Methamphetamine Abuse
Original Editors - Seth Pinkerton & Jessica Sparks from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Top Contributors - Seth Pinkerton, Jessica Sparks, Niha Mulla, Admin, Kim Jackson, Elaine Lonnemann, 127.0.0.1, WikiSysop, Lucinda hampton and Wendy Walker
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Methamphetamine is one of the powerful stimulants of the central nervous system (CNS). It is sometimes used as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity; however, methamphetamine is better known as a recreational drug. Street names include meth, speed, ice, glass, chalk, and many others.[1]
Methamphetamine was first discovered in 1893. In 1919 methamphetamine originated from amphetamine in Japan. In the 1930s, the drug was introduced to the United States as a bronchial inhaler and a nasal decongestant and later, it was used to treat obesity. Prescribing this medication is limited due to its neurotoxic potential and risk of recreational use as a euphoriant. Today, there are safer medications of choice with the same treatment efficacy, and hence, the use of methamphetamines in the United States is very limited. Due to illicit trafficking and recreational use the agent is classified as a schedule II, controlled substance in the United States and the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances.
Use of methamphetamine triggers: elevated mood; alertness; increase concentration; energy; decreased appetite; causes weight loss, and increased sexual libido.
The use of methamphetamine in higher doses can induce: psychosis; bleeding in the brain; skeletal muscle breakdown; seizures. Chronic use can cause: violent behavior; mood swings; psychosis such as paranoia, delirium, auditory and visual hallucination, and delusions.
Chronic long-term methamphetamine use can be highly addictive, and if it discontinued abruptly, may lead to withdrawal symptoms that can be persistent for months after use.[2]
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Methamphetamine is a central nervous system stimulant similar to the drug amphetamine and is classified as a Schedule II drug due to its high potential for abuse. It affects the brain by increasing the release and blocking the reuptake of dopamine which is a common mechanism of action for most drugs that are abused.[1]
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter responsible for the reward, motivation, and pleasure centers of the brain. Methamphetamine causes a rapid release of dopamine in the brain resulting in an intense euphoric or grandeur feeling which is the addictive property of the drug.[1]
Methamphetamine is a white, odorless, bitter tasting crystalline powder which can easily be dissolved in water or other liquids. It is taken orally, intranasally (snorting), by smoking, or intravenously.[1] [3]
Meth can be made from common household substances including:
- Pseudoephedrine - decongestant
- Iodine crystals
- Battery acid
- Red phosphorus – match boxes and road flares
- Anhydrous ammonia – fertilizer or countertop cleaner
- Toluene – an aromatic hydrocarbon. The solvent is found in certain paint thinners, permanent markers, and some types of glue
- Hydrochloric acid
- Acetone – nail polish remover or paint thinner
- Sodium hydroxide - lye
- Sulfuric acid – drain or toilet bowl cleaner[4]
Etiology[edit | edit source]
There is no one known cause of methamphetamine abuse but it is thought that the following can lead someone to try any drug including meth and subsequently become addicted:
- Genetics (if a parent has an addiction problem it is thought that the child will be more likely to have an addiction problem as well)[5]
- Mental illness (31.3% of people with a serious mental illness have used illicit drugs)[6]
- History of physical or psychological abuse[5]
- Risk seeking personality
- Peer pressure or curiosity
- Low self-esteem
- Anxiety
- Loneliness or Depression[5]
Prevalence[edit | edit source]
