Pelvic Fractures
Original Editors - Rachael Lowe
Top Contributors - Descheemaeker Kari, Julie Stainier, Lynn Wright, Jentel Van De Gucht, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Lucinda hampton, 127.0.0.1, Kim Jackson, Rosie Swift, Scott Buxton, Claire Knott, Lauren Lopez, Aminat Abolade, Siobhán Cullen, Karen Wilson and Vidya Acharya
Search Strategy[edit | edit source]
We searched for information in different scientific medical databases like PubMed, Pedro and Web of Science. Also, we went to a library and lend some books.
We started our search with the following key words: pelvis, fractures, pelvic fracture, physiotherapy, rehabilitation, surgery, … We searched these words by using Mesh terms. We specified our search by looking for recent articles (publication date last five years: 2011-2016).
Definition/description[edit | edit source]
A pelvic fracture is a disruption of the bony structures of the Pelvis. An anatomic ring is formed by the fused bones of the ilium, ischium and pubis attached to the sacrum. A pelvic fracture can occur by low-energy mechanism or by high-energy impact. They can range in severity from relatively benign injuries to life-threatening, unstable fractures.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
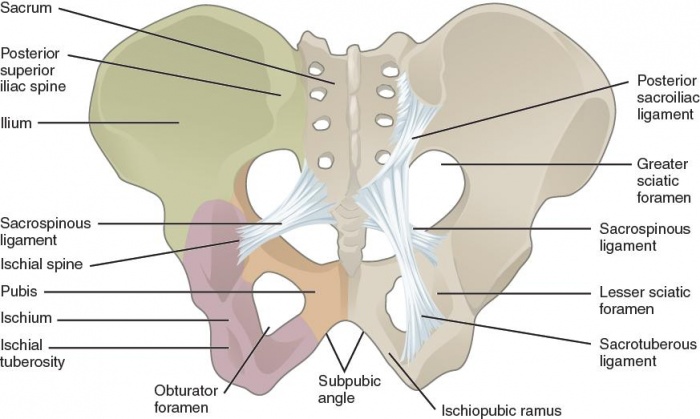
The bony pelvis is the entire structure formed by the two hip bones, the sacrum, and the coccyx, which is attached inferiorly to the sacrum. The paired hip bones are the large, curved bones that form the lateral and anterior aspects of the pelvis. Each adult hip bone is formed by three separate bones that fuse together during the late teenage years. These bony components are the ilium, ischium and pubis. [1](level of evidence: 5)
The stability of the pelvis relies on the integrity of the posterior weight-bearing sacroiliac complex and the transfer of weight bearing forces from the spine to the lower extremities. The SI joint (between sacrum and ilium) transmits forces from the upper limbs and spine to the hip joints and lower limbs and vice versa. This joint also acts as a shock absorber. Several muscles influence the movement and the stability of the SI joint either through attachment to the sacrum or the ilium, or ligamentous attachment to the strong anterior and posterior SI-joint ligaments. ⅔ of the joint includes the posterior superior ligamentous section and ⅓ of the joint includes the anterior inferior synovial component. [2] [3](level of evidence: 2B, 4)
The pelvis contains sliding, tilting and rotation movement components.
Major nerves, blood vessels, and portions of the bowel, bladder, and reproductive organs all pass through the pelvic ring. The pelvis protects these important structures from injury. It also serves as an anchor for the muscles of the hip, thigh and abdomen.
Epidemiology/Etiology[edit | edit source]
Pelvic fractures occur after both low-energy and high-energy events. The appearance of pelvic fractures is the greatest in people aged between 15 and 28. In persons, younger than 35, pelvic fractures occur more in males than in females. In persons, older than 35, pelvic fractures are more likely to happen to females than males[4]. In younger people, pelvic fractures occur mostly as a result of high-energy mechanisms. In older people, they occur from minimal trauma, such as a low fall. Elderly people with osteoporosis have a higher risk factor.
