Brainstem
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Lucinda hampton, Olajumoke Ogunleye, Pacifique Dusabeyezu, Evan Thomas, Wendy Walker, Kim Jackson, Garima Gedamkar, Aya Alhindi, WikiSysop, Tarina van der Stockt, Daniele Barilla and Carina Therese Magtibay
Description[edit | edit source]
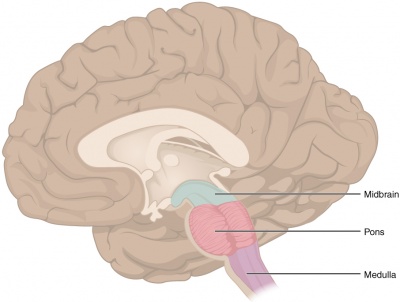
The Brainstem lies at the base of the brain and the top of the spinal cord. It houses many of the control centres for vital body functions, such as swallowing, breathing, and vasomotor control. The 3 structures of the brainstem are coloured in diagram to right.
Structure[edit | edit source]
The brainstem is generally said to be composed of three parts.
Components, from above downward:
- Midbrain (or Mesencephalon)
- Pons (part of the metencephalon)
- Medulla AKA Medulla Oblongata (myelencephalon)
Midbrain:[edit | edit source]
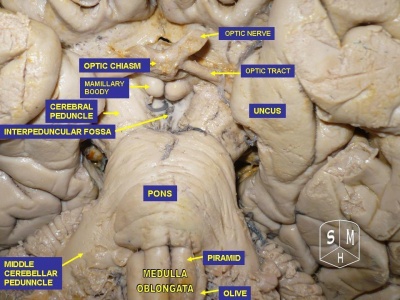
This consists of 3 parts: the tectum, the tegmentum and paired cerebral peduncles. These peduncles are the anterior part of the midbrain that connects the remainder of the brainstem to the thalami. They are paired, separated by the interpeduncular cistern, and contain the large white matter tracts that run to and from the cerebrum[1].The substantia nigra lies in the cerebral peduncles.
Pons:[edit | edit source]
Consists of a posterior part, the tegmentum, and an anterior basilar part.
Medulla:[edit | edit source]
The "bulb" is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata, and in modern clinical usage the word bulbar (e.g. bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves and tracts connected to the medulla, and also by association to the muscles thus innervated, such as those of the tongue, pharynx and larynx.[2]
Anatomical Relations[edit | edit source]
The brainstem is located in posterior cranial fossa[3].
Above, the midbrain is continuous with the cerebral hemisphere.
Below, the medulla is continuous with the spinal cord.
Posteriorly, the pons and medulla are separated from the cerebellum by the fourth ventricle.
Function[edit | edit source]
The brainstem has three broad functions:
1. Serves as a conduit for the ascending tracts and descending tracts connecting the spinal cord to the different parts of the higher centres in the forebrain
2. Contains important reflex centres associated with the control of:
- respiration
- cardiovascular system
- consciousness
3. Contains the nuclei of Cranial Nerves III to XII.
The brain stem is responsible for, and regulatory of, the following functions of the human body:
- Alertness
- Attention
- Arousal
- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Conveys information and signals shared between the peripheral nerves and spinal cord to the upper brain
- Other autonomic functions such as digestion, salivation, perspiration, dilation or contraction of the pupils, urination, etc.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
A Stroke affecting the brainstem can cause severe symptoms which include:
- Problems with vital functions, such as breathing - frequently resulting in death
- Difficulty with chewing, swallowing, and speaking
- Weakness or paralysis in the arms, legs, and/or face
- Problems with balance or sensation
- Hearing loss
- Vision problems
- Vertigo
- Locked-in Syndrome
- Coma [4]
The 9 minute video below gives a good summary of brainstem and stroke
Brainstem lesions frequently occur in Multiple Sclerosis, with visual problems including blurred double vision being a common early symptom of MS.
Central pontine myelinolysis is a concentrated, frequently symmetric, noninflammatory demyelination within the pons.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Cerebral Peduncles Radiopedia Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/cerebral-peduncles (last accessed 28.11.2019)
- ↑ World Heritage Encyclopedia. Medulla Oblungata. http://www.ebooklibrary.org/Articles/Medulla%20oblongata?&Words=Medulla (accessed 8 april 2017)
- ↑ Nolte J. The Human Brain. 3rd. St. Louis, Missouri: Mosby Year Book; 1993
- ↑ Brain Injury Explanation. http://www.braininjury-explanation.com/consequences/impact-by-brain-area/brainstem (accessed 8 april 2017)
- ↑ Soton brain hub Brainstem Stroke Syndromes Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qxiRfP9XmpE (last accessed 28.11.2019)