Iliopsoas: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
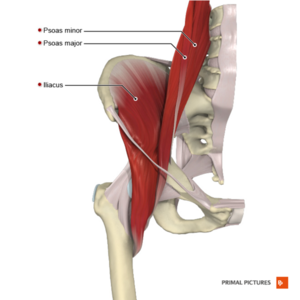
[[File:Iliopsoas.png|thumb|A compound muscle composed of the iliac and psoas muscles]] | [[File:Iliopsoas.png|thumb|A compound muscle composed of the iliac and psoas muscles]] | ||
The iliopsoas muscle complex is made up of three muscles that include the [[iliacus]], [[Psoas Major|psoas major]] and [[Psoas Minor|psoas minor]]. | The iliopsoas muscle complex is made up of three muscles that include the [[iliacus]], [[Psoas Major|psoas major]] and [[Psoas Minor|psoas minor]]. This complex muscle system can function as a unit or intervene as separate muscles.<ref name=":1">Bordoni B, Varacallo M. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531508/ Anatomy, bony pelvis and lower limb, Iliopsoas Muscle]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Jul 21. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531508/ (accessed 15.2.2022)</ref> | ||
The iliopsoas muscle is the strongest [[Hip Flexors|hip flexor]] and assists in external rotation of the [[femur]], playing an important role in maintaining the strength and integrity of the [[Hip Anatomy|hip joint]]. It is | The iliopsoas muscle is the strongest [[Hip Flexors|hip flexor]] and assists in external rotation of the [[femur]], playing an important role in maintaining the strength and integrity of the [[Hip Anatomy|hip joint]]. It is essential for correct standing or sitting lumbar posture, and during walking and running. | ||
The [[fascia]] covering the iliopsoas muscle creates multiple fascial connections, relating the muscle with different viscera and muscle areas<ref name=":1" />.<ref name=":0">Physiopedia [[Iliopsoas Tendinopathy]] Available:https://www.physio-pedia.com/Iliopsoas_Tendinopathy?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=related_articles&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal (accessed 15.2.2022)</ref> | |||
== Sub Heading 2 == | == Sub Heading 2 == | ||
The iliopsoas | The iliopsoas musculotendinous unit is part of the inner muscles of the hip and forms part of the posterior [[Abdominal Muscles|abdominal wall]], lying posteriorly at the retroperitoneum level.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
'''Origin''': The iliopsoas muscle has its origin at the fusion of the psoas major and iliacus muscles. This fusion occurs at the level of L5-S2, and the combined muscles pass from the [[pelvis]] to the thigh under the [[Inguinal Ligament|inguinal ligament]]. | '''Origin''': The iliopsoas muscle has its origin at the fusion of the psoas major and iliacus muscles. This fusion occurs at the level of L5-S2, and the combined muscles pass from the [[pelvis]] to the thigh under the [[Inguinal Ligament|inguinal ligament]]. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
'''Insertion''': The iliopsoas muscle inserts into the lesser trochanter of the femur via the psoas tendon. . | '''Insertion''': The iliopsoas muscle inserts into the lesser trochanter of the femur via the psoas tendon. . | ||
'''Bursa''': The largest bursa of the hip joint is the iliopsoas bursa which is located deep to the iliopsoas musculotendionous junction and anterior to the hip joint capsule. The bursa has been reported to communicate with the hip joint in ~15% of patients. | '''Bursa''': The largest bursa of the hip joint is the iliopsoas bursa which is located deep to the iliopsoas musculotendionous junction and anterior to the hip joint capsule. The bursa has been reported to communicate with the hip joint in ~15% of patients. It helps the muscle glide and slide over the front of the hip during movement. | ||
'''Innervation''': [[Femoral Nerve|femoral nerve]] (iliacus part); direct branches of the [[Lumbar Plexus|lumbar plexus]] (psoas part) | '''Innervation''': [[Femoral Nerve|femoral nerve]] (iliacus part); direct branches of the [[Lumbar Plexus|lumbar plexus]] (psoas part) | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
== Sub Heading 3 == | == Sub Heading 3 == | ||
Injury to the iliopsoas may cause hip pain and limited mobility. | |||
Snapping hip syndrome | |||
Impingement of the Iliopsoas Tendon: Following an operation to replace the femoral head, movement of the artificial head may during a hip extension press against the surrounding soft tissues, including the tendon of the iliopsoas complex. The surgeon decides the course of action. | |||
Iliopsoas Bursitis: Bursitis that involves the tendon of the iliopsoas complex is an inflammation that enlarges the volume of the bursa and produces pain on movement. | |||
In pediatrics, in the presence of spasticity eg cerebral palsy and the presence of important contractures, surgery is performed with distal tenotomy. This reduces the difficulty of walking and enables a posture that makes the child independent when possible. | |||
