Wheelchair Assessment - Body Measurements
Original Editor - Naomi O'Reilly as part of the Wheelchair Service Provision Content Development Project
Top Contributors - Naomi O'Reilly, Rucha Gadgil, Kim Jackson, Amrita Patro and Olajumoke Ogunleye
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A well-fitted wheelchair or seating system requires a ‘made-to-measure’ solution. Generally, the more seating surface that is in contact with the client, the more body measurements that will need to be obtained for a wheelchair prescription. Accurate measurement of the client will enable clinicians to allow the wheelchair user to trial correctly sized equipment, reduce the number of transfers and improve time management during trials by pre-setting the seating and wheelchair according to body measurement prior to an appointment. It will also ensure an accurate reference for the final wheelchair configuration during the prescription phase or any future equipment trials where applicable. Finally it will assist the wheelchair service personnel to outline the clinical reasoning behind the specifications of wheelchair prescriptions in funding applications. [1][2]
Measuring Tools[edit | edit source]
- Use a retractable metal tape measure
- clipboards/books can be used to help measure accurately (see process below).
- Large callipers are an additional tool that can be very useful. These can be made locally from wood.
- Foot-blocks can also be used to support the wheelchair user’s feet at the correct height. [1]
Basic Measurements[edit | edit source]
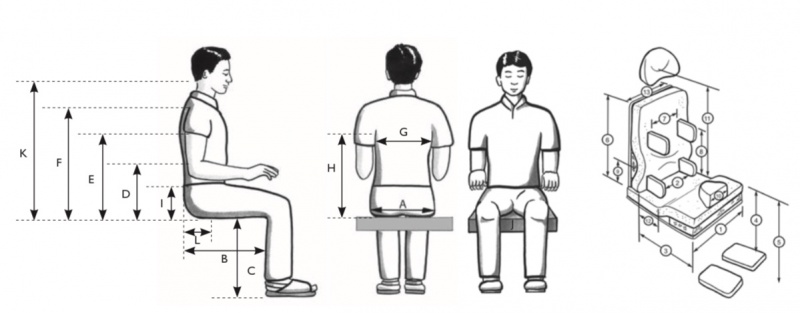
Six measurements from the wheelchair user are needed to choose the best available size of wheelchair for for a wheelchair user that has good trunk control and does not require additional postural support.[1][3]
- Seat Width; Measured from the widest aspect of the user’s buttocks, hips or thigh. It should be wide enough to avoid pressure on the hips.
- Seat Depth; Measured from the user’s posterior buttock, along the lateral thigh to the popliteal fold with your palm horizontal to the seat. Usually, a space of about 2 inches is preserved to avoid pressure from the front edge of the seat against the popliteal space. You should be able to fit 3-4 fingers between the front edge of the seat and the back of your knee.
- Seat Height; Determined by the height of the individual and if the wheelchair is self-propelled. When using the feet to propel, the seat height should allow for them to reach the floor with their heel. Those using footrests have higher seat heights. It is measured from the user’s heel to the popliteal fold. The bottom of the footrest is 2 inches from the floor.
- Armrest Height; Should allow user sit erect, with level shoulders when bearing weight on the forearms as they rest on the armrest.It is determined by measuring the distance between the seat of the chair and olecranon and adding one inch.
- Backrest Height; The inferior angles of the scapula should be approximately 1 finger-breadth above the back when the user sits with erect posture. It is determined by measuring the distance between the seat of the chair to the patient’s axilla, and subtracting four inches. The height of the backrest depends on the needs of the user. Wheelchair users who push themselves need a backrest which allows their shoulders to move freely. Wheelchair users who have difficulty sitting upright may need a higher backrest which gives more support to the spine.
- Footrest Length; Affects the support of both the feet and the thighs and the clearance of the footplates and the ground. The footplate must be about 1 to 2 inches off the ground to permit adequate ground clearance.
Process[edit | edit source]
Ask the wheelchair user to sit as upright as possible with the wheelchair user’s feet supported either on the floor or on foot-blocks if they cannot reach the floor comfortably with the hips in a neutral position. For all measurements, make sure the tape measure is held straight and the wheelchair user is sitting upright. Holding a clipboard/book on either side of the wheelchair user can help in obtaining an accurate measurement. Bend down to ensure you are viewing the tape measure at the correct angle.[1]<div
| A | Check there is nothing in wheelchair user’s pockets before measuring.