Low-energy fractures are usually stable fractures of the pelvic ring. High-energy pelvic fractures arise commonly after motor vehicle crashes, motorcycle crashes, motor vehicles striking pedestrians and falls. Those high-energy pelvic fractures are one of the major injuries that lead to death. The presence of coma, shock, and head and chest injuries are predictors of death. [5] (level of evidence: 2B)
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
A pelvic fracture should always be considered when history of a significant trauma is present. Pelvic fractures may be recognized by: tenderness, pain, bruising, swelling and crepitus of the pubis, iliac bones, hips and sacrum. Other presenting factors are: haematuria, rectal bleeding, haematoma and neurological and vascular abnormalities in the legs. Physical findings could include abnormal position of the lower limbs and pelvic deformity or pelvic instability. With avulsion injuries, there is often pain associated with contraction of the involved muscles.[6]
There must be a differentiation between high impact unstable fractures and low impact stable pelvic fractures. This can be done by determination of the circumstances of the trauma. Patients with unstable fractures are usually unable to stand, in contrast to patients with stable fractures who can often walk unaided.
Pelvic fractures can be classified by several classification systems. The two most commonly used systems are Tiles classification and the Young-Burgess Classification.
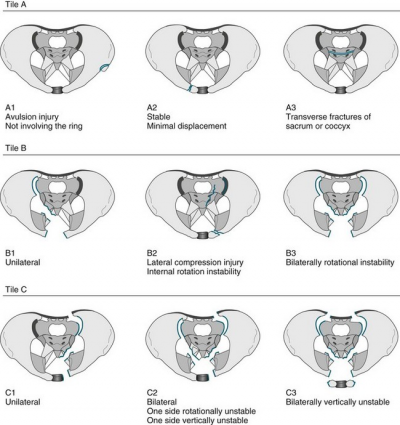
Classification of pelvic fractures by Tile is based on the integrity of the posterior sacroiliac complex. [1] [2] (level of evidence: 5, 2B)
- Type A: rotationally and vertically stable, the sacroiliac complex is intact. Type A fractures are mostly managed non-operatively.
o A1: avulsion fractures
o A2: stable iliac wing fractures or minimally displaced pelvic ring fractures
o A3: transverse sacral or coccyx fractures - Type B: rotationally unstable and vertically stable, caused by external or internal rotational forces, results in partial disruption of the posterior sacroiliac complex.
o B1: open-book injuries
o B2: lateral compression injuries
o B3: bilateral rotational instability - Type C: rotationally unstable and vertically unstable, complete disruption of the posterior sacroiliac complex. These unstable fractures are mostly caused by high-energy trauma like falls from height, motor vehicle accidents or crushing injuries.
o C1: unilateral injury
o C2: bilateral injuries in which one side is rotationally unstable and the controlateral side is vertically unstable
o C3: bilateral injury in which both sides are vertically unstable
Seventy to eighty percent of all pelvic injuries are type A or type B fractures.[3] (level of evidence: 4)
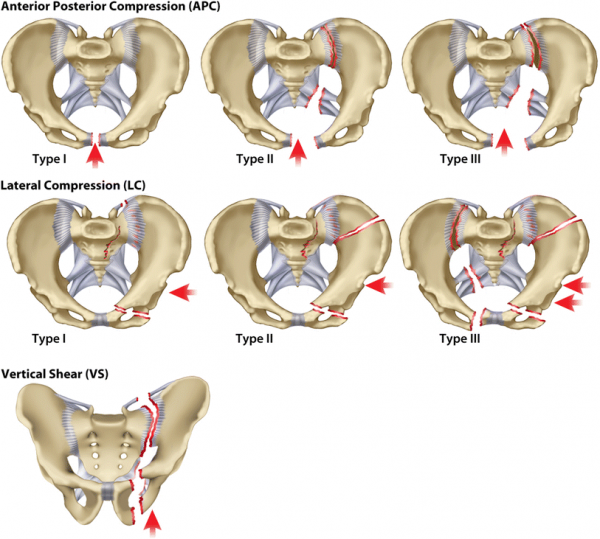
Classification of pelvic fractures by Young and Burgess is based on the mechanism of injury. [7][8][9] (level of evidence: 5, 3A, 5)
- Anterior posterior compression
- Lateral compression
- Vertical shear
- Complex: a combination of any three primary patterns
The Young and Burgess classification system is limited as it provides little guidance for treatment. [10] (level of evidence: 3A)
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Pelvic fractures rarely occur as a single injury. They should be differentiated from, or could be accompanied by many disorders like: [11][12][13][14] (levels of evidence: 4)
- avascular necrosis of the femoral head
- cancer
- hip dislocation
- hip fractures
- osteomyelitis
- osteoporosis
- genito-urinary injuries
- bowel injury
- muscular injuries
- neurovascular injuries
- bladder injury
- urethral injury
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of a pelvic fracture mostly will be made by medical imaging. Imaging tests can determine the location of a fracture, how many bones are affected and whether an injury has damaged surrounding soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, blood vessels or nerves: [15] (level of evidence: 5)