The iliopsoas muscle can cause compression of the femoral nerve and cause knee pain. Before deciding on surgical treatment and releasing of the femoral nerve, the patient should learn stretching exercises to reduce the tension generated by the muscle. Generally, if the patient can follow the physiotherapy indications, the use of surgery can be avoided. | |||
Hypertrophy of the muscle may be responsible for the compression of the femoral nerve and cause knee pain. Before deciding on surgical treatment to release the femoral nerve, the patient should learn stretching exercises to reduce the tension generated by the muscle. Generally, if the patient can follow the physiotherapy indications, the use of surgery can be avoided. <ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 06:10, 15 February 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Wendy Snyders, Vidya Acharya, Ewa Jaraczewska and Ahmed M Diab
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The iliopsoas muscle complex is made up of three muscles that include the iliacus, psoas major and psoas minor. This complex muscle system can function as a unit or intervene as separate muscles.[1]
The iliopsoas muscle is the strongest hip flexor and assists in external rotation of the femur, playing an important role in maintaining the strength and integrity of the hip joint. It is essential for correct standing or sitting lumbar posture, and during walking and running.
The fascia covering the iliopsoas muscle creates multiple fascial connections, relating the muscle with different viscera and muscle areas[1].[2]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
The iliopsoas musculotendinous unit is part of the inner muscles of the hip and forms part of the posterior abdominal wall, lying posteriorly at the retroperitoneum level.[1]
Origin: The iliopsoas muscle has its origin at the fusion of the psoas major and iliacus muscles. This fusion occurs at the level of L5-S2, and the combined muscles pass from the pelvis to the thigh under the inguinal ligament.
Insertion: The iliopsoas muscle inserts into the lesser trochanter of the femur via the psoas tendon. .
Bursa: The largest bursa of the hip joint is the iliopsoas bursa which is located deep to the iliopsoas musculotendionous junction and anterior to the hip joint capsule. The bursa has been reported to communicate with the hip joint in ~15% of patients. It helps the muscle glide and slide over the front of the hip during movement.
Innervation: femoral nerve (iliacus part); direct branches of the lumbar plexus (psoas part)
Vascular supply: Iliolumbar artery & medial femoral circumflex artery.
Function: Flexor of the thigh and trunk; Assists in external rotation of the femur; Lateral flexor of the lower vertebral column[2]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Injury to the iliopsoas may cause hip pain and limited mobility.
Snapping hip syndrome
Impingement of the Iliopsoas Tendon: Following an operation to replace the femoral head, movement of the artificial head may during a hip extension press against the surrounding soft tissues, including the tendon of the iliopsoas complex. The surgeon decides the course of action.
Iliopsoas Bursitis: Bursitis that involves the tendon of the iliopsoas complex is an inflammation that enlarges the volume of the bursa and produces pain on movement.
In pediatrics, in the presence of spasticity eg cerebral palsy and the presence of important contractures, surgery is performed with distal tenotomy. This reduces the difficulty of walking and enables a posture that makes the child independent when possible.
The iliopsoas muscle can cause compression of the femoral nerve and cause knee pain. Before deciding on surgical treatment and releasing of the femoral nerve, the patient should learn stretching exercises to reduce the tension generated by the muscle. Generally, if the patient can follow the physiotherapy indications, the use of surgery can be avoided.
Hypertrophy of the muscle may be responsible for the compression of the femoral nerve and cause knee pain. Before deciding on surgical treatment to release the femoral nerve, the patient should learn stretching exercises to reduce the tension generated by the muscle. Generally, if the patient can follow the physiotherapy indications, the use of surgery can be avoided. [1]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bordoni B, Varacallo M. Anatomy, bony pelvis and lower limb, Iliopsoas Muscle. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Jul 21. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531508/ (accessed 15.2.2022)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Physiopedia Iliopsoas Tendinopathy Available:https://www.physio-pedia.com/Iliopsoas_Tendinopathy?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=related_articles&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal (accessed 15.2.2022)