Hip Osteoarthritis
Original Editor - Eric Robertson, Kim Presiaux
Top Contributors - Kim Presiaux, Dorien De Strijcker, Lucinda hampton, Davy Duverger, Leana Louw, Kim Jackson, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Laura Ritchie, Johnathan Fahrner, Van Horebeek Erika, Scott Buxton, Vidya Acharya, Kai A. Sigel, Eric Robertson, Areeba Raja, Marius De Bruyn, Kevin Vandebroucq, 127.0.0.1, Bram Van Roost, Shaimaa Eldib, Lauren Lopez and Loïc Byl
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
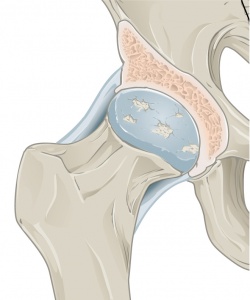
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition as a result of mechanical overload in a weight bearing joint.[1] Hip osteoarthritis mainly affects the articular cartilage, as well as causing changes to the subcondral bone, synovium, ligaments and capsule.[2] This degeneration lead to loss of joint space, which can potentially be symptomatic.[2] It is one of the top 15 contributors of global disability.[3] Hip osteoarthritis is prevalent in 10% of people above 65, where 50% of these cases are symptomatic.[4] The hip is defined as the second most painful joint (after the knee) as a result of osteoarthritis according to a Italian study.[5]
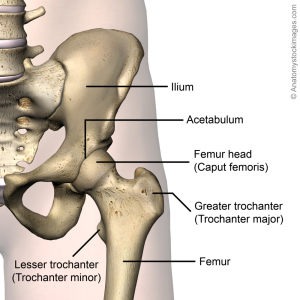
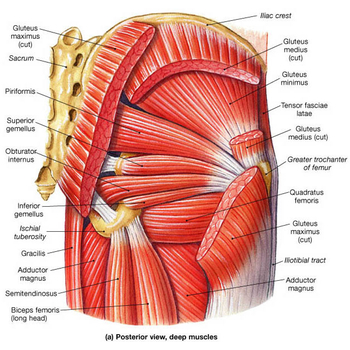
Clinically relevant anatomy[edit | edit source]
For detailed information, see the hip anatomy page.
Epidemiology & etiology[edit | edit source]
Prevalence[edit | edit source]
Hip osteoarthritis is prevalent in 10% of people above 65, where 50% of these cases are symptomatic.[4] Research suggest that there are a 25% risk of developing hip osteoarthritis for people who live to the age of 85,[1]
Primary osteoarthritis[edit | edit source]
Mostly caused by abnormality of the articular cartilage, but can also be a secondary result of developmental changes and abnormalities such as femeroacetbular impingement.[6] Abnormalities normally include acetabular displasia. Pistol grip deformities are seen in some cases, mostly linked with slipped upper femoral epiphysis. Although seen as a specific condition, it is often linked with metabolic abnormalities.[7]
Secondary osteoarthritis[edit | edit source]
Secondary osteoarthritis is caused by predisposing anatomic abnormalities such as developmental or congenital deformities.[6][8]
Risk factors[edit | edit source]
- Previous hip trauma (causing injury or fracture) - mostly resulting in unilateral hip osteoarthritis
- Primary inflammatory arthritis (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis)
- Joint morphology
- Genetics
- Congenital and developmental hip disease (e.g. congenital hip dislocation, Perthe's disease, slipped upper femoral epiphysis, developmental hip dysplasia)
- Subchondral bone defects
- Obesity - mostly resulting in bilateral hip osteoarthritis
- Occupation causing excessive strain on hips (e.g. manual labor causing repeated loading)
- Increase in age
- Gender (female > male)
- Sport (higher impact sport at a younger age can cause increase in articular cartilage strength, where low impact sport do not change the composition of the cartilage)
- Menopause
- Metabolic diseases and acromegaly
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Femoroacetabular impingement
- Avascular necrosis
- Ethnicity - 80-90% less prevalent in the Asian population when compared to the Caucasian population in the USA
- Diet - low Vitamin D, C and K levels
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Signs & symptoms:[10][11][12][13]
- Pain:
- Progressively increasing
- Aggravated - movement; when hip is loaded wrong or too long; cold weather
- Eased with continuous movement
- Commonly in groin/thigh, radiating to buttocks or knee
- End-stage: Constant pain, night pain
- Stiffness:
- Morning stiffness with end-stage osteoarthritis, usually eased with movement (<1 hour)
- "Locking" of hip movement
- Decreased range of motion - leading to joint contractures and muscle atrophy
- Crepitis with movement
- Gait abnormalities - short limb gait, antalgic gait, trendelenburg gait, stiff hip gait
- Leg length discrepancy
- Local inflammation
Differential diagnosis[14][edit | edit source]
- Muscle contusion
- Muscle strains - gluteus and adductors
- Athletic pubalgia
- Piriformis syndrome
