Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Difference between revisions
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
In particular, VZV antigen detection by direct immunofluorescence assay (DFA) is used, which has sensitivity of 90% and specificity close to 99%<ref>Coffin SE, Hodinka RL. Utility of direct immunofluorescence and virus culture for detection of varicella-zoster virus in skin lesions. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Oct. 33(10):2792-5</ref>. | In particular, VZV antigen detection by direct immunofluorescence assay (DFA) is used, which has sensitivity of 90% and specificity close to 99%<ref>Coffin SE, Hodinka RL. Utility of direct immunofluorescence and virus culture for detection of varicella-zoster virus in skin lesions. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Oct. 33(10):2792-5</ref>. | ||
Structural lesions (such as Acoustic Neuroma) can be ruled out by MRI or CT scan.<br> | |||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
Revision as of 23:00, 7 December 2015
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Lead Editors
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to clinically relevant anatomy of the condition
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the mechanism of injury and/or pathology of the condition
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The presenting feature is often pain deep within the ear.
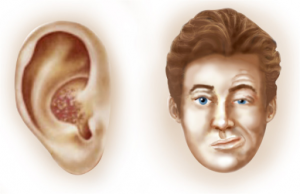
A herpetic rash or blisters, which may be on the skin of the ear canal, auricle or both.
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
In most cases, the diagnosis is made purely on clinical findings: the presence of herpetic blisters in and around the ear, accompanied in most cases by pain in and around the ear and an ipsilateral facial palsy.
On occasions virological studies, both serological and molecular, can be used to confirm the clinical diagnosis.
In particular, VZV antigen detection by direct immunofluorescence assay (DFA) is used, which has sensitivity of 90% and specificity close to 99%[1].
Structural lesions (such as Acoustic Neuroma) can be ruled out by MRI or CT scan.
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Key Evidence[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to key evidence with regards to any of the above headings
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Case Studies[edit | edit source]
add links to case studies here (case studies should be added on new pages using the case study template)
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Coffin SE, Hodinka RL. Utility of direct immunofluorescence and virus culture for detection of varicella-zoster virus in skin lesions. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Oct. 33(10):2792-5