Child Development
Original Editor - The Open Physio project.
Top Contributors - Naomi O'Reilly, Siobhán Cullen, Admin, Chelsea Mclene, Kim Jackson, Oyemi Sillo, Lucinda hampton, Tony Lowe, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Lauren Kwant, 127.0.0.1, WikiSysop, Claire Knott, Rucha Gadgil, Amrita Patro, Jess Bell, Rachael Lowe, Olajumoke Ogunleye, Paule Morbois, Matt Huey, Scott Buxton and Saeed Dokhnan
Introduction[edit | edit source]
As a child grows, they learn and acquire more refined gross and fine motor skills, as well as developing social and emotional skills. As the child matures, primitive reflexes that are initially developed to aid survival, become integrated into more refined movements. Children tend to acquire these skills in an orderly fashion and within certain age brackets. This pattern of skill acquisition, often referred to as "Typical Development", is used to monitor a child's developmental progress. In some cases late acquisition of these 'milestones' can indicate developmental delay. However, it must be remembered that the time span within which acquisition of these skills are still considered 'typical', are wide [1], and that some children may skip a milestone altogether. (eg. crawling)[2]
The average age at which gross motor, fine motor and social skills are acquired is outlined below.
Principles of Typical Development[edit | edit source]
- Cranial to Caudal
- Proximal to Distal
- Flexion to Extension
- Asymmetry - Symmetry - Asymmetry
- Gross to Fine; Simple to Complex
- Global Patterns in 3 Planes (Frontal, Sagittal, Transverse) [3]
Typical Development Global Patterns & Positions[edit | edit source]
0 - 2 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2 Month Milestone Checklist here.
|
Asymmetry and Flexion Period. Physiological Flexion. Mass Movements. Slight intentioned movements of the head in prone and supine. In supine there are large movements of the upper limbs. In prone activities are limited to the lifting and turning of the head to breathe. Slight increase of extensor muscles control head / neck. The baby is more alert, begins to respond to the environment. MORO Primitive Reflex Active. ATNR Present. |
[4]
2 Month Milestone: Makes Smoother Movements with Arms and Legs. |
| SUPINE | PRONE |
|
Functional Achievement: Slight movements in rotation of the head + lateral flexion of the trunk when trying to move the head, gesture, stare at the mother. Posture: Head Position:
Trunk Position:
Upper Limbs:
Pelvic Girdle:
Lower Limbs:
|
Functional Achievement: Raises head less than 45°, pushes the floor with the fists trying to lift head against gravity and against the resistance of spinal and hip that remain in flexion. Weightbearing: On cheek, hands, forearms and upper chest. Posture: Head Position:
Upper Limbs:
Trunk Position:
Pelvic Girdle:
Lower Limbs:
|
3 Months[edit | edit source]
|
Symmetry Begins. (Control of Bilateral Neck Muscles) Begins orientation to the midline of head. The Tonic Grasp Reflex is gone so can play with hands; hand-hand coordination and hand-eye coordination begins. Increase of Extension. TACR and MORO decreased or disappear. Increased visual control independent from the head also can do visual tracking of 180 degrees of rotation of head to follow an object. | |
| SUPINE | PRONE |
|
Functional or Antigravity Achievement: Stares and visual tracking. Head control and maintains in midline. Coordination between; hands-mouth, hand-hand and feet-feet these are up of the plane of support. Immature kicking. Posture: Head Position:
Upper Limbs:
Trunk Position:
Pelvic Girdle:
Lower Limbs:
|
Antigravity Movement: Pushes against surface to raise head at least 45°. Chest elevated. Weightbearing: Symmetrically distributed on forearms (epitroclea and hands) and abdomen. Posture: Head Position:
Upper Limbs:
Trunk Position:
Pelvic Girdle:
Lower Limbs:
|
4 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 4 Month Milestone Checklist here.
|
Development of Sagittal Plane. Strong symmetry, flexion and extension increased; Beginning of Landau Reaction in Extension. Strong synergy between flexor and extensor muscles of the neck, chin in more retraction. Begins gripping feature, can hold an object but loose it by chance. Lateral rocking. Able to remove a blanket from the face with both hands |
[5]
Brings Hands to Mouth |
| SUPINE | PRONE |
|
Antigravity Movement:
|
Weightbearing:
Antigravity Movement:
|
5 Months[edit | edit source]
| Good lateral weight transfer, symmetry enables coordination between both sides. Increased Landau Reaction. Swimming Position. Important manipulative strategies in supine. | |
| SUPINE | PRONE |
|
Antigravity Movement: Touches knees with hands, choosing to do it both hands at the same time or independence one from the other. Grasp and manipulate in the midline staring the toy. Gripping still from the ulnar side of the hand, with palmar flexion and supination to explore the toy with mouth. |
Antigravity Movement: Chin tucked and chest elevated. Flexion and extension of knees, may play with feet together, lateral weight shift to wrap with the opposite hand. The infant may also push backward in this position. Weightbearing: Weight on hands, lower abdomen and thighs. Triangle base of support between nape elbow and thigh and face knee. Uses this base of support to liberate the face arm and wrap a toy with more stability. |
6 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 6 Month Milestone Checklist here.