- Hamstring syndrome
- Inflammatory disorders
- Snapping hip syndrome
- Hip bursitis
- Arthritis
- Septic arthritis of the hip
- Avascular necrosis
- Labral tears
- Hip fractures
- Hip dislocations
- Tumors
- Chondral defect
- Ligamentus teres injury
- Sciatica
- Nerve irritation (especially obturator & lateral femoral cutaneous)
- Joint capsule disorders
- Inguinal ligament strain
Diagnostic procedures[edit | edit source]
Hip osteoarthritis can be diagnosed by a combination of the findings from a history and physical examination. The most used criteria in the diagnosis of hip osteoarthritis are those from the
American College of Rheumatology:.[1][15]
Clinical criteria A
- Hip pain
- Hip internal rotation <15°
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) ≤45mm/h OR hip flexion ≤115° if ESR not available
Clinical criteria B
- Hip pain
- Pain with hip internal rotation
- Morning stiffness ≤1 hour
- >50 years
Clinical plus radiographic criteria
- Hip pain
- Two of the following:
- ESR <20mm/h
- Osteophytes on hip x-rays
- Joint space narrowing on x-rays
Sutlive et al. published a list of variables for detecting hip osteoarthritis in patients with unilateral hip pain. If there are 3/5 variables present, the chance of having OA is 68%. With 4-5/5 the chance increases to 91%. The variables are positive when there’s pain or a limited range of motion in the tests.[16] The five variables are:
- Flexion
- Internal rotation
- Scour test: external and internal rotation in abduction and adduction of the hip.
- Patrick’s or FABER test: flexion,abduction and external rotation of the hip.
- Hip flexion test [17]
Physical examination[edit | edit source]
A consultation with an orthopaedic surgeon would include the following:[10][11][12] (Also see the page for hip examination)
- Observation
- Subjective interview:
- Complaints of pain, deformity, stiffness and/or limp
- Previous history linked to hip pain (congenital or childhood problems, previous trauma)
- Physical examination:
- Standing
- Trendelenberg test
- Gait
- Supine (including leg length)
- Objective observation (posture, deformities, muscle atrophy)
- Palpation:
- Tenderness at the hip
- Pain and sensitivity over greater trochanter
- Range of motion:
- Early signs of hip osteoarthritis is limited abduction and rotation. As the disease progresses, flexion, extension and adduction becomes more difficult.
- Normally painful at end of available range of motion
- Crepitis with movement
Special investigations[edit | edit source]
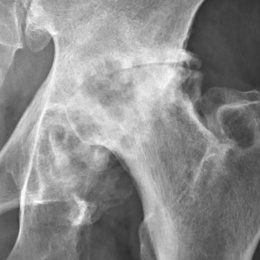
Hip osteoarthritis can be diagnosed by clinical presentation only, but special investigation (e.g. x-rays) are vital to monitor the progression of the disease.
- X-rays: Findings include joint space narrowing, marginal osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, and bone cysts.[18] This is normally the first investigation done that aids in the diagnosis of hip osteoarthritis.
- MRI: More effective in detecting early change in the bone structure, such as focal cartilage defects and bone marrow lesions in the subchondral bone.[15]
- CT scan
- Bone scan: Aids in assessing the condition of soft tissue and bone of the hip
Outcome measures[edit | edit source]
- Patient acceptable symptom state (PASS)
- Visual analogue scale (VAS)
- Hip disability and osteoarthritis outcome score (HOOS)
- Western Ontario and McMaster universities osteoarthritis index (WOMAC)
- Harris hip score
- Oxford hip score (OHS)
- Algofunctional index (AFI)
- Intermittent and constant osteoarthritis pain index (ICOAP)
- Lequesne index
- 6 Minute Walking Test
- Timed up and go test
- Patients specific complaints list (PSC)
- SF-36
- Fear Avoidance Belief Score
- International Hip Outcome Tool
- Ibadan Knee/Hip Osteoarthritis Outcome Measure
Medical management[edit | edit source]
Medical management of hip osteoarthritis focuses on treating the symptoms. Effective disease-modifying interventions have not been estabilished yet, thus a major focus should be on primary prevention strategies.[1] The optimal management of hip osteoarthritis consists of a combination of pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical treatment modalities. It is also important to take the patient's wishes and expectations into consideration.