Measure hips or widest part of thighs. Holding two clipboards/books against each side of the wheelchair user can help in obtaining an accurate measurement. |
|---|---|
| B | Place a clipboard/book at the back of the wheelchair user to help get an accurate measurement.
Measure from the back of the pelvis to the back of the knee in a straight line. Always measure both legs. If there is a difference between the two legs, check that the wheelchair user is sitting up with the pelvis level. If there is still a difference, make the wheelchair prescription for the shorter side. |
| C | Measure from the back of the knee to the base of the heel.
Make sure the wheelchair user’s ankles are bent at 90 degrees (if possible). Always measure both legs. The wheelchair user should wear the shoes he/she wears most days (if any) |
| D | Measure the seat to the bottom of the rib cage.
To help find the bottom of the rib cage, place hands on both sides of the pelvis. Gently squeeze hands inwards and slide hands upwards. The bottom of the rib cage is just above the waist. |
| E | Measure from the seat to the bottom of the shoulder blade in a vertical line.
To help find the bottom of the shoulder blade, ask the user to shrug their shoulder |
| Body Measurement | Measurement | Change Body Measurement to Ideal Wheelchair Size | Wheelchair Measurement (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Hip Width | Hip Width = Seat Width | |||
| B | Seat Depth | L | B less 30 - 60 mm = Seat Depth
If Length is different, Use Shorter One) |
||
| R | |||||
| C | Calf Length | L | = Top of Seat Cushion* to Footrests Height or = Top of Seat Cushion* to Floor for Foot Propelling | ||
| R | |||||
| D | Bottom of Rib Cage | = Top of Seat Cushion* to Top of Backrest
Measure D or E - Depending on the User’s Need |
|||
| E | Bottom of Shoulder Blade | ||||
| * Check the height of the cushion that the wheelchair user will use | |||||
Complex Measurements[edit | edit source]
Measuring a wheelchair user to select the correct wheelchair size and location of Postural Support Devices. On the measurements part of the intermediate wheelchair assessment form there are twelve body measurements listed. Six measurements are the same measurements as above in the Basic measurements. One additional backrest height body measurement is added to the intermediate wheelchair assessment form. Seat to top of shoulder measurement is used to measure a wheelchair user for a high backrest. There are six more measurements, which will help to decide the size and/or location of Postural Support Devices. Sometimes it may be necessary to take more measurements, depending on the Postural Support Devices prescribed. There is space on the intermediate wheelchair assessment form to record ‘other’ measurements. [2]
Each body measurement that is taken relates to the size of the wheelchair or the location and size of Postural Support Devices. On the intermediate wheelchair assessment form the body measurements are listed on the left hand side and the components that each body measurement relates to are listed on the right hand side. For example:
- A wheelchair user’s hip width (body measurement A) equals the wheelchair seat width or the distance between the pelvis side pads (component measurements 1 or 2);
- A wheelchair user’s seat to axilla (armpit) (measurement H) less 30 mm is themaximum distance between the top of the cushion and the top of trunk side pads/wedges (wheelchair component measurement 8).
The examples above demonstrate that the body measurement does not always equal the wheelchair component measurement and some calculations are needed. In some cases there is a formula to help work out the wheelchair component measurement. Adjustments are often needed at the fitting. However accurate body measurements can help to prepare the wheelchair well ahead of the first fitting. The illustrations on the intermediate wheelchair assessment form help to guide wheelchair service personnel as they take the body measurements and relate them to the location and size of Postural Support Devices.
