Neglected Bilateral Clubfoot
Original Editor - Rosalind When in conjunction with Africa Clubfoot Training Team as part of ICRC and GCI Clubfoot Content Development Project
Top Contributors - Naomi O'Reilly, Kim Jackson and Aminat Abolade
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The standard treatment for neglected clubfoot deformity in children with age of 2 years and below is conservative treatment by manipulation, serial casting, and relapses are not uncommon. However Management of the neglected club foot deformity in older children having no flexibility in feet is an orthopedic challenge for physical therapist. There are different approaches of treatment for correcting club foot deformity depends upon the severity and flexibility of the child foot or feet. But the choice of treatment is Ponseti technique now days giving 95% to 100% result in clubfoot patients if followed properly. [1]
Patient Characteristics[edit | edit source]
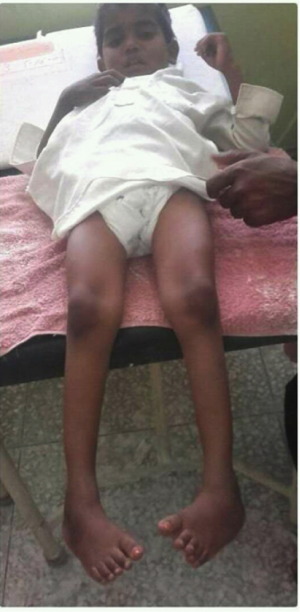
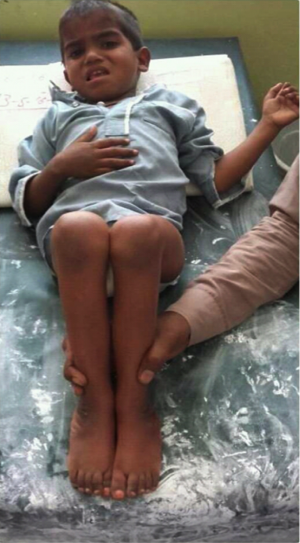
Tanvir Abbas is a 4 year old child, referred to Ponseti Clinic for treatment. The initial screening and detailed assessment confirmed the diagnosis of bilaterally neglected clubfeet. As he belong to a very poor family and nobody in his family was able to support his treatment. Therefore he remained untreated. After arrival in Ponseti clinic and conformed diagnose the treatment sponsored by ICRC.
Examination Findings[edit | edit source]
After screening the case forwarded for detail assessment to identify the type of clubfoot, previous history of treatment and effect on the body. From the subjective history of the patient it was found that he had not previously had any treatment for the clubfoot deformity, and so was considered to be Neglected Congenital Talipes Equino Varus bilaterally. Initially it was observed that the child was walking on lateral border of the feet, and the calcanous-cuboid joint was very prominent with the forefeet internally rotated. The hip joints were normal but during walking there were slight internal rotation with the knee in 10 degrees Genu Valgum. Perani Scoring and detailed history chart was used to determine the severity of the deformity. It was determined that the Perani Score was 6/6 for both feet, with slight rigidity in left foot.
Clinical Hypothesis[edit | edit source]
- To find out the outcome of ponseti technique in a patient with sever neglected club feet case.
- To find out the relation of ponseti technique and flixibilty in ankle joint of a club foot patient.
Intervention[edit | edit source]
Treatment used was the Ponseti Method with 5 Serial Casts required for this case. The following was the procedure followed:
1st Serial Cast:[edit | edit source]
Perani Score was 6/6 with general history mentioned above. Manipulation was done on head of talus for both feet, each for 15 repetitions and held in press position for 8 seconds to ensure proper stretch of Abductor Hallucis Longus, Tibialis Posterior muscles and ligament. Post manipulation POP Cast was applied for one week.
2nd Serial Cast:[edit | edit source]
Perani Scoring following the first casting was observed as 5/6. The child general condition was examined and it was observed that patient has some skin irritation on the medial side of the thigh but was considered very minor so the second cast was applied. In this case the medial side of the cast was kept down so that the affected area of the skin would remain open and the same procedure as 1st Serial Cast was completed with a little more stretch on the Abductor Hallucis Longus, Tibialis Posterior Muscles with the feet maintained in a supinated position with maximum abduction.