Primary prevention[edit | edit source]
- Patient education - especially in primary health care
- Muscle strengthening
- Joint preserving surgery prior to onset of hip osteoarthritis/early in disease process
- Modification of risk factors:
- Weight control
- Switching from high-impact to low-impact activities
- Minimization of pain aggravating activities
Pharmacological management[edit | edit source]
- Symptom-relief drugs:
- Treatment of choice: Paracetamol
- NSAIDs:
- Low doses and duration due to side effects
- To be used for patients not responding well to paracetamol
- Patients with high risk of developing gastrointestinal side effects: Non-selective NSAID together with a gastroprotective agent OR selective COX-r inhibitor
- Duloxetine - works on central nervous system to inhibit pain
- Opioids:
- Tramadol (non-narcotic opioid)
- Can be used in combination with paracetamol
- Alternative if not NSAIDS and COX-2 inhibitors are not effective or contraindicated
- Intra-articular injections:
- Corticosteroids
- Consider when patients are having flare-ups and is not responding to paracetamol and NSAIDs.
- Platelet-rich plasma (evidence still lacking)
- Corticosteroids
- Hyaluronic acid - Evidence still lacking for effectiveness in the management of hip osteoarthritis
- Disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs (research on this topic still ongoing)
Surgical intervention[edit | edit source]
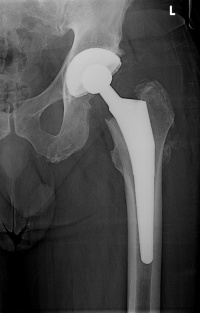
Total hip replacement[edit | edit source]
90% of total hip replacements are done as a result of end-stage hip osteoarthritis. It is a successful orthopaedic procedure in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis, when conservative management has failed and is highly effective at relieving symptoms.
Hip resurfacing[edit | edit source]
This is normally done for the younger, more active population with painful dysplasia and deformities.
Hip osteotomy[edit | edit source]
An osteotomy is preformed to realign the hip joint to lessen pressure. This is not a common in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Joint preserving surgery[edit | edit source]
- Arthroscopic debridement
- Surgical dislocation with offset reconstruction
Physiotherapy management[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy plays in major role in the management of patients with hip osteoarthritis, with special focus on pain management and functional adaptions. Patient-specific exercise programmes has shown to decrease pain and improve function in hip osteoarthritis.[1][15] A biopsychosocial approach to the management of hip osteoarthritis leads to patients experiencing less anxiety, even though the condition may not always improve.[15] It is important to consider the rest of the multidisciplinary team as well. Dietitians, occupational therapists and psychologists can play an important part in the management of hip osteoarthritis.
Education[edit | edit source]
- Pathology and disease process
- Role of physiotherapy and expected outcomes of physiotherapy interventions
- Importance of weight reduction (combination of diet and exercise)
- Self-management of pain:
- Use of modalities such as heat and ice
- Relaxation techniques
- Coping strategies
- Exercise
Assistive devices[edit | edit source]
Mobility assistive devices like walking sticks/canes, crutches, or walking frames can improve mobility and independence of the patient. Occupational therapy also plays a role here, as they often also assists the patients with functional assistive devices like a long-handled reacher to pick up low-lying things, which will helps to avoid movements that may cause pain.
Exercise therapy[edit | edit source]
Exercise therapy is an effective treatment modality for hip osteoarthrosis.[15] Specific exercises can increase range of motion and flexibility, as well as strengthen the muscles of the hip and leg. Physiotherapists work together with the patient to develop an individualized, customized exercise program that meets the needs and lifestyle of the patient.[15][19] The benefits of exercise can assist the patients in their self-management of hip osteoarthritis.
