaluating the functional performance of cartilage in health and disease. Annual review of biomedical engineering]. 2017 Jun 21;19:27-55.</ref> | * [[Cartilage|Hyaline cartilage]]: connective tissue located at the ends of bones. Its primary cells are chondrocytes. Their role is to maintain the cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) which is responsible for biological and mechanical function of the cartilage. Hyaline cartilage ECM contains:<ref>Lakin BA, Snyder BD, Grinstaff MW. [https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044525 Assessing cartilage biomechanical properties: techniques for evaluating the functional performance of cartilage in health and disease. Annual review of biomedical engineering]. 2017 Jun 21;19:27-55.</ref> | ||
** Collagen type II (10-20%) | ** Collagen type II (10-20%) | ||
** Proteoglycan (1-10%) | ** Proteoglycan (1-10%) | ||
** Water (65-85%) | ** Water (65-85%) | ||
* Fibrocartilage is a "transitional tissue between hyaline cartilage and dense regular connective tissue such as tendons and ligaments"<ref name=":3" />It contains: | * [[Cartilage|Fibrocartilage]] is a "transitional tissue between hyaline cartilage and dense regular connective tissue such as tendons and ligaments"<ref name=":3" /> It contains: | ||
** High levels of type I collagen | ** High levels of type I collagen | ||
** Type II collagen | ** Type II collagen | ||
** Small component of ground substance.<ref name=":3" /> | ** Small component of ground substance.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
* Elastic cartilage: flexible connective tissue cartilage | * [[Cartilage|Elastic cartilage]]: flexible connective tissue cartilage with ability to withstand repeated bending.<ref name=":3" /> Elastic cartilage components are:<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** | ** Type II collagen | ||
Subchondral bone | ** Elastic fibres | ||
** Large chondrocytes | |||
[[Bone|Subchondral bone]] is located below the hyaline cartilage and cement line and is responsible for providing mechanical and nutritional support for cartilage. Its mechanical properties include shock absorption. <ref>Hu Y, Chen X, Wang S, Jing Y, Su J. [https://www.nature.com/articles/s41413-021-00147-z.pdf Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain]. Bone research. 2021 Mar 17;9(1):1-3.</ref>The subchondral bone contains vessels that have a direct contact with hyaline cartilage layer. 50% of cartilage nutrients are distributed via perfussion of the subchondral bone vessels.<ref>Imhof H, Sulzbacher I, Grampp S, Czerny C, Youssefzadeh S, Kainberger F. Subchondral bone and cartilage disease: a rediscovered functional unit. Investigative radiology. 2000 Oct 1;35(10):581-8.</ref> | |||
Osteochondral lesions (OCL) are defects affecting the structure of the cartilaginous surface and underlying subchondral bone. When lesion's healing phase starts and tissue is formed, the fibrocartilage is often the new tissue, which has mechanical disadvantage to the hyaline. In some cases, hyaline cartilage forms during the repair process, but the mechanism of hyaline vs fibrocartilage formation is unknown.<ref name=":3" /> | '''Osteochondral lesions (OCL)''' are defects affecting the structure of the cartilaginous surface and underlying subchondral bone. When lesion's healing phase starts and tissue is formed, the fibrocartilage is often the new tissue, which has mechanical disadvantage to the hyaline. In some cases, hyaline cartilage forms during the repair process, but the mechanism of hyaline vs fibrocartilage formation is unknown.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
=== OCL Etiology === | === OCL Etiology === | ||
Revision as of 20:18, 3 August 2022
Definitions[edit | edit source]
Cartilage is a connective tissue characterised by three components: polysaccharides ( a cellular component composed of ground substance), fibrous proteins, and interstitial fluid with water as a main component.[1] It gets its nutrition via diffusion from surrounding tissues as it has no direct blood supply, lymphatics and nerves.[1] There are three types of cartilaginous tissues, each with different composition and function: hyaline, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage.