| Body Measurements (mm) | Wheelchair Component Measurements (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seat Width, Depth and Footrest Height | ||||
| A | Hip Width | = Seat Width or | 1 | |
| = Distance between Pelvis Side Pads | 2 | |||
| B | Seat Depth | L | B less 30 - 50 mm = Seat Depth
If L and R Lengths are different, Use Shorter |
3 |
| Back Pelvis to Back Knee | R | |||
| C | Calf Length | L | = Distance between Top of the Seat to Footrest OR
= Distance between Top of the Seat to Floor for Foot Propelling |
4 |
| R | 5 | |||
| Backrest Height | ||||
| D | Seat* to Bottom of Rib Cage | = Distance between Top of Seat to Top of Backrest
Measure D, E or F - Depending on the Wheelchair User’s Need |
6 | |
| E | Seat* to Bottom of Shoulder Blade | |||
| F | Seat* to Top of Shoulder | |||
| Modifications and/or Postural Support Devices | ||||
| G | Trunk Width | = Distance between Trunk Side Pads / Wedges | 7 | |
| H | Seat* to Axilla Armpit | L | H less 30 mm = Maximum Distance between the Top of the Seat and the Top of Trunk Side Pads / Wedges
Adjust According to Hand Simulation |
8 |
| R | ||||
| I | Seat* to Top of Pelvis (PSIS) | = Distance between the Top of the Seat and Mid-height of Rear Pelvis Pad | 9 | |
| J | Distance between Knees | = Width of Knee Separator Pad | 10 | |
| K | Seat* to Base of Skull | = Distance between the Top of Seat to Middle of Headrest | 11 | |
| L | Back of Pelvis to Seat Bones | L plus 20 - 40 mm = Distance from the Backrest Support to the Beginning of the Pre Seat Bone Shelf | 12 | |
| Other | ||||
How to take Accurate Measurements[edit | edit source]
Mistakes in measuring can cause big problems. However taking accurate measurements can sometimes be difficult. This is particularly a problem when a wheelchair user is very small or finds it hard to sit still or has difficulty sitting upright. Some ways to help take accurate measurements include;
- Always use a firm tape measure - not a ‘dress makers’ tape measure; the firm tape measure will not bend as much, resulting in an inaccurate measurement;
- Use of calipers can help to increase the accuracy of measurements;
- Take measurements of the wheelchair user sitting upright, in the posture that has been identified as the most upright, comfortable and functional for them during the hand simulation. If a wheelchair user is measured lying down, the measurements will not be accurate because when lying down the wheelchair user may lengthen or stretch out. It is better to get assistance to support the wheelchair user sitting upright than to lie them down.
| How To Measure | Wheelchair Components | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| A. Hip Width | Seat Width | |
| Check there is nothing in the wheelchair user’s pockets before measuring. Measure the wheelchair user’s hips or the widest part of his/ her thighs.
Hold two clip boards against each side of the wheelchair user to help to get an accurate measurement. Calipers can also be used. |
Hip width equals the seat width or the distance between pelvis side pads. | If pelvis side pads are provided, the wheelchair seat width may need to be wider.
Always try to keep the wheelchair width to a minimum. In countries with cold climates where thick clothes may be worn, some allowance may be needed. |
| B. Seat Depth | Seat Depth | |
| Place a clip board at the back of the wheelchair user to help get an accurate measurement. Measure from the back of the wheelchair user’s pelvis to the back of his/her knee in a straight line.
Always measure both legs. If there is a difference between the left and right side, check that the wheelchair user is sitting upright with their pelvis level. If there is still a difference, make the wheelchair prescription for the shorter side. |
Seat depth less 30 - 50 mm equals the depth of the seat of the wheelchair. | For a wheelchair user whose knees are bent a lot less than 90 degrees, the seat depth may need to be slightly shorter.
See the box `For wheelchair users with a fixed posterior tilt of the pelvis or fixed forward bent trunk`. |
| C. Calf Length | Footrests Height | |
| Measure from the back of the wheelchair user’s knee to the base of his/her heel. Make sure the wheelchair user’s ankles are bent at 90 degrees (if possible).
Always measure both legs. If the wheelchair user wears shoes, measure with the shoes he/she wears most days. If the foot is fixed in plantar flexion (pointing downwards), measure to the toe. |
The calf length height equals the top of the cushion to the footrests OR the top of the cushion to the floor if the wheelchair user is foot propelling. | The exact footrest location will change slightly depending on how much the cushion compresses when the wheelchair user sits on it.Final adjustment is always needed at fitting. |
| D, E and F | Backrest Height | |
| D: Seat to bottom of rib cage:
Measure from the wheelchair user’s seat to the bottom of the rib cage. To help find the bottom of the rib cage, place hands on both sides of the pelvis. Gently squeeze hands inwards and slide hands upwards. The bottom of the rib cage is just above the waist. |
Measurements D, E and F help decide the height of the backrest.