Hydrotherapy is effective in the management of hip osteoarthritis. The combination of buoyancy and the reduction of gravity greatly assists patients that are struggling to weight-bear as a result of the pain from the hip osteoarthritis.[19]
A study on a 6 week education and exercise programme has shown significant and sustained improvements in pain and disability on patients wait-listed for joint replacement surgery. Further positive results included improvements in function, knowledge and psycho-social aspects.[20] Clinical trials further suggest that it can postpone the need of total hip replacement surgery.[19]
Manual therapy[edit | edit source]
A range of manual therapies is used in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis:[15]
- Soft tissue techniques and stretches
- Mobilization of accessory and physiological movements
- Manipulation
Research is inconclusive on the effect of manual therapy in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis.[1] The immediate effect of a manual therapy, specifically joint mobilization decrease pain and improve hip range of motion, especially in the elderly population. Joint mobilization might reduce pain, might ‘provide a stretching effect on the joint capsules and muscles, thus restoring normal arthrokinematics or may induce pain inhibition and improved motor control’ and might reduce kinesiophobia.[21]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Patient workbook on "living with osteoarthritis"
Clinical bottom line[edit | edit source]
Management of hip osteoarthritis varies according to the severity of the condition. A combination of pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical modalities is recommended for the optimal management of the condition. Physiotherapy plays an important role in customized exercise programmes for patients living with hip osteoarthritis.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Murphy NJ, Eyles JP, Hunter DJ. Hip osteoarthritis: Etiopathogenesis and implications for management. Advances in therapy 2016;33(11):1921-46.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cooper C, Javaid MK, Arden N. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. In: Atlas of Osteoarthritis. Tarporley: Springer Healthcare, 2014. p22.
- ↑ Cross M, Smith E, Hoy, Nolte S, Ackerman I, Fransen M, Bridgett L, Williams S, Guillemin F, Hill CL, Laslett LL, Jones G, Cicuttini F, Osborne R, Vos T, Buchbinder R, Woolf A, March L. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2014;73:1323-1330.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Nüesch E, Dieppe P, Reichenbach S, Williams S, Iff S, Jüni P. All cause and disease specific mortality in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis: population based cohort study. Bmj 2011;342:1165.
- ↑ Cimmino MA, Sarzi-Puttini P, Scarpa R, Caporali R, Parazzini F, Zaninelli A, Marcolongo R. Clinical presentation of osteoarthritis in general practice: determinants of pain in Italian patients in the AMICA study. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism 2005;35(1):17-23).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ganz R, Leunig M, Leunig-Ganz K, Harris WH. The etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2008;466(2):264-72.
- ↑ Harris WH. Etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1986; 213:20-33.
- ↑ Hoaglund FT, Steinbach LS. Primary osteoarthritis of the hip: Etiology and epidemiology. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2001;9(5):320-7.
- ↑ Reginister J-Y, Pelletier J-P, Martel-Pelletier J, Henrotin Y, editors. Osteoarthritis: Clinical and experimental aspects. Berlin: Springer, 1999.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Diseases and conditions: Osteoarthritis of the hip.https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/osteoarthritis-of-the-hip (accessed 14/07/2018).
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Crielaard JM, Dequeker J, Famaey JP, Franchimong P, Gritten CH., Huaux JP. Osteoartrose. Brussels: Drukkerij Lichtert, 1985.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Walters J, editor. Orthopaedics - A guide for practitioners. 4th Edition. Cape Town: University of Cape Town, 2010.
- ↑ Kim C, Nevitt MC, Niu J, Clancy MM, Lane NE, Link TM, Vlad S, Tolstykh I, Jungmann PM, Felson DT, Guermazi A.. Association of hip pain with radiographic evidence of hip osteoarthritis: Diagnostic test study. BMJ. 2015;351:5983.
- ↑ Fernandez M, Wall P, O’Donnell J, Griffin D. Hip pain in young adults. Aust Fam Physician. 2014;43(4):205–9.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 Bennell K. Physiotherapy management of hip osteoarthritis. J Physiother. 2013; 59(3):145–157.
- ↑ Sutlive TG, Lopez HP, Schnitker DE, Yawn SE, Halle RJ, Mansfield LT et al. Development of a clinical prediction rule for diagnosing hip osteoarthritis in individuals with unilateral hip pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(9):542-50.
- ↑ Physiotutors. Cluster of Sutlive | Hip Osteoarthritis Diagnostic Cluster. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8xrDWgIUMO4
- ↑ Brandt CD. Diagnosis and non-surgical management of osteoarthritis. USA: Professional Communications, Inc. 2010.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 19.5 Zhang W, Doherty M, Arden N, Bannwarth B, Bijlsma J, Gunther KP, Hauselmann HJ, Herrero-Beaumont G, Jordan K, Kaklamanis P, Leeb B. EULAR evidence based recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis: Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Annals of the rheumatic diseases 2005;64(5):669-81.
- ↑ Saw MM. The effects of a six-week physiotherapist-led exercise and education intervention in patients with osteoarthritis, awaiting an arthroplasty in the South Africa [dissertation]. Cape Town: University of Cape Town. 2015.
- ↑ Beselga C, Neto F, Alburquerque-Sendín F, Hall T, Oliveira-Campelo N. Immediate effects of hip mobilization with movement in patients with hip osteoarthritis: A randomised controlled trial. Man Ther. 2016;22:80-5.