|
[6]
Rolls Over in Both Directions Front to Back, Back to Front |
[7]
When Standing, Supports Weight on Legs and Might Bounce |
[8]
Rocks Back and Forth, Sometimes Crawling Backward before Moving Forward |
| SUPINE | PRONE | PIVOTING |
|
Antigravity Movement: Eyes-feet-hands coordination, rolls from supine to prone. Movement initiated by shoulder, pelvis or head. Posture during Rolling:
Upper Limbs:
Trunk Position:
Pelvic Girdle:
Lower Limbs:
Weightbearing in Rolling:
|
Antigravity Movement: Swimming posture. Active weight shift to one side and grasp with the other hand. Weightbearing: Weight on one forearm or open hands, and distal thigh. Posture: Head Position:
Upper Limbs:
Pelvic Girdle:
Lower Limbs:
|
Weightbearing: Weight on trunk, arms and hands. Posture: Head Position:
Antigravity Movement Pivots:
|
7 Months[edit | edit source]
|
Supporting legs on hands and knees (four legs) Comando creeping Lateral sitting Can pass one object from one hand to the other Can take one object in each hand Answers to name Starts eating some solid food | |
| SUPINE | PRONE |
|
Antigravity Movements:
|
Antigravity Movements:
|
8 Months[edit | edit source]
| |
| PRONE | |
|
Antigravity Movements:
| |
9 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 9 Month Milestone Checklist here.
|
Pulling with the arms can stand starting from a kneeling position. Will remain standing only a few seconds. Mature Crawling. Bisyllables “Papa”, Tata” Waves “Bye, Bye” with hand | |
|
[9]
Can get into Sitting Position. |
[10]
Crawls. |
10 - 12 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 12 Month Milestone Checklist here.
| [11]
Makes side/lateral walking supported by hand on a table. Stands alone. |
[12]
May Take a Few Steps without Holding On. |
12 - 18 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 18 Month Milestone Checklist here.
|
Walks Autonomously. Squat Position. | |
|
[13]
Walks Alone. |
[14]
May Walk Up Steps and Run. |
|
[15]
Pulls Toys While Walking. |
[16]
Can Help Undress Herself. |
18 - 24 Months[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 24 Month Milestone Checklist here.
|
Runs, walking on toes and heels. Jumping on the same spot. Walks up and down stairs with handrail. Tower of 6 bricks, turns pages of a book. Bladder Control. | |
|
[17]
Begins to Run. |
[18]
Makes or Copies Straight Lines and Circles. |
3 Years[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 3 Year Milestone Checklist here.
|
Pedal Tricycle. One Leg Standing. Uses Scissors. Uses Spoon and Fork. | ||
|
[19]
Runs Easily. |
[20]
Takes Turns in Games. | |
5 Years[edit | edit source]
You can download the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 5 Year Milestone Checklist here.
Walk in a High Narrow Line.
