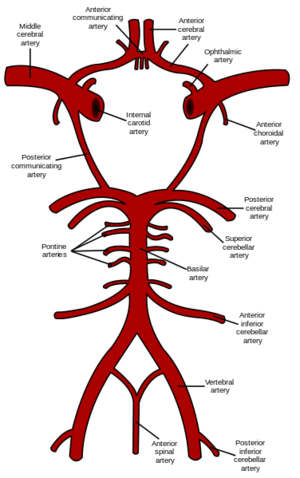
Middle Cerebral Artery
Description[edit | edit source]
Middle cerebral artery. is the largest branch and the second terminal branch of internal carotid artery. It lodges in the lateral sulcus between the frontal and temporal lobes and is part of the circle of Willis within the brain,and it is the most common pathologically affected blood vessel in the brain.[1][2][3]
Structure[edit | edit source]
The MCA divides into four main surgical segments, denominated M1 to M4.[4]
- The M1 segment extends from the ending of the internal carotid artery, perforating the brain up to its division.
- The M2 segment bifurcates or occasionally trifurcates. It travels laterally to the Sylvian fissure, and its branches end in the cerebral cortex.
- The M3 segment travels externally through the insula into the cortex. Finally,
- the M4 segments are thin and extend from the Sylvian fissure to the cortex
Function[edit | edit source]
It supplies the greater part of the lateral cerebral surface (including the main motor and sensory areas) as well as giving the striate arteries which supply deep structures including the internal capsule[1][2]
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
The middle cerebral artery is the most common, pathologically affected blood vessel overall[4]
Embolism of the MCA
An embolism is transported through the blood vessels until it is lodged in the MCA. The arterial occlusion impedes perfusion of oxygenated blood to the brain parenchyma, resulting in an ischemic stroke causing cerebral edema and brain parenchyma tissue necrosis.
. A stroke of the MCA is denoted as middle artery syndrome. presents with:
- contralateral sensory loss of the legs, arms, and lower two-thirds of the face due to tissue necrosis of the primary somatosensory cortex.
- Contralateral paralysis of the arms, legs, and face may be observed due to necrosis of the primary motor cortex, which is observed clinically as muscle weakness, spasticity, hyperreflexia, and resistance to movement (upper motor neuron signs).
- Ipsilateral eye deviation is observed due to frontal cortex Brodmann area 8 becoming ischemic, impairing planning of eye movement, symptoms that are exacerbated by contralateral homonymous hemianopsia. A dominant, most commonly left-sided, hemisphere stroke results in Broca aphasia if the superior division of the MCA is affected. In contrast, Wernicke’s or conduction aphasia may be seen if the inferior division of the MCA is affected. A non-dominant, most commonly right-sided, hemisphere stroke results in hemineglect syndrome, presenting with anosognosia, apraxia, and hemispatial neglect.
Lenticulostriate Infarct
Infarction of the deep, perforating lenticulostriate branches of the MCA also is most likely caused by an embolism of cardiac origin.
Arteriovenous Malformations
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are congenital arteriovenous connections which can be found anywhere in the brain.
Saccular Aneurysms (Berry aneurysms)
Saccular aneurysms are the most common subtype of an aneurysm. These usually present in areas of bifurcation/trifurcation due to blood vessel weakness and outpouching. Saccular aneurysms present about a third of the time in the MCA. They are associated with risk factors such as autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADKPKD), Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, cigarette smoking, hypertension, and age. Risk factors increase the probability of rupture and intracerebral hemorrhage.
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Snell RS. Clinical neuroanatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Faiz O, Blackburn S, Moffat D. Anatomy at a Glance. John Wiley & Sons; 2011 Nov 30.
- ↑ Feneis H, Dauber W. Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy. Thieme; 2000.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Navarro-Orozco D, Sánchez-Manso JC. Neuroanatomy, Middle Cerebral Artery. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Jan 16. StatPearls Publishing.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526002/
- ↑ Steve Jacques's Video :Middle Cerebral Artery. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JXrY0LajqOw[last accessed 19/10/2019]