Ankle Joint: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Naomi O'Reilly|Naomi O'Reilly]] | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Naomi O'Reilly|Naomi O'Reilly]] | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
The Ankle Joint, also known as the Talocrural Articulation, is a synovial hinge joint connecting the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus. The ankle joint is maintained by the shape of the talus and its tight fit between the tibia and fibula. In the neutral position, there are strong bony constraints. With increasing plantar flexion, the bony constraints are decreased and the ligaments are more susceptible to strain and injury. The articulation between the tibia and the talus bears more weight than that between the smaller fibula and the talus. <ref name="Allen F. ANderson Anatomy">Allen F. Anderson Sports Medicine. Anatomy Ankle Available from: http://www.drallenfanderson.com/ankle/anatomy [last accessed 20/03/2015]</ref> | The Ankle Joint, also known as the Talocrural Articulation, is a synovial hinge joint connecting the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus. The ankle joint is maintained by the shape of the talus and its tight fit between the tibia and fibula. In the neutral position, there are strong bony constraints. With increasing plantar flexion, the bony constraints are decreased and the ligaments are more susceptible to strain and injury. The articulation between the tibia and the talus bears more weight than that between the smaller fibula and the talus. <ref name="Allen F. ANderson Anatomy">Allen F. Anderson Sports Medicine. Anatomy Ankle Available from: http://www.drallenfanderson.com/ankle/anatomy [last accessed 20/03/2015]</ref> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
=== Articulating Surfaces === | === Articulating Surfaces === | ||
*Trochlea of Talus | *Trochlea of Talus | ||
*Malleolar Mortis formed by Tibia & Fibula | *Malleolar Mortis formed by Tibia & Fibula | ||
*Lateral & Medial Malleolus<br> | *Lateral & Medial Malleolus<br> | ||
=== Joint Capsule | === Joint Capsule === | ||
<div align="justify"> | <div align="justify"> | ||
The articular capsule surrounds the joints, and is attached, above, to the borders of the articular surfaces of the tibia and malleoli; and below, to the talus around its upper articular surface. The joint capsule anteriorly is a broad, thin, fibrous layer, posteriorly the fibres are thin and run mainly | The articular capsule surrounds the joints, and is attached, above, to the borders of the articular surfaces of the tibia and malleoli; and below, to the talus around its upper articular surface. The joint capsule anteriorly is a broad, thin, fibrous layer, posteriorly the fibres are thin and run mainly transversely blending with the transverse ligament and laterally the capsule is thickened, and attaches to the hollow on the medial surface of the lateral malleolus. The synovial membrane extends superiorly between Tibia & Fibula as far as the Interosseous Tibiofibular Ligament.<ref name="Essential Clinical Anatomy">Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinial Anatomy. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2011.</ref> <br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
=== | === Ligaments === | ||
==== '''Lateral Ligaments of Ankle''' ==== | ==== '''Lateral Ligaments of Ankle''' ==== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 30: | ||
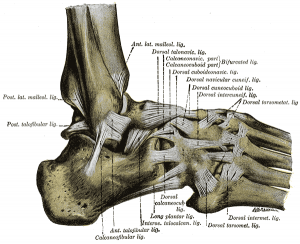
[[Image:Ankle.png|thumb|left|Lateral ligament]] | [[Image:Ankle.png|thumb|left|Lateral ligament]] | ||
Reinforce Joint Laterally through three ligaments. These ligaments stabilize the ankle, and serve as a guide to direct ankle motion by attaching the lateral malleolus to the bones below the ankle joint. They are responsible for resistance against inversion and internal rotation stress. | Reinforce Joint Laterally through three ligaments. These ligaments stabilize the ankle, and serve as a guide to direct ankle motion by attaching the lateral malleolus to the bones below the ankle joint. They are responsible for resistance against inversion and internal rotation stress. <ref name="Essential Clinical Anatomy" /> | ||
{| width="100%" border="1" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| width="100%" border="1" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
| Line 45: | Line 43: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Anterior Talofibular Ligament | Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) | ||
(ATFL) | |||
| | | | ||
Flat Weak Band that extends Anteriomedially. | Flat Weak Band that extends Anteriomedially. | ||
Most commonly damaged ligament of the ankle. | Most commonly damaged ligament of the ankle. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 59: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Posterior Talofibular Ligament | Posterior Talofibular Ligament | ||
