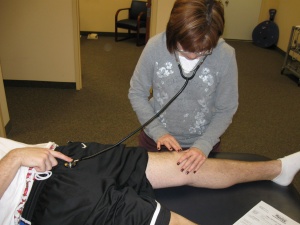
Patellar-Pubic Percussion Test
Original Editor - Michael Conaway
Top Contributors - Admin, Michael Conaway, Kim Jackson, Laura Ritchie, Fasuba Ayobami, WikiSysop, 127.0.0.1, Tony Lowe, Evan Thomas, Kai A. Sigel and Claire Knott
Purpose[edit | edit source]
To identify occult hip fractures.
Technique[edit | edit source]
The Patellar-Pubic Percussion Test is a form of Osteophony or auscultatory percussion which is used in the assessment of bone integrity by analyzing its vibrations through the use of a stethoscope and bony prominence percussion.[1]
Sensitivity/Specificity[edit | edit source]
Tiru et al[3] found a sensitivity of .96 and a specificity of .86 for the PPPT in the diagnosis of femoral neck fractures.
Evidence[edit | edit source]
In the United States hip fractures have a yearly incidence of about 300,000. This number is expected to double or possibly triple by the year 2040. Morbidity and mortality are reported to be as high as 14-36% in the first year after injury.[4][5] In 2-10% of those patients that present to the ER with a painful hip after trauma, initial radiographs will not show the occult fracture.[6] Adams et al[7] reported an interrater agreement of 90.2% for the PPPT.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Borgerding LJ, Kikillus PJ, Boissonnault WG. Use of the Patellar-Pubic Percussion Test in the Diagnosis and Management of a Patient with a Non-Displaced Hip Fracture. J Manual and Manipulative Therapy.2007;15:E78-E84.
- ↑ BJSM Videos. Patellar pubic percussion test, with Mike Reiman. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bZccYojlDvQ [last accessed 25/01/14]
- ↑ Tiru M, Goh SH, Low BY. Use of percussion as a screening tool in the diagnosis of occult hip fractures. Singapore Med J 2002;43:467-469.
- ↑ Perron AD, Miller MD, Brady WJ. Orthopedic Pitfalls in the ED: Radiographically occult hip fracture. Am J Emerg Med 2002;20:234-237.
- ↑ Brunner LC, Eshilian-Oates L, Duo TY. Hip Fractures in adults.Am Fam Phys 2003;68:537-542.
- ↑ Lubovsky O, Liebergall M, Mattan Y, Weil Y, Moshieff R. Early diagnosis of occult hip fractures: MRI versus CT scan. Injury Int J Care Injured 2005;36:788-792.
- ↑ Adams SL, Yarnold PR. Clinical use of the patellar pubic percussion sign in hip trauma. Am J Emerg Med 1997;15:173-175.