- X-rays: antero-posterior view, inlet view and outlet view
- CT scan
- Ultrasound
- Bone scans
The severity and correlated injuries can be investigated by: [16] (level of evidence: 2B)
- Urinalysis
- Measurement of haemoglobin and hematocrit: to measure blood loss
- Retrograde urethrography
- Arteriography
- Cystography
Outcome measures[edit | edit source]
To measure the outcome of patients with pelvic fractures many questionnaires can be used. They can be divided in disease specific or patient specific outcome measures. [17] (level of evidence: 3B)
- Disease specific:
- Harris Hip score
- Mayo Hip scores
- Patient specific outcome measures:
- Oxford Hip scores,
- SF-36,
- WOMAC
- iHOT
Examination[edit | edit source]
Because a high-energy trauma could damage the primary organ systems, the examination of a pelvic fracture should start with investigation of life-threatening injuries. The abdomen, perineum, genitals, rectum and lower back must be examined very carefully. [6] (level of evidence: 2B) High-energy fractures are often associated with severe injuries of other organs. [8](level of evidence: 3A) When life-threatening injuries are excluded the examination should include an inspection and palpation of the pelvis to identify crepitus and to determine pelvic stability. It is necessary to examine whether related injuries are present. Some injuries that could be associated with pelvic injuries are: soft-tissue injuries, urethral injuries, skeletal injuries, neurovascular injuries and neurologic injuries.
Soft-tissue injuries like hematomas, abrasions and lacerations commonly accompany pelvic ring injuries. Hematomas located at the scrotum, labium, flank and the inguinal region are indicative of intrapelvic hemorrhage [18](level of evidence: 4). Lacerations of the perineum, rectum and vagina are indicative of severe injuries and could be indicative for contamination by urine or stool. Ohmori et al. concluded that the risk factors for massive hemorrhage are: Lactate level, AO/OTA classification, and pelvic extravasation of contrast fluid on CT. They created a new effective predictive score of massive hemorrhage in pelvic ring fractures. [12](level of evidence: 4)
Pelvic fracture urethral injury is an uncommon but potentially devastating result of pelvic fracture. Symptoms of urethral injuries are blood at the external urethral meatus, a high-riding (nonpalpable) prostate gland in man, and perineal and genital swelling. Pelvic fractures often are present with bladder disruptions. The disruption may be intraperitoneal, extraperitoneal, or both. In patients with a bladder disruption gross hematuria will be present.[13] (level of evidence: 4)
Frequently pelvic fractures are associated with skeletal injuries. It is necessary that the clinician examines the spine and extremities. There could be limb length discrepancies, or internal/external rotational deformities.
Because many structures transverse the pelvis, it is possible that a pelvic injury causes injury to a neurovascular structure. Vascular injuries occur more often than arterial injuries. Both may contribute to hemorrhage. A certain injury is very urgent to treat. [14] (level of evidence: 4)
Sometimes there will also be neurological injuries. The nerve roots that are typically injured are L5 and S1. Sometimes L4 (severe pelvic injury) or S2-S5 nerves (sacral injuries) can be damaged too. The clinician should carefully detect these nerve injuries by a neurological examination.
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
Pelvic fractures should be considered in the context of a polytrauma management, rather than in isolation. The treatment and management of each patient requires careful, individualized decision making (3) (level of evidence: 4). Medical management of pelvic fractures consists of many parts. First of all, if necessary, resuscitation must be done. Afterwards, the patient and the fracture should be stabilized. After the medical management is finished the rehabilitation can start.