(PTFL) | (PTFL) | ||
| Line 70: | Line 66: | ||
Thick, fairly strong band that runs horizontally medially.<br> | Thick, fairly strong band that runs horizontally medially.<br> | ||
This ligament is under greater strain in full dorsiflexion of ankle. | This ligament is under greater strain in full dorsiflexion of ankle. | ||
Rarely injured because bony stability protects ligaments when ankle in dorsiflexion. | Rarely injured because bony stability protects ligaments when ankle in dorsiflexion. | ||
| Line 79: | Line 75: | ||
Forms the back wall of the recipient socket for the talus' trochlea. | Forms the back wall of the recipient socket for the talus' trochlea. | ||
Resists posterior displacement of the talus. | Resists posterior displacement of the talus. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Calcaneofibular Ligament | Calcaneofibular Ligament (CFL) | ||
(CFL) | |||
| Round cord that passes posterioinferiorly | | Round cord that passes posterioinferiorly | ||
| Line 99: | Line 93: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==== '''Medial Ligaments of Ankle''' | ==== '''Medial Ligaments of Ankle''' ==== | ||
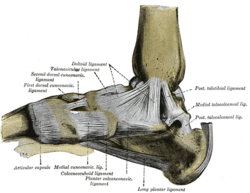
[[Image:Med ankle.png|thumb|left|Medial ligament]] | [[Image:Med ankle.png|thumb|left|Medial ligament]] | ||
Known collectively as the Deltoid Ligament the medial ligaments of the ankle attaches proximally to the Medial Malleolus and fan out to attach distally to the Talus, Calcaneus and Navicular via four adjacent and continuous parts. | Known collectively as the Deltoid Ligament the medial ligaments of the ankle attaches proximally to the Medial Malleolus and fan out to attach distally to the Talus, Calcaneus and Navicular via four adjacent and continuous parts. The deltoid ligament is triangular in shape and consists of a superficial and deep layer which connect the talus to the medial malleolus. It reinforces the joint capsule medially. Stabilise’s the ankle joint during eversion of the foot and prevents subluxation of the ankle joint. <ref name="Essential Clinical Anatomy" /><br> | ||
{| width="100%" border="1" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| width="100%" border="1" align="center" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
| Line 144: | Line 138: | ||
| | | | ||
Forms most anterior part of the | Forms most anterior part of the Deltoid Ligament | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | Dorsomedial Aspect of Navicular | | align="center" valign="middle" | Dorsomedial Aspect of Navicular | ||
| Line 161: | Line 155: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=== Muscles | === Muscles === | ||
==== Plantarflexion ==== | ==== Plantarflexion ==== | ||
Muscles which contribute to Plantarflexion | Muscles which contribute to Plantarflexion | ||
| Line 187: | Line 180: | ||
| Gastrocnemius | | Gastrocnemius | ||
| width="25%" | | | width="25%" | | ||
Plantarflexion when Knee | Plantarflexion when Knee Extended<br> | ||
Flexion Knee<br> | Flexion Knee<br> | ||
Raises Heel during | Raises Heel during Walking | ||
| | | | ||
'''Lateral Head: | '''Lateral Head:''' Lateral Aspect of Lateral Femoral Condyle | ||
''' | '''Medial Head:''' Popliteal Surface of Femur Superior to Medial Femoral Condyle | ||
| rowspan="3" align="center" valign="middle" | | | rowspan="3" align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
Posterior Surface Calcaneus | Posterior Surface Calcaneus via Calcaneal Tendon (Achilles Tendon) | ||
Calcaneal Tendon | |||
Tendon) | |||
| rowspan="3" align="center" valign="middle" | | | rowspan="3" align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
| Line 227: | Line 216: | ||
| Plantaris | | Plantaris | ||
| | | | ||
Weakly Assists | Weakly Assists Gastrocnemius in Plantarflexion | ||
| | | | ||
Inferior end Lateral Supracondylar | Inferior end Lateral Supracondylar Line of Femur <br> | ||
Oblique Popliteal Ligament | Oblique Popliteal Ligament | ||
| Line 245: | Line 234: | ||
Inversion<br> | Inversion<br> | ||
Supports Medial | Supports Medial Longitudinal Arch | ||
| | | | ||
Interosseous Membrane<br> | Interosseous Membrane<br> | ||
Posterior Surface Tibia inferior to | Posterior Surface Tibia inferior to Soleal Line <br> | ||
Posterior Surface Fibula | Posterior Surface Fibula | ||
| Line 269: | Line 258: | ||
Plantarflexion | Plantarflexion | ||
Flexion Lateral Four | Flexion Lateral Four Digits<br> | ||
Supports Longitudinal | Supports Longitudinal Arch | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 291: | Line 280: | ||
Weak Plantarflexion | Weak Plantarflexion | ||
Flexion Big Toe at all | Flexion Big Toe at all Joints <br> | ||
Supports Medial | Supports Medial Longitudinal Arch | ||
| | | | ||
Inferior 2/3 Posterior Surface Fibula<br> | Inferior 2/3 Posterior Surface Fibula<br> | ||
Inferior Part Interosseous | Inferior Part Interosseous Membrane | ||
| Base Distal Phalanx of Big Toe | | Base Distal Phalanx of Big Toe | ||
