Quadratus Lumborum
Original Editor - Vanessa Rhule
Top Contributors - Vanessa Rhule, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Ahmed Nasr, George Prudden, Joao Costa, Naomi O'Reilly, WikiSysop, Wanda van Niekerk, Admin and Wendy Walker
Description[edit | edit source]
The word quadratus comes from the Latin word "quadrus" meaning “square” while Lumborum comes from the Latin word "lumbus" for “loin.”
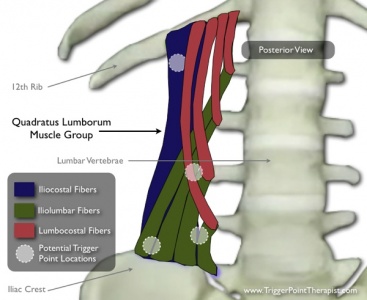
A thick, irregular, quadrilateral-shaped muscle sheet that lies in the posterior abdominal wall.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[1][edit | edit source]
Posterior Iliac Crest
Insertion[1][edit | edit source]
Medial half of 12th rib and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
Nerve Supply[1][edit | edit source]
Subcostal nerve (T12)
Iliohypogastric and Ilioinguinal nerve (both from L1)
Branches from the ventral rami (L2 and L3)
Blood Supply[2][edit | edit source]
Branches of the subcostal artery
Branches of the lumbar arteries
The lumbar branch of the iliolumbar artery
The arteria lumbalis ima from the median sacral artery.
Function[edit | edit source]
Actions[2][edit | edit source]
Quadratus Lumborum fixes the12th rib to stabilise diaphragm attachments during inspiration
Lateral flexes the vertebral column
Extends lumbar vertebrae
Functional contributions[edit | edit source]
The primary antagonist to each Quadratus Lumborum muscle is the Quadratus Lumborum muscle on the other side of the body.[3]
The muscle group is considered a postural muscle group.
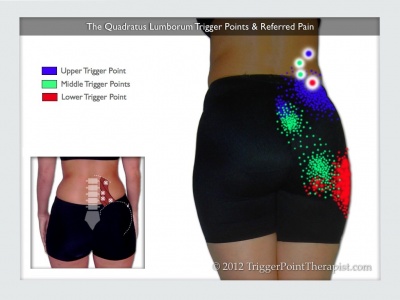
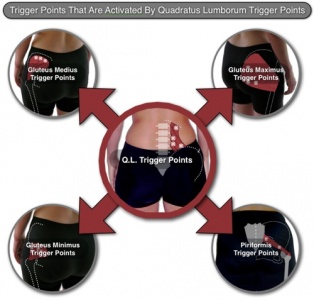
Trigger Point Referral Pattern[edit | edit source]
Techniques[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Related Pathologies[edit | edit source]
Dysfunction of the Lumbar structures whether degenerative, neuropathy, and/or inflammatory, may contribute to poor muscle firing and weak stabilization by the QL. [4]
Lumbar spine pathologies like bulging discs, and facet joint hypertrophy from chronic inflammation may effect nerve conduction and response to the QL and Iliopsoas resulting in poor muscle stabilization and mechanical stress from chronic contracture. [4]
Moaratty-Koehler Syndrome (MKS) is another condition related to QL dysfunction
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Anatomyexpert.com. AnatomyEXPERT: Quadratus lumborum - Structure Detail [Internet]. 2015 [cited 15 August 2015]. Available from: http://www.anatomyexpert.com/app/structure/5307/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Jarvis M. Quadratus lumborum | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org [Internet]. Radiopaedia.org. 2015 [cited 15 August 2015]. Available from: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/quadratus-lumborum
- ↑ Perry D. Quadratus Lumborum Trigger Points: Masters of Low Back Pain | TriggerPointTherapist.com [Internet]. Triggerpointtherapist.com. 2011 [cited 15 August 2015]. Available from: http://www.triggerpointtherapist.com/blog/quadratus-lumborum-trigger-points/ql-trigger-points-masters-low-back-pain/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Reller P. Low Back and Lower Body Myofascial Pain Syndromes | Acupuncture Integrated [Internet]. Acupunctureintegrated.com. 2015 [cited 22 August 2015]. Available from: http://www.acupunctureintegrated.com/articles/low-back-and-lower-body-myofascial-pain-syndromes