|
[21]
Stands on One Foot for 10 Seconds or Longer. |
[22]
Hops; May be able to Skip. | |
Gross Motor Activities[edit | edit source]
|
Activity |
Age |
| Lifts head to 45° | 2/12 |
| Props on forearms in prone | 3/12 |
| Rolls over | 5/12 |
| Prone on extended arms | 6/12 |
| Balance reactions | 6/12 |
| No Head lag | 5/12 |
| Sitting without support | 6-8/12 |
| Pulls to stand | 8-9/12 |
| Cruises | 8-9/12 |
| Crawls reciprocally | 9/12 |
| Stands alone | 11/12 |
| Walks alone | 12/12 |
| Runs | 18-24/12 |
| Walks up and down stairs with handrail | 2 yrs |
| Pedals tricycle | 3 yrs |
| Walks narrow line | 5 yrs |
Fine Motor Skills[edit | edit source]
|
Activity |
Age |
| Follows objects with eyes | 1-2/12 |
| Grasps objects | 4/12 |
| Hand to hand transfers | 5/12 |
| Finger feeds | 6/12 |
| Objects into container | 12/12 |
| Builds 2 block tower | 14/12 |
| Helps with dressing | 15/12 |
| Builds 6-7 cube tower | 2 yrs |
| Uses fork and spoon skilfully | 2.5 yrs |
| Holds pencil with adult grasp | 4 yrs |
| Colours inside lines | 5 yrs |
Social Skills[edit | edit source]
| Activity/Interaction | Age |
| Smiles when stimulated | 1/12 |
| Vocalises to self | 6/12 |
| Plays peek-a-boo | 8/12 |
| Stranger anxiety | 8/12 |
| Drinks from cup | 12/12 |
| Uses spoon | 13/12 |
| 2-6 words | 15/12 |
| Feeds self fully | 2 yrs |
| Bladder and bowel control | 2 yrs |
| Has 50+ words, understands 1000+ | 2 yrs |
| Undresses | 2.5 yrs |
| Gramatically correct speech | 4 yrs |
| Fluent | 5 yrs |
Age Ranges of Skill Acquisition[edit | edit source]
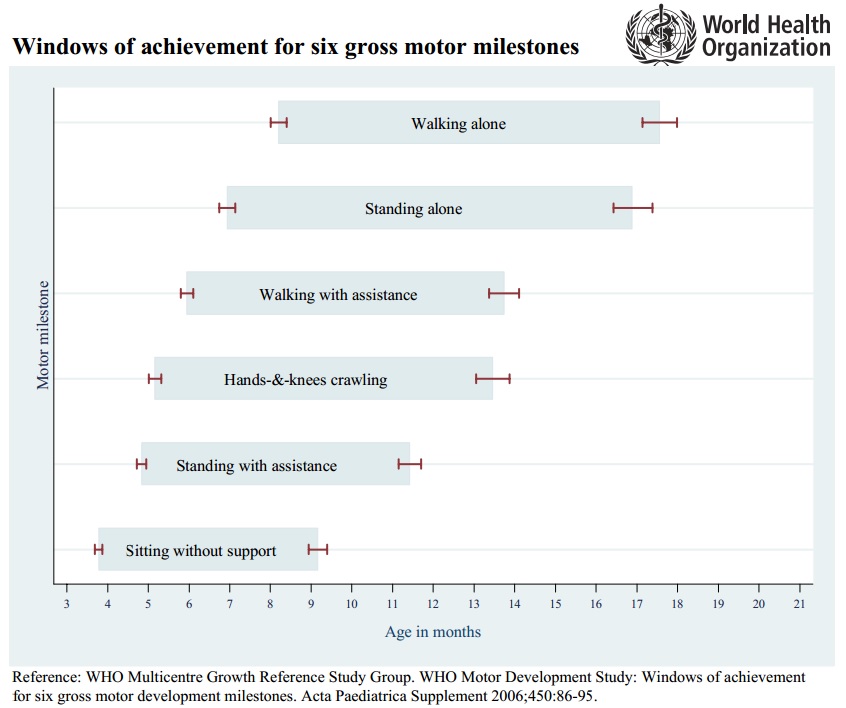
While motor milestones are undoubtedly a useful way of monitoring a child's development, it must be remembered that each child is different and will achieve the various milestones at different rates. There is a wide window for achievement of these milestones, during which achievement of the milestone is still considered to be in line with normal development. A study published by the World Health Organization in 2006 demonstrates just this. This study recorded the variations in milestone achievement in 816 children and generated windows during which achievements of these milestones is considered to be normal development, these are outlined in the table below. It should also be noted that this study found that 4.3% of participants never exhibited the hands and knees crawling milestone. [1]
Primitive Reflexes[edit | edit source]
The primitive reflexes are movement patterns that can be involuntarily elicited in a newborn. They exist to enhance chances of survival. These reflexes should be integrated as the child's motor development matures. The persistence of these reflexes beyond the usual ages of integration is suggestive of ischemic brain injury. Below several of the primitive reflexes, their appearance and integration dates are discussed.
Rooting Reflex[edit | edit source]
The rooting reflex can be elicited by gently stroking the child's cheek. The reflex is intact if the child's response is to attempt to bring the object to their mouth.[26] This is demonstrated in the video below.
Age of Integration: 3-4 months
Palmar Grasp[edit | edit source]
This reflex can be elicited by stimulating the palmar surface of the child's hand. The reflex is intact if the child reflexively grasps the object stimulating the palm[26]. Both this and the plantar grasp reflex are seen in the next video clip.