3rd Serial Cast:[edit | edit source]
Perani Score following the second casting was 4/6 for right side so improvement seen, but maintained at 5/6 for left side so it is observed that the case got relapse due to damaging the POP casting .so the position given in the second cast got Recurrent and no improvement seen in left side of foot.
Again manipulation done and post manipulation serial casting applied and this time more stretch applied to the abductor hallucis longus, tibialis posterior longus, flexor digitorum longus lateralis and counter pressure on head of talus applied for over correction of left foot.
4th Serial Cast:[edit | edit source]
Previous POP cast observed and there is again mild damage in bilateral pop cast but the feet position were same and only toes were in mild adducted position.POP cast removed and perani scoring done which is 3/6 for both feet with only adduction in big metatarsal.
This time manipulation done and pop cast applied but also dyanacast applied over the POP cast for the maintenance of the position.
5th Serial Cast:[edit | edit source]
Position checked in Dyanacast which is normal. Then after removal of cast the perani scoring done which is 2/6 for right side and 2.5/6 for left side. it is also observed that there is only equines in bilateral feet and only mild abduction limitation in left side. So it is decided that left side foot will need over correction in post tenotomy POP cast.
Tenotomy:[edit | edit source]
Previous POP cast observed which is normal so after removal of the cast the perani scoring done which is 0.5/6 for right side and for left side it is observed as 1.5/6 so case proceeded for tenotomy and proper positioning, knife (BP Blade-15/11 size) was placed parallel to tense tendoachillis approximately 1 cm above the insertion at calcaneus.
Then blade is turn 90 degree, perpendicular to tendon. Then tendon is cut from medial to lateral direction. A “POP” sound is felt as the tendon is released. An additional 10 to 15 degree of dorsiflexion is typically gained after tenotomy. POP cast applied and more abduction given in the left side for achieving the best result.
Foot Abduction Brace:[edit | edit source]
After 3 weeks the pop cast removed and gain the perani scoring done for the case it is observed that the feet are completely normal 0/6 bilateral and ready for another phase of treatment as (preventive phase), so we applied abduction brace name as Dennis brown splint and fixed with angle 70 degree abduction and 20 degree dorsiflexion.
Outcome[edit | edit source]
This case study gave a brief clue about the unawareness of the people regarding the Ponseti treatment or any other treatment for rehabilitation of the club foot ,as there is no pre and post natal diagnose or any investigation done for the identification of the kid with this deformity. The result of this study is consistent with that of study by Birhanu Ayana and Peter J Klungsoyr [2].
In our study Ponseti method has successfully treated the neglected club foot which is supported by study of Laurenco et al. (2007) in Brazil, which has successful results in 17 children having average age of 3.9 yrs [3].
In under developed countries, studies have shown good results of Ponseti techniques in the neglected club feet children. Adequate deformity correction was achieved in age ranging 1.5 yrs to 4 yrs children in the study at Malawi [4].
A study done in Istanbul, Turkey also reported the efficacy of Ponseti technique using Perani score in children aging more than 20 months which is in favor of our study finding [5].
It is concluded that Ponseti method can be used for the neglected clubfeet children. If the treatment technique is used properly then the result will be significant enough to reduce the requirement of surgical intervention.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Irani RN, Sherman MS. The Pathological Anatomy of Club Foot. JBJS. 1963;45(1):45-52.
- ↑ Ayana B, Klungsøyr PJ. Good Results after Ponseti Treatment for Neglected Congenital Clubfoot in Ethiopia: A Prospective Study of 22 Children (32 `eet) from 2 to 10 Years of Age. Acta Orthopaedica. 2014;85(6):641-5.
- ↑ Lourenço A, Morcuende J. Correction of Neglected Idiopathic Clubfoot by the Ponseti Method. Bone & Joint Journal. 2007;89(3):378-81.
- ↑ Tindall AJ, Steinlechner CW, Lavy CB, Mannion S, Mkandawire N. Results of Manipulation of Idiopathic Clubfoot Deformity in Malawi by Orthopaedic Clinical Officers using the Ponseti Method: A Realistic Alternative for the Developing World? Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2005;25(5):627-9.
- ↑ Yagmurlu MF, Ermis MN, Akdeniz HE, Kesin E, Karakas ES. Ponseti Management of Clubfoot after Walking Age. Pediatrics International. 2011;53(1):85-9.