The stabilization of pelvic fractures has historically been treated non-operatively. Lately operative management has increased in the treatment of unstable pelvic fractures. Operative management of an unstable pelvic ring injury allows earlier mobilization, and thereby diminishes the complications of immobilization. Stabilization may also be important for the survival of the patient and may be desirable to improve the long-term functional results. It allows correction and prevention of significant pelvic deformities, so the clinical outcomes of the patient will improve [19].(level of evidence: 4)
In emergency, the fracture will be stabilized by an external fixator (for antero-posterior injuries) or a ‘C-clamp’ (for vertical shear injuries). The definitive fixation can be done anteriorly or posteriorly and internal or external. Mostly plates or screws are used to stabilize a fracture. Rommens et al. (2015) concluded that more studies are needed to find the optimal treatment for each type of instability. [20] (level of evidence: 4)
Other methods used to treat pelvic fractures are traction, spica casts, pelvic slings, and turnbuckles.
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Physical therapy is an important part of the rehabilitation in both, low-energy and high-energy pelvic fractures. Low-energy injuries are usually managed with conservative care. This includes bed rest, pain control and physical therapy. [6](level of evidence: 2B) High-energy injuries, especially the unstable fractures must be reduced by surgical treatment. Afterwards physical therapy includes the same treatment as in low-energy fractures. Early mobilization is very important because prolonged immobilization can lead to many complications, including respiratory and circulatory dysfunctions. Physical therapy helps the patient to get out of bed as soon as possible.
The goals of the physical therapy program should provide the patient with an optimal return of function by improving functional skills, self-care skills and safety awareness. [21] The main goals are to improve the pain level, strength, flexibility, speed of healing, and the motion of the hip, spine and leg. Another important goal is to shorten the time needed to return to activity and sport.
The intensity of the rehabilitation depends on whether the fracture was stable or unstable.
In people with surgical treatment, physical therapy starts after 1 or 2 days of bed rest. It is initiated with training of small movements, transfers and exercise training. The following exercises can start immediately after surgery and should be done at least four times a day (unless told otherwise). The number of repetitions are guidelines and can vary with every patient. [22] (level of evidence: 5)
Plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the feet
Sit up or lie down. Keep your legs straight and move your feet up and down at the ankles, pointing your toes and then relaxing.
Repeat 10 – 15 times every hour.
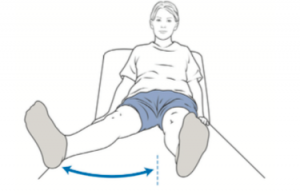
Abduction of the hip
Move your leg out to the side and then back to the middle.
Repeat both sides 10 times.
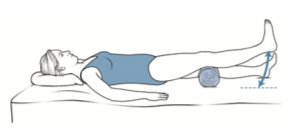
Contraction of the quadriceps
Keep your legs flat on the bed. Push the knee down so that your leg is straight and then tighten your thigh muscle and hold for five seconds.
Repeat 5 – 10 times.
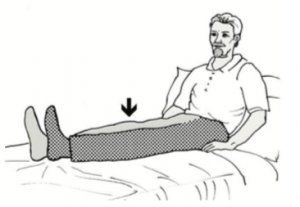
Extension of the knee: lying
Lie on your back. Put a rolled towel under your knee.
Tighten your thigh muscles and straighten your knee, lifting your heel off the bed. Hold your leg straight for five seconds and lower it gently.
Repeat both sides 10 times.
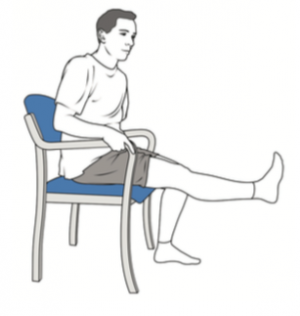
Extension of the knee: sitting
Once you can sit in a chair or wheelchair comfortably: Pull your foot up towards you, tighten your thigh muscle and straighten your knee. Hold this position for five seconds.
Repeat 10 – 15 times every hour.
Short-term goals for patients after surgery are: independence with transfers and wheelchair mobility. Depending on the medical status of the patient these goals can be achieved in 2 to 6 weeks. The physical therapy program can be continued in the hospital or at home. The home-based program includes basic range of motion, stabilizing and strengthening exercises intended to prevent contracture and reduce atrophy.