Age of Integration: 4 Months [28]
Plantar Grasp[edit | edit source]
This reflex is elicited by stimulating the plantar aspect of the child's foot, just below the toes. The reflex is intact if this causes toe flexion.
Age of Integration: 9 Months [28]
Moro:[edit | edit source]
The Moro reflex is typically elicited by rapid extension of the child's neck. However it can also occur in response to loud noises. The reflex is intact if the child symmetrically and simultaneously abducts and extends the upper limbs, and extends the trunk. The upper limbs then immediately adduct[26]. This reflex is demonstrated in the clip below.
Age of Integration: 3 - 6 Months [28]
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR)[edit | edit source]
This reflex is elicited by turning the child's head to one side. A normal response is seen if the baby's extensor tone increases on the side the head is facing, and flexor tone increases on the opposite side.[26] This is demonstrated in the clip below.
Age of Integration: 6 Months[28]
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. ‘WHO Motor Development Study: Windows of achievement for six gross motor milestones’. Acta Paediatrica. 2006: Suppl 450; 86-95.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Piper MC. Motor Assessment of the Developing Infant. WB Saunders Company; 1994.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Stamer MH. Posture and movement of the child with cerebral palsy. 2015.
- ↑ Boystown Hospital Your Baby at 2 Months - Boys Town Pediatrics Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DyfAsyPzcqQ (last accessed 5.11.2019)
- ↑ All About Kids - 4 Months Developmental Milestone - Brings Hands to Mouth. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QmbVMBzmOxw[last accessed 16/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 6 Month Developmental Milestone: Rolls Over in Both Directions. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JCaRhaVa9ag [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 6 Month Developmental Milestone: When Standing, Supports Weight on Legs and Might Bounce. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mJ5iQvo21gg [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 6 Month Developmental Milestone: Rocks Back and Forth. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=21R8sfKcBB4 [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 9 Month Developmental Milestone - Can get into sitting position. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2ziOzwPxB04 [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 9 Month Developmental Milestone - Crawls. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WnpDAS1baZM [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ Multicare health system Child Development: Your Baby at 12 Months Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kX6u5TtCdvE (last accessed 5.11.2019)
- ↑ All About Kids - 1 Year Developmental Milestone - May Take a Few Steps without Holding On. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uF868EjMOkg [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 18 Month Developmental Milestone - Walks Alone. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=svEsKRr0fXI [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 18 Month Developmental Milestone - May Walk Up Steps. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QwQlEY3JMws [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 18 Month Developmental Milestone - Pulls Toys While Walking https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=omlXVQawO88 [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 18 Month Developmental Milestone - Can Help Undress Herself. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8kpwwsg-dmI [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 24 Month Developmental Milestone - Begins to Run. https://youtu.be/UYJs3xeeGyw [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 24 Month Developmental Milestone - Makes or Copies Straight Lines and Circles. https://youtu.be/awgzy2_0p1E [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 3 Year Developmental Milestone - Runs Easily. https://youtu.be/L-HqbAbuu5I [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 3 Year Developmental Milestone - Takes Turns in Games. https://youtu.be/spnLFau1FKw [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 5 Year Developmental Milestone - Stands on One Foot for 10 Seconds or Longer. https://youtu.be/8UefHBk6yq4 [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ All About Kids - 5 Year Developmental Milestone - Hops; May be able to Skip. https://youtu.be/bdt0Nk_Ur4U [last accessed 24/11/22]
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Bly L. Motor skills acquisition in the first year: An illustrated guide to normal development. ed. 1. Great Britain: Elsevier Science & Technology books, 1998.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Sheridan M. D. Sharma A. and Cockerill H. From birth to five years. ed. 3. London: Routledge, 2008.
- ↑ World Health Organization Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. ‘WHO Motor Development Study: Windows of Achievement for Six Gross Motor Milestones’. Acta Paediatrica. 2006: Suppl 450; 86-95.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC and Nowalk AJ. 2012. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. Ed. 6. Philadelphia: Elsevier
- ↑ sapnachakraborty Rooting reflex Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xneStHZ0Kho (last accessed 5.11.2019)
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 28.3 Votroubek W. 2009. Pediatric Home Care for Nurses: A Family-Centred Approach. Ed. 3. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett Pblishers Inc.
- ↑ onlinemedicalvideo. Physical exam-Newborn normal: Primitive reflexes-grasp. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BF1j1PXRq-I [last accessed: 17/06/13]
- ↑ qumar81 Moro reflex Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTz-iVI2mf4 (last accessed 5.11.2019)
- ↑ betapics ATN reflex Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dPyBzlD-854 (last accessed 5.11.2019)