In a response to an increase of methamphetamine abuse in South Carolina researchers found that compared to abusers of other drugs, methamphetamine abusers were more likely to be female, between 20 and 40 years old, and of non-Hispanic white ethnicity. Further, more methamphetamine users had occupational/economic problems and problems with their primary support group.[7] Another study in California following an increase in abuse found that amphetamine abuse was greatest in rural areas with more young low-income whites, a greater amount of retail and alcohol vendors, and fewer restaurants. However, growth rates were greater in higher-income areas with larger non-White and Hispanic populations. This shows that methamphetamine abuse can quickly become popular in a multitude of cultures and communities.[8]
In the mid 2000's, Mexico began to limit imports of pseudoephedrine and further restrictions were placed on the sale of over-the-counter cold medication used in the production of methamphetamine. Further, illegal importation of 60 + tons of pseudoephedrine via a "rogue" Mexican chemical company was halted in the mid 2000's, as well as a ban on all pseudoephedrine and ephedrine products in Mexico resulted in a decrease in methamphetamine purity and therefore decrease in treatment admission in Texas and Mexico. The purity increased following a procedural shift to the P2P process, that utilizes chemicals other than pseudoephedrine.[9]
Despite slight decrease since mid-decade peaks in treatment admission, levels of methamphetamine admissions remain high in several states at levels seen in the early 2000's, well above levels from the 1990's. For example, methamphetamine admissions accounted for 6.1% of the total in 2008 compared to 1.4% in 1992 nationwide, and 27.4% in California in 2009 compared to 7.8% in 1992. It is clear that education on methamphetamine abuse prevention and abuse treatment are increasing on an national level.[9]
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Meth abusers can present with a variety of physical characteristics which can include the following:
- Increased heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration
- Hyperthermia
- Excessive sweating
- Dry skin with multiple scabs or open wounds on the face or arms
- Scratching or “picking” skin
- Track marks on arms or other parts of the body
- Rapid speech
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Insomnia[10]
More chronic meth users can also present with the following:
- Anorexic appearance (extreme weight loss)
- Violent behavior
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
- Paranoia
- Psychosis
- Seizures
- "Formication" or Delusions of feeling bugs crawling under skin (which leads to excessive scratching and open wounds)
- Delusions of grandeur
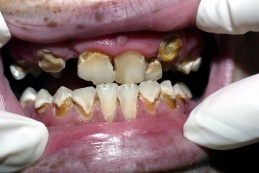
- "Meth Mouth" - severe tooth decay[10]
Associated Co-morbidities[edit | edit source]
Crystal meth abusers report feeling:
- Powerful/ confident
- Endless energy
- Increased productivity
- Enhanced sexual performance
- Reduced appetite[12]
Short Term/Identification/Acute Use Causes:
- Euphoria followed by depression
- Dilated pupils
- Nervousness
- Decreased appetite
- Rapid eye movement
- Dilated pupils
- Excessive swearing
- Hallucinations
- Aggression
- Impaired speech
- Increased heart rate[13]
Overdose can cause:
- Convulsions
- Heart attack
- Kidney failure
- Stroke (days after OD)[14]
- Spike in BP
- Abrupt rise in temperature
- Rapid respiration
- Collapse[13]
Chronic methamphetamine use causes:
- Kidney disorders
- Lung disorders
- Brain damage
- Liver damage
- Extreme weight loss
- Nose bleeds
- Constant scratching/picking of the skin
- Damaged blood vessels
- Insomnia
- Malnutrition/ extreme anorexia[13]
- Raise in blood pressure, which in severe cases leads to rupture of the aorta
- Temporary blindness
- Severe permanent vision impairment (temporary loss of blood flow to optic nerve)
- Ulcers of the cornea
- Temporary emphysema
- Concealed heart damage (repairable upon cessation of drug use)[14]
- Dependence[13]
In smokable format (considered twice as strong):
- Pulmonary edema
- Skin affliction
- Vasoconstriction (leading to increased BP and/or acidosis)
- Ischemic colitis
- Duodenal ulcers
- Malignant giant gastric ulcers[14]
In inhalant format:
- Excessive wear on teeth[14]
With diabetes:
- Affects insulin needs[14]
IV/ Sexual Activity:
- Blood-to-blood transfers/ sharing drug paraphernalia leads to Hepatitis-C and/or HIV.
