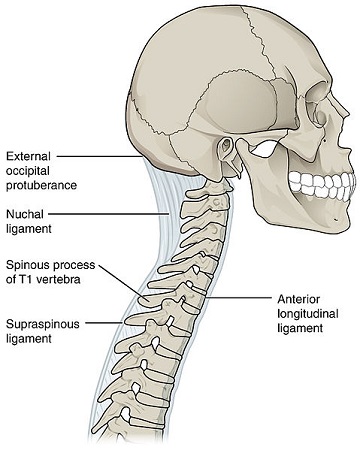
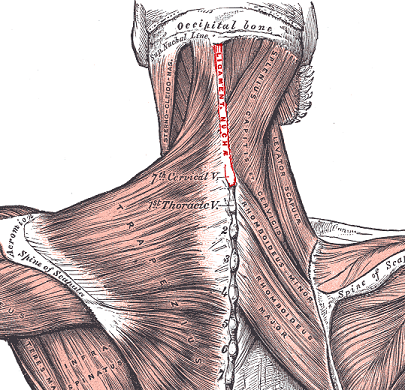
Supraspinous ligament
Original Editor Aarti Sareen
Top Contributors - Aarti Sareen, Ahmed Nasr, Kim Jackson and Naomi O'Reilly
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The supraspinous ligament, or supraspinal ligament,along with the vetebral colunm ,is a strong, fibrous cord that connects together the apices of the spinous processes of the seventh cervical vertebra to the sacrum; at the point of attachment to the tips of the spinous process. From vertebra C7 to the skull, the ligament becomes structurally distinct from more caudal parts of the ligament and is called the ligamentum nuchae.[1]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin: It originates from C7 vetebra.
Insertion/Terminates: Sacrum
The supraspinous ligament is well developed only in the upper lumbar region and may terminate at L3, although the most common termination site appears to be at L4. The ligament is almost always absent at L5/S1.[2] It is thicker and broader in the lumbar than in the thoracic region, and intimately blended, in both situations, with the neighboring fascia. The most superficial fibers of this ligament extend over three or four vertebræ; those more deeply seated pass between two or three vertebræ while the deepest connect the spinous processes of neighboring vertebræ.The deep layer of the supraspinous ligament is reinforced by tendinous fibers of the multifidus muscle. Between the spinous processes it is continuous with the interspinal ligaments.The middle fibers of the supraspinous ligament blend with the dorsal layer of the thoracolumbar fascia.
Function[edit | edit source]
- Limits flexion along with other ligaments of vetebral column.
- The supraspinous ligament serves as a midline attachment for some important muscles.
- The supraspinous ligament helps maintain the upright position of the head.