During the non-weight bearing status the patient performs isometric exercises of the gluteal muscle and quadriceps femoris muscle, range of motion exercises and upper-extremity resistive exercises (for example shoulder and elbow flexion and extension) until fatigued. The number of repetitions can vary with the patient. [23] (Level of evidence: 4)
Once weight-bearing is resumed, physical therapy consists of gait training and resistive exercises for the trunk and extremities, along with cardiovascular exercises (for example treadmill or bicycle training). Stabilization exercises and mobility training should also be remained in the program. [24] Aquatherapy is also good and helpful when available. [23] (Level of evidence: 4)
Mobility training is useful to regain the range of motion in the hip, knee and ankle after immobilization. Gait training should start with walking between parallel bars. Afterwards the patient should learn how to walk with a walker or with a cane. Balance and proprioception training should also be included in the rehabilitation. Resistive training should be progressive to improve the muscle strength in the hip and leg. In the final stage functional exercises should be included to provide the patient with an optimal return of function.
Because pelvic fractures mostly occur in the elderly population, the rehabilitation process will be focused on optimizing their quality of life.
Zidén et al. (2010), investigated the long-term effect of a home rehabilitation program. They concluded that one year after the start of the rehabilitation process, most patients didn’t consider themselves fully recovered, compared to their situation before the fracture. [25](level of evidence: 1B) There should be more investigations to describe the short-term and long-term effects of the rehabilitation for hip fractures.
Key Research[edit | edit source]
Little research is focused on an optimal conservative management of pelvic fractures. Most studies focus on the medical management. There is more evidence needed to define an optimal physical therapy protocol.
Resources[edit | edit source]
Pelvic Fracture Overview : M.D. Nabil A. Ebraheim www.youtube.com/watch
Fracture pelvis : Overview : Dr. Atul Patil www.youtube.com/watch
Clinical Bottom Line[edit | edit source]
First, the type of pelvic fracture should be determined. The medical management and further rehabilitation depends whether the fracture is stable or unstable. If the fracture is unstable, mostly surgery will be necessary.Pelvic fractures should be considered in the context of polytrauma management, rather than in isolation due to the complexity of the injuries leading to pelvic fractures. In people with surgical treatment, physical therapy starts after 1 or 2 days of bed rest. Physical therapy starts with non-weight bearing exercises. Only when the fracture is stable enough weight bearing exercises can be initiated. Walking aids will be necessary and must be reduced gradually.
We can conclude that the treatment and management of each patient requires careful, individualized decision making and thereby see this as the main idea regarding pelvic fractures.
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Li et al., 2014, investigated the clinical efficacy of two types of operative treatment in unstable pelvic fractures. They compared percutaneous sacroiliac screw internal fixation with sacroiliac joint anterior plate fixation. Perioperative period clinical indicators, the postoperative Matta score and the postoperative Majeed function score were measured in both groups. The results of the study revealed less injury, less bleeding, less pain and more rapid recovery in patients treated with percutaneous sacroiliac screws compared to the plate fixation. The complication rate was significantly lower and the rate of Matta score and Majeed function score were significantly higher in the group with percutaneous sacroiliac screw fixation. [26] (level of evidence: 1B)
Sherrington et al., 2016, is a randomised controlled trial that aims to evaluate the effects of an exercise and fall prevention self-management intervention on mobility-related disability and falls in older people following fall-related lower limb or pelvic fracture. Unlike previous post-fracture studies, the intervention and follow-up will be long-term, and the majority of exercise will be undertaken independently, aiming for a balance between sufficient intensity for effectiveness and reduced cost for feasibility of implementation. As the proportion of older rises globally, the costs associated with lower limb and pelvic fractures will increase. There is systematic review evidence that outcomes after fall-related fractures can be improved with well-designed intervention programs but the best approach to improve function is not evident. Existing trials of post-fracture rehabilitation leave many questions unanswered. Almost all of the studies included in these earlier systematic reviews give evidence for hip fracture rehabilitation and not specific for pelvic fractures.[27] (level of evidence: 1B)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Russel G. V. Et al, Pelvic Fractures, medscape, january 2016. LOE: 5