- 70% of MA- dependent women report histories of physical and sexual abuse.[15]
Children of MA abusing parents:
- Negligence/abuse
- Erratic behavior
- Psychiatric instability
- High risk for exposure to toxic precursors of MA[15]
Safety Issues re Healthcare Workers[edit | edit source]
Due to the unpredictable behaviors, irritability, and the possibility of psychotic behavior of methamphetamine users especially during the hospital visit due to the overdose, or complication, the safety of medical and security staff are important. Hence, it is always advised to use precautions when dealing with these patients. Another healthcare worker or security personnel should always accompany these patients. The triage nurse should be fully aware of the adverse effects of amphetamine and ensure that the emergency department is fully aware of the individual admitted.[2]
Medications[edit | edit source]
There is no one drug that is used to cure methamphetamine addiction but this list offers help to those individuals who are in the process of recovering:
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin) - used to treat depression and cravings (also used by patients who have stopped smoking)[16]
- Topiramate (Topamax) –used to treat cravings and seizures that can occur during withdrawal
- Modafinil – non-amphetamine stimulant shown to improve cognitive functioning[15]
These drugs along with psychological treatment at a drug/rehab facility offer the best hope for the addict to have a successful recovery.[15]
Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values[edit | edit source]
Urine, hair, breath, saliva, sweat, and blood, along with behavioral and psychological cues are used most often in drug testing. Due to ease of retrieving a sample, speed of analysis, and low cost, urinalysis is most often utilized. Urinalysis detects the presence of drug metabolites or physical byproducts of the drug’s use. Most accurate is the use of blood testing, which measures the actual presence of the drug or its metabolite in the blood at the time of the testing. However, these tests are more invasive, expensive, and more time consuming. Hair testing uses the same technology as a urinalysis, but has advantages for detecting use. Using hair testing, drugs can be detected in hair for weeks to months, as opposed to 2-3 days with blood or urine testing.[17]
Systemic Involvement[edit | edit source]
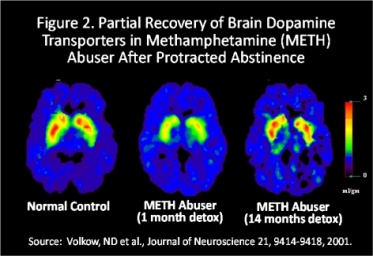
Crystal meth increases dopamine levels in the brain in two ways. First, it increases dopamine release, therefore increasing dopamine in the intercellular space. Because dopamine is a neurotransmitter, this increase produces stronger nerve signals. Second, methamphetaminne prevents reuptake of dopamine into the brain cell. Methamphetamine blocks the dopamine transporters, trapping more dopamine within the intercellular space. Because of both of these actions, dopamine accumulates and the cell is bombarded, causing increased stimulation and a stronger signal transmission. Using methamphetamine can cause a 1,500 percent increase in dopamine.
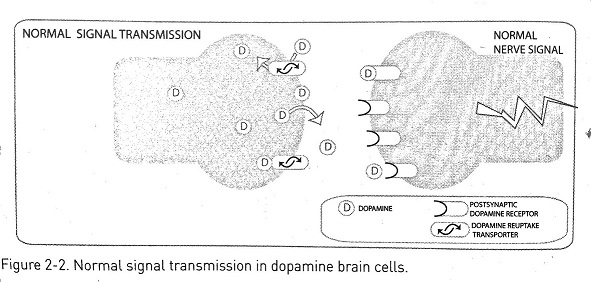
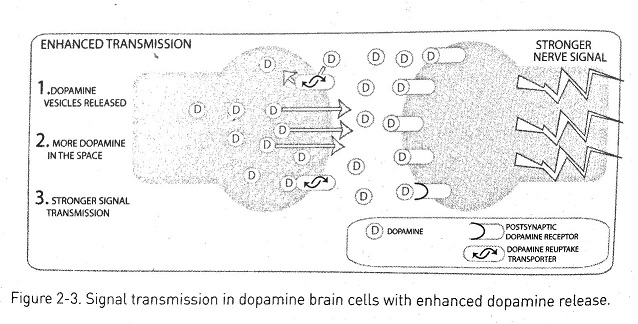
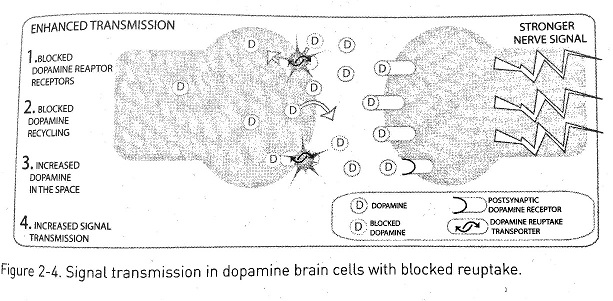 [18]
[18]
Dopamine is not just utilized in the brain. It is used throughout the entire body to initiate the flight-or-flight response.
