Behavioral problems in children
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Redisha Jakibanjar, Lucinda hampton and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Behavioral problems don't have the exact definition They are behaviors that contradict to specific age, culture, social values and norms. According to Achenbach et al. behavioral problems can be categorized into “Internalizing” and “Externalizing”.[1]
Internalizing behavioral problem[edit | edit source]
Behavioral problems that are directed from internal like, anxiety, sadness, depression, complaining of somatic pains frequently, some specific phobias. Internalizing behavioral problems are common among girls.
Externalizing behavioral problem[edit | edit source]
Behavioral problems that are directed from external and are expressed in actions like, being angry,violence, overactive, attention problems. These problems are common boys.[2][3]
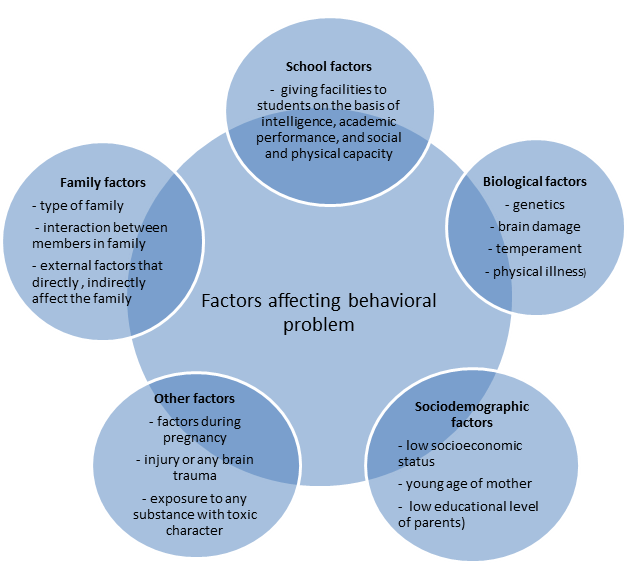
Factors affecting the behavioral problem in children[2][3][edit | edit source]
Consequences of behavioral problems[edit | edit source]
Internalization and externalization disorders in early life constantly show externalizing and internalizing problems in later life if left untreated. The behavioral problems affect the mental health of a child.
Good behavior is the sign of good mental health whereas the problem in mental health leads to aggressive behavior, anxiety, stress, restless and decreased self-esteem.
Mental health of a child has direct impact on cognitive, social and learning development.[2]
Early identification and intervention of behavioral problem[edit | edit source]
Early detection is the important path for the early intervention of the problem.
Early intervention can improve the QOL of the individual and decrease burden created to family society and nation.
Behavioral problem can be identified in preschool age group and the period around the transition to school has been identified as a particularly effective time to intervene for the behavioral problem.
Early intervention programs for individuals with early signs of mental problem have been highlighted as crucial and effective strategies to prevent development of mental disorders[3].[4]
Some of the outcome tools for detecting behavioral problem are:
- Adaptive Behavior Assessment System (ABAS) Infant and Preschool
- Child Behavioral Checklist (CBCL)
- Rutter Questionnaire
- Conner’s Teacher Rating Scale
- Brief Infant-Toddler Social and Emotional Assessment
- Toddler Behavior Screening Inventory
- Strength and Difficulty Questionnaire
- Student Risk Screening Scale (SRSS)
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Achenbach TM, Edelbrock CS. The Child Behavior Profile: II. Boys Aged 12-16 and Girls Aged 6-11 and 12-16. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1979;47:223-33.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Santos LM, Queiros FC, Barreto ML, Santos DN. Prevalence of behavior problems and associated factors in preschool children from the city of Salvador, state of Bahia, Brazil. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2016;38(1):46-52
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Jetishi P. Evaluation Of Emotional And Behavioral Problems In Preschool Children Aged 2-5, In The City Of Pristina. European International Virtual Congress of Researchers. 2016:25-34
- ↑ Reid K, Littlefield L, Hammond SW. Early intervention for preschoolers with behaviour problems: Preliminary findings for the Exploring Together Preschool Program. Australian e-Journal for the Advancement of Mental Health (AeJAMH),. 2008;7(1):1-15.