The height depends on the needs of the wheelchair user. The information from assessment will guide wheelchair service personnel to decide how high the backrest needs to be to provide the right support for the wheelchair user. |
If backrest recline or tilt in space is needed, the backrest height must be at least standard (up to the bottom
of wheelchair user’s shoulder blades). Remember to consider if the wheelchair users will be propelling the wheelchair themselves, they need freedom to move their shoulder blades. |
| E: Seat to shoulder blade: Measure from the wheelchair user’s seat to the bottom of the shoulder blade in a vertical line.
To help find the bottom of the shoulder blade ask the wheelchair user to shrug their shoulders. | ||
| F: Seat to top of shoulder: Measure from the wheelchair user’s seat to the top of the shoulder. | ||
| G: Trunk Width | Trunk Side Pads or Wedges (Distance Between) | |
| Measure the width of the wheelchair user’s trunk just below the axilla (armpits). | Trunk width is the distance between trunk side pads
or wedges. |
The final position of the trunk side pads or wedges may change during fitting, if they are to be placed lower than just below the axilla. |
| H: Seat to axilla (Armpit) | Trunk Side Pads or Wedges (Height) | |
| Measure from the seat to the axilla (armpit). | The seat to axilla measurement less 30 mm is the maximum distance between the top of the cushion and the top of trunk side pads/wedges. | This measurement
is a guide. The final height depends on the assessment and fitting. Trunk side pads should never be high enough to put pressure into the axilla (armpit). This can be uncomfortable and cause permanent nerve damage. There should always be at least 30 mm clearance between the top of a trunk side pad and the axilla. See the box `Measuring side trunk supports for a wheelchair user with scoliosis`. |
| I: Seat to the top of the pelvis (PSIS) | Rear Pelvis Pad (Mid-height) | |
| Measure from the seat to the top of the pelvis (PSIS). | The seat to the top of the pelvis (PSIS) measurement is used to locate the mid- height of the rear pelvis pad. | The depth (thickness) of a rear pelvis pad depends on the results of assessment. |
| J: Distance Between Knees | Knee Separator Pad | |
| Measure the distance between the two knees – with the knees placed as close to neutral as is comfortable for the wheelchair user. | The distance between the two knees equals the width of a knee separator pad.
The distance will depend on the wheelchair user’s sitting posture. |
|
| K: Seat to base of skull | Headrest (Height) | |
| Measure from the seat to base of skull. | The measurement from the seat to the base of the skull helps to locate the headrest. | |
| I: Back of Pelvis to Seat Bones | Pre Seat Bone Shelf | |
| Measure from the back of the pelvis to the seat bones.
From the side of the wheelchair user place your hand (palms up) under the wheelchair user’s bottom to find the seat bones. Locate the seat bones with one finger and then withdraw your hand to the side of the wheelchair user. Measure from the back of the wheelchair user’s pelvis to the finger that is located at the seat bones. Wheelchair service personnel may mark on the assessment bed in some way (for example with a piece of chalk) alongside the wheelchair user in line with their seat bones and measure from the mark to the back of the pelvis. |
The measurement from the back of pelvis to seat bones plus 20–40 mm is the distance from the backrest support to the beginning of the pre seat bone shelf. | If a wheelchair user has a fixed posterior tilt
of the pelvis or fixed forward bent trunk the measurement may be different (see the box `For wheelchair users with a fixed posterior tilt of the pelvis or fixed forward bent trunk`). |
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Sarah Frost, Kylie Mines, Jamie Noon, Elsje Scheffler, and Rebecca Jackson Stoeckle. Wheelchair Service Training Package - Reference Manual for Participants - Basic Level. World Health Organization, Geneva. 2012
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sarah Frost, Kylie Mines, Jamie Noon, Elsje Scheffler, and Rebecca Jackson Stoeckle. Wheelchair Service Training Package - Reference Manual for Participants - Intermediate Level. World Health Organization, Geneva. 2013
- ↑ Fairchild, Sherly L, Pierson and Fairchild’s Principles & Techniques of Patient Care, 5th edition, 2013