- Hyaline cartilage: connective tissue located at the ends of bones. Its primary cells are chondrocytes. Their role is to maintain the cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) which is responsible for biological and mechanical function of the cartilage. Hyaline cartilage ECM contains:[2]
- Collagen type II (10-20%)
- Proteoglycan (1-10%)
- Water (65-85%)
- Fibrocartilage is a "transitional tissue between hyaline cartilage and dense regular connective tissue such as tendons and ligaments"[1] It contains:
- High levels of type I collagen
- Type II collagen
- Small component of ground substance.[1]
- Elastic cartilage: flexible connective tissue cartilage with ability to withstand repeated bending.[1] Elastic cartilage components are:[1]
- Type II collagen
- Elastic fibres
- Large chondrocytes
Subchondral bone is located below the hyaline cartilage and cement line and is responsible for providing mechanical and nutritional support for cartilage. Its mechanical properties include shock absorption. [3]The subchondral bone contains vessels that have a direct contact with hyaline cartilage layer. 50% of cartilage nutrients are distributed via perfussion of the subchondral bone vessels.[4]
Osteochondral lesions (OCL) are defects affecting the structure of the cartilaginous surface and underlying subchondral bone. When lesion's healing phase starts and tissue is formed, the fibrocartilage is often the new tissue, which has mechanical disadvantage to the hyaline. In some cases, hyaline cartilage forms during the repair process, but the mechanism of hyaline vs fibrocartilage formation is unknown.[1]
OCL Etiology[edit | edit source]
The aetiology of the osteochondral lesion can be:[5]
- traumatic (most cases)
- joint malalignments
- instability
- genetic predisposition
- endocrine factors
- avascular necrosis
There are three types of trauma leading to development of OCL: compaction, shearing or avulsion.
Osteochondral Lesion of the Ankle[edit | edit source]
According to Ferkel et al[6] a high percentage of patients with lateral ankle instability developed intra-articular pathology. In the ankle joint, the osteochondral lesion can be found in the talar. The osteochondral lesion of the talar cartilage (OCT) and subchondral bone can cause a partial or complete detachment of the fragment. There are six categories of the lesion:
- chondral (cartilage only)
- chondral-subchondral (cartilage and bone)
- subchondral (intact overlying cartilage)
- cystic
In addition to the above categories of the lesion, OCT can be stable or unstable, non-displaced or displaced.
Classification System for OCT[edit | edit source]
- Berndt and Harty[7] classification system for radiographic staging of osteochondral lesions of the talus. It applies to traumatic and non-traumatic aetiology of the lesion:[8]
- Stage I: with the foot in inverted position, the lateral border is compressed against the face of the fibula, the collateral ligament remains intact.
- Stage II: with progressive foot inversion, lateral ligament is ruptured and the avulsion of the chip begins
- Stage III: the chip is fully detached but remains in place
- Stage IV: detached chip is displaced following inversion
- Loomer et al[9] added a stage V to Berndt and Harty classification system:[8]
- Stage I -IV as above
- Stage V: presence of a subchondral cyst.
- Ferkel and Sgaglione [10] developed a classification system based on computed tomography (CT)
- Stage I: Cystic lesion with dome of talus (intact roof)
- Stage IIa:Cystic lesion with communication to talar dome surface
- Stage IIb: Open articular surface lesion with overlying undisplaced fragment
- Stage III: Undisplaced lesion with lucency
- Stage IV: Displaced fragment[11]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patient with OCL will report deep ankle pain associated with weightbearing, restricted range of motion, impaired function,stiffness, catching, locking and swelling. [8]
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
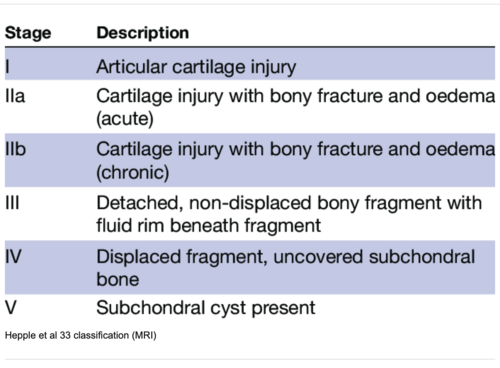
MRI is widely accepted because of its ability to capture the integrity of soft tissue and subchondral cancellous bone. MRI is superior to conventional radiography and computed tomography because of its superior soft tissue contrast, multiplanar capabilities, and lack of ionizing radiation.[13]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Intervention[edit | edit source]
General principles in rehabilitation management[edit | edit source]
- Lack of high quality evidence
- Follow biological phases of healing
- Comprehensive and mili-modal functional training
- Minimum six weeks of supervised rehabilitation training including:
- postural control, balance and proprioception retraining
Healing of Osteochondral Lesions[edit | edit source]
Osteochondral lesions have poor healing capacity. [14]The study completed in animals[15] demonstrates four stages of healing:[14]
- initial fibrin repair,
- mesenchymal cell recruitment,
- cartilage formation starting adjacent to the damaged cartilage
- bone formation.