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gruen, Gary S., et al. "Functional outcome of patients with unstable pelvic ring fractures stabilized with open reduction and internal fixation." Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 39.5 (1995): 838-845. LOE : 2B
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Tile, Marvin. "Acute pelvic fractures: I. Causation and classification." Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 4.3 (1996): 143-151. LOE: 4
- ↑ Melton LJ 3rd, Sampson JM, Morrey BF, Ilstrup D. Epidemiologic features of pelvic fractures. Clin Orthop. 1981 Mar-Apr. (155):43-7. LOE: 4
- ↑ Ooi, Chee Kheong, et al. "Patients with pelvic fracture: what factors are associated with mortality?" International journal of emergency medicine 3.4 (2010): 299-304. LOE: 2B
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Aghababian, Richard. Essentials of emergency medicine. Jones&Bartlett Publishers, 2010.(book)
- ↑ Mechemm C. C. et al, Pelvic Fracture in Emergency Medicine, medscape, august 2015. LOE: 5
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Tai D. K. C. et al, Retroperitoneal Pelvic Packing in the Management of Hemodynamically Unstable Pelvic Fractures: A Level I Trauma Center Experience, J Trauma. 2011;71: E79–E86. LOE: 3A
- ↑ Flint, Lewis, and H. Gill Cryer. "Pelvic fracture: the last 50 years." Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 69.3 (2010): 483-488. LOE: 5
- ↑ Alton, Timothy B., and Albert O. Gee. "Classifications in brief: young and burgess classification of pelvic ring injuries." Clinical orthopaedics and related research 472.8 (2014): 2338. LOE : 3A
- ↑ PELTIER, LEONARD F. "Complications associated with fractures of the pelvis." J Bone Joint Surg Am 47.5 (1965): 1060-1069. LOE: 4
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Ohmori, T. et al. “Scoring system to predict hemorrhage in pelvic ring fracture.” Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery&Research(2016) LOE:4
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Watnik, Neil F., Michael Coburn, and Michael Goldberger. "Urologic injuries in pelvic ring disruptions." Clinical orthopaedics and related research 329 (1996): 37-45. LOE:4
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Schield DK, Tile M, Kellam JF. Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Pelvic Ring Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1991. 5(2):226. LOE: 4
- ↑ Furtado, C., R. Amaral, and P. Amaral. "Pelvic insufficiency fractures in the elderly: a challenging diagnosis." Acta reumatologica portuguesa (2016). LOE: 5
- ↑ Choi, Wilson, Handoo Rhee, and Eric Chung. "Lower urinary tract imaging in pelvic fracture: an 11‐ year review of genitourinary complications and clinical outcomes." ANZ Journal of Surgery (2016). LOE: 2B
- ↑ Mclean, James M., et al. "Normal population reference values for the Oxford and Harris Hip Scores– electronic data collection and its implications for clinical practice." Hip International (2016). LOE: 3B
- ↑ PELTIER, LEONARD F. "Complications associated with fractures of the pelvis." J Bone Joint Surg Am 47.5 (1965): 1060-1069. LOE: 4
- ↑ Rice, Phillip L., and Melissa Rudolph. "Pelvic fractures." Emergency medicine clinics of North America 25.3 (2007): 795-802. LOE: 4
- ↑ Rommens, P. M., et al. "Fragility Fractures of the Pelvis: Should they Be Fixed?." Acta chirurgiae orthopaedicae et traumatologiae Cechoslovaca 82.2 (2015): 101-+. LOE: 4
- ↑ Dutton, Mark. Orthopaedics for the physical therapist assistant. Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 2011. (book)
- ↑ King’s health partners, Pelvic fracture- physiotherapy after surgery, King’s college hospital, 2015. LOE: 5
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Hakim, Renée M., Gary S. Gruen, and Anthony Delitto. "Outcomes of patients with pelvic-ring fractures managed by open reduction internal fixation." Physical therapy 76.3 (1996): 286-295. LOE: 4
- ↑ Stephenson, Rebecca Gourley, and Linda J. O'Connor. Obstetric and gynecologic care in physical therapy. Slack Incorporated, 2000. (book)
- ↑ Zidén, Lena, Margareta Kreuter, and Kerstin Frändin. "Long-term effects of home rehabilitation after hip fracture–1-year follow-up of functioning, balance confidence, and health-related quality of life in elderly people." Disability and rehabilitation 32.1 (2010): 18-32. LOE: 1B
- ↑ Li, C. L. "Clinical comparative analysis on unstable pelvic fractures in the treatment with percutaneous sacroiliac screws and sacroiliac joint anterior plate fixation." Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18.18 (2014): 2704-8. LOE: 1B
- ↑ Sherrington, Catherine, et al. "Exercise and fall prevention self-management to reduce mobility-related disability and falls after fall-related lower limb fracture in older people: protocol for the RESTORE (Recovery Exercises and STepping On afteR fracturE) randomised controlled trial." BMC geriatrics 16.1 (2016): 1. LOE: 1B