Cardiovascular[edit | edit source]
Dopamine causes an increased heart rate and vasoconstriction in other areas of the body. Because of these responses, the heart requires more oxygen delivered to other organs of the body. However, an increase in blood pressure to accommodate for this need can sometimes prevent blood from returning to the heart due to a decreased motility of blood through the vessels. In some cases, blood vessels that feed the heart constrict, preventing the heart from receiving an adequate blood supply, leading to myocardial infarction. It is possible that instead of experiencing one traumatic event, some methamphetamine abusers suffer multiple small MI’s over time.
Gastrointestinal[edit | edit source]
GI motility decreases due to decreased blood flow, which secondarily causes a decreased appetite and less frequent bowel movements. In extreme cases, patients can suffer from bowel ischemia due to insufficient blood flow.
Renal[edit | edit source]
When methamphetamine abusers binge, they typically do not drink enough fluids, causing dehydration. Due to dehydration, blood pressure dramatically decreases, causing decreased blood flow to the kidneys. Because of this decrease, binging methamphetamine users are susceptible to kidney failure.
Musculoskeletal[edit | edit source]
Methamphetamine use can lead to muscle breakdown, increasing the level of breakdown products such as creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), which is toxic to the kidneys in high concentrations. Continued and increased muscular breakdown can lead to rhabdomyolysis, a condition involving extreme muscle breakdown and possible kidney failure. These comorbidities can be prevented by staying hydrated.[18]
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
The most effective treatments being used today to treat methamphetamine abuse or addiction involves cognitive and behavioral interventions. Trained psychotherapists who specialize in the area of drug addiction are the preferred medical professionals to carry out these interventions.[19]
Initially, the meth abuser needs to attend a detox center with trained medical staff to be assessed and treated for physical and psychological complications that can occur as the person’s body is going through withdrawal from the drug.[19]
Cognitive and Behavioral Interventions Used to Treat Meth Abuse[edit | edit source]
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): is based on the idea that thoughts and feelings cause our behaviors, not external factors such as people, situations, and events. This type of therapy aims to help the addict change the way they think and behave to increase coping skills with the stresses of life.[20]
- The Matrix Model: includes intensive individual and group therapy to promote behavioral changes needed to prevent relapse, be abstinent, and establish a lifestyle unrelated to drugs. This can include changing their where they live, the people they associate with, and even their profession.[20]
- Motivational Incentives for Enhancing Drug Abuse Recovery (MIEDAR): an incentive based treatment promoting meth abstinence is another treatment that has shown efficacy in meth abusers through the National Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network.[19]
Medications such as Wellbutrin are used in conjunction with psychological therapy to treat depression which many recovering addicts suffer from along with the willingness to change can lead to a successful recovery.