Special Concerns[edit | edit source]
In the management of the osteochondral lesions the following rehabilitation considerations must apply:
- Avoid shear forces
- Avoid comprehensive forces
- Recovery is slow
- Monitor pain
- Prevent development of the compensatory movements
Shear forces[edit | edit source]
Shear forces are to be avoided over 3 months shear focus often underlying cause for OCL in Chronic Ankle Instability
Compressive forces[edit | edit source]
Fibre cartilage is not as strong as hyaline cartilage
Slow Recovery[edit | edit source]
Cartilage repair takes time
Monitor pain[edit | edit source]
Compensatory movements[edit | edit source]
Early motion is required for healing delay full weight bearing for 6 weeks or longer based on certain clinical factors, semi-rigid braces, or lace-up braces, crutches
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Armiento AR, Alini M, Stoddart MJ. Articular fibrocartilage - Why does hyaline cartilage fail to repair? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Jun;146:289-305.
- ↑ Lakin BA, Snyder BD, Grinstaff MW. Assessing cartilage biomechanical properties: techniques for evaluating the functional performance of cartilage in health and disease. Annual review of biomedical engineering. 2017 Jun 21;19:27-55.
- ↑ Hu Y, Chen X, Wang S, Jing Y, Su J. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone research. 2021 Mar 17;9(1):1-3.
- ↑ Imhof H, Sulzbacher I, Grampp S, Czerny C, Youssefzadeh S, Kainberger F. Subchondral bone and cartilage disease: a rediscovered functional unit. Investigative radiology. 2000 Oct 1;35(10):581-8.
- ↑ Mosca M, Grassi A, Caravelli S. Osteochondral Lesions of Ankle and Knee. Will Future Treatments Really Be Represented by Custom-Made Metal Implants?. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022 Jul 1;11(13):3817.
- ↑ Ferkel RD, Chams RN. Chronic lateral instability: arthroscopic findings and long-term results. Foot Ankle Int. 2007 Jan;28(1):24-31.
- ↑ BERNDT AL, HARTY M. Transchondral fractures (osteochondritis dissecans) of the talus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959 Sep;41-A:988-1020.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Badekas T, Takvorian M, Souras N. Treatment principles for osteochondral lesions in foot and ankle. Int Orthop. 2013 Sep;37(9):1697-706. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2076-1.
- ↑ Loomer R, Fisher C, Lloyd-Smith R, Sisler J, Cooney T. Osteochondral lesions of the talus. Am J Sports Med. 1993 Jan-Feb;21(1):13-9.
- ↑ Ferkel RD, Sgaglione NA, DelPizzo W. Arthroscopic treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus: long-term results. Orthop Trans. 1990;14:172–173.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Elghawy AA, Sesin C, Rosselli M. Osteochondral defects of the talus with a focus on platelet-rich plasma as a potential treatment option: a review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2018 Feb 1;4(1):e000318.
- ↑ Hepple S, Winson IG, Glew D. Osteochondral lesions of the talus: a revised classification. Foot Ankle Int. 1999 Dec;20(12):789-93.
- ↑ Sophia Fox AJ, Bedi A, Rodeo SA. The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2009 Nov;1(6):461-8.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Lydon H, Getgood A, Henson FMD. Healing of Osteochondral Defects via Endochondral Ossification in an Ovine Model. Cartilage. 2019 Jan;10(1):94-101.
- ↑ Shapiro F, Koide S, Glimcher MJ. Cell origin and differentiation in the repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993 Apr;75(4):532-53.