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
There is currently minimal evidence on PT management of methamphetamine abuse. Instead, we are encouraged to treat the many comorbidities. Physical Therapy involvement in methamphetamine abuse predominantly involves referral to authorities (e.g. home health), psychological care, or other appropriate medical staff.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Seizure Disorders
- Parkinson-Plus Syndrome
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Cardiomyopathy
- Hypertensive Heart Disease
- Myocardial Ischemia
- Myocarditis
- Cocaine abuse
- Mushroom abuse
- PCP abuse
- Ketamine abuse
- LSD abuse
- Mescaline abuse[21]
Case Reports/ Case Studies[edit | edit source]
- Crystal methamphetamine-induced acute pulmonary edema: a case report
- The unique histology of methamphetamine cardiomyopathy: A case report
- Intracerebral hemorrhage and characteristic angiographic changes associated with methamphetamine--a case report
- Toxicological and histopathological analysis of a patient who died nine days after a single intravenous dose of methamphetamine: A case report
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Methamphetamine
- Click here to find publicly funded treatment facilities in the USA by state
- Methamphetamine Treatment
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 National Institute on Drug Abuse. http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/infofacts/methamphetamine. (accessed 25 March 2012)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yasaei R, Saadabadi A. Methamphetamine.available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535356/ (last accessed 12.1.2020)
- ↑ Addiction Treatment Centers. Methamphetamine. http://www.addictiontreatmentcenters.net/about-the-drugs/methamphetamine (accessed 1 April 2012)
- ↑ Meth Project. What's in Meth. http://www.methproject.org/answers/whats-meth-made-of.html?gclid=CI3C--m7j68CFYMKKgodIkCUyQ#Whats-in-Meth (accessed 25 March 2012)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Help Guide. http://www.helpguide.org/mental/drug_substance_abuse_addiction_signs_effects_treatment.htm (accessed 2 April 2012)
- ↑ Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2010 NSDUH: Mental Health Findings and Detailed Tables. http://www.samhsa.gov/data/nsduh/2k10MH_Findings/2k10MHResults.htm#4.1 (accessed 2 April 2012)
- ↑ Kortea JE, Hiotta FB, Bradyb KT, Malcolmb RJ, Seec RE. Distinctive characteristics of methamphetamine users presenting at public clinics: Steep rise in South Carolina, United States, 2000–2005. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2011, May 1; 112(1-2): 9-15.
- ↑ Gruenwald PJ, Johnson FW, Ponicki WR, Remer LG, Lascala EA. Assessing Correlates of the Growth and Extent of Methamphetamine Abuse and Dependence in California. Substance Use & Misuse. 2010 Oct 1;45:1948–1970.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Maxwella JC, Brechtb ML. Methamphetamine: Here we go again? Addictive Behaviors. 2011 Dec 1;36(12):1168-1173.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Mayo Clinic. Drug Addiction. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/drug-addiction/DS00183/DSECTION=symptoms (accessed 26 March 2012)
- ↑ 2 Stop Meth. http://www.2stopmeth.org/_global/?q=node/52 (accessed 1 April 2012)
- ↑ Buxton J, Dove N. The burden and management of crystal meth use. CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association Journal [serial on the Internet]. (2008, June 3), [cited April 17, 2012]; 178(12): 1537-1539. Available from: Academic Search Premier.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Fisher G, Roget N. Encyclopedia of Substance Abuse Prevention, Treatment, & Recovery. California: SAGE, 2009.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 Miller R. The Encyclopedia of Addictive Drugs. Connecticut: Greenwood Press, 2002.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 Galanter M, Kleber H. The American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of Substance Abuse Treatment. Fourth edition. Virginia: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc., 2008. p169-176.
- ↑ Drugs.com. Wellbutrin. http://www.drugs.com/wellbutrin.html. Accessed 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Potter B, Orfali S. Drug Testing at Work: A Guide for Employers. California: Ronin Publishing, Inc., 1998.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Lee S. Overcoming Crystal Meth Addiction. New York: Marlowe & Company, 2006.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 National Institute on Drug Abuse. Topics in Brief: Methamphetamine Addiction: Progress, but Need to Remain Vigilant. http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/topics-in-brief/methamphetamine-addiction-progress-need-to-remain-vigilant (accessed 1 April 2012)
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Rawson R, Casey P, Dickow A, Frazier Y, Gallagher C, Galloway G, et al. A multi-site comparison of psychosocial approaches for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence. Addiction 2004; 99: 6. p708-717.
- ↑ Medscape. Methamphetamine Toxicity Differential Diagnoses. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/820918-differential (accessed 2 April 2012)