| Line 310: | Line 299: | ||
| | | | ||
Weak Plantarflexion | Weak Plantarflexion | ||
Eversion | Eversion | ||
| Line 316: | Line 305: | ||
| Inferior 2/3 of Lateral Surface Tibia | | Inferior 2/3 of Lateral Surface Tibia | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | | | align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
Dorsal Surface Tuberosity of | Dorsal Surface Tuberosity of Base | ||
5th Metatarsal | 5th Metatarsal | ||
| Line 332: | Line 321: | ||
| | | | ||
Weak Plantarflexion | Weak Plantarflexion | ||
Eversion | Eversion | ||
Supports | Supports Transverse Arch | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 369: | Line 358: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Tibialis Anterior | Tibialis Anterior | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 376: | Line 365: | ||
Inversion<br> | Inversion<br> | ||
Supports Medial | Supports Medial Longitudinal Arch | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 383: | Line 372: | ||
Superior ½ Lateral Surface Tibia<br> | Superior ½ Lateral Surface Tibia<br> | ||
Interosseous Membrane | Interosseous Membrane | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | | | align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
Medial & Inferior Surfaces | Medial & Inferior Surfaces<br> | ||
Medial Cuniform<br> | Medial Cuniform<br> | ||
Base of 1st Metatarsal | Base of 1st Metatarsal | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | | | align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
| Line 397: | Line 386: | ||
(Deep Fibular Nerve)<br> | (Deep Fibular Nerve)<br> | ||
L4-L5 | L4-L5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Extensor Digitorum | Extensor Digitorum | ||
Longus | Longus | ||
| | | | ||
Dorsiflexion | Dorsiflexion<br> | ||
Extends Lateral Four | Extends Lateral Four Digits | ||
| | | | ||
Lateral Condyle Tibia<br> | Lateral Condyle Tibia<br> | ||
Superior ¾ Anterior Surface | Superior ¾ Anterior Surface | ||
Interosseous Membrane | Interosseous Membrane | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | | | align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
Middle & Distal Phalanges of | Middle & Distal Phalanges of Lateral Four Digits | ||
Lateral Four Digits | |||
| rowspan="3" align="center" valign="middle" | | | rowspan="3" align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
| Line 433: | Line 420: | ||
Extensor Hallucis | Extensor Hallucis | ||
Longus | Longus | ||
| | | | ||
Dorsiflexion<br> | Dorsiflexion<br> | ||
Extends Big Toe | Extends Big Toe | ||
| | | | ||
Middle Part Anterior Surface Fibula<br> | Middle Part Anterior Surface Fibula<br> | ||
Interosseous Membrane | Interosseous Membrane | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | | | align="center" valign="middle" | | ||
Dorsal Aspect of Base Distal | Dorsal Aspect of Base Distal | ||
Phalanx of Big Toe | Phalanx of Big Toe | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Peroneus Tertius | Peroneus Tertius | ||
| | | | ||
Dorsiflexion<br> | Dorsiflexion<br> | ||
Aids Eversion | Aids Eversion | ||
| | | | ||
Inferior 1/3 Anterior Surface | Inferior 1/3 Anterior Surface Fibula<br> | ||
Interosseous Membrane | Interosseous Membrane | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" | Dorsum Base 5th Metatarsal | | align="center" valign="middle" | Dorsum Base 5th Metatarsal | ||
| Line 470: | Line 457: | ||
Derived from Malleolar Branches of: | Derived from Malleolar Branches of: | ||
*Peroneal Artery | *Peroneal Artery | ||
*Tibial Artery | *Tibial Artery | ||
=== Nerve Supply === | === Nerve Supply === | ||
*Common Peroneal Nerve | *Common Peroneal Nerve | ||
*Tibial Nerve | *Tibial Nerve | ||
| Line 482: | Line 467: | ||
=== Motions Available === | === Motions Available === | ||
*Talocrural Joint is a uniaxial hinge joint which has just 1° of Motion | |||
Talocrural Joint is a uniaxial hinge joint which has just 1° of Motion | *Dorsiflexion 0° - 20° | ||
*Plantarflexion 0° - 50° | |||
Dorsiflexion 0° - 20° | |||
Plantarflexion 0° - 50° | |||
=== Closed Packed Position === | === Closed Packed Position === | ||
*Maximum Dorsiflexion | |||
Maximum Dorsiflexion | |||
=== Open Packed Position === | === Open Packed Position === | ||
*10° Plantarflexion | |||
=== Structures Limiting Movement === | === Structures Limiting Movement === | ||
| Line 511: | Line 491: | ||
| Medial Ligament<br>Calcaneofibular Ligament<br>Posterior Talofibular Ligament<br>Posterior Joint Capsule Tension<br>Contact of Talus with Tibia<br>Plantarflexors Tension | | Medial Ligament<br>Calcaneofibular Ligament<br>Posterior Talofibular Ligament<br>Posterior Joint Capsule Tension<br>Contact of Talus with Tibia<br>Plantarflexors Tension | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 531: | Line 496: | ||
=== Assessment === | === Assessment === | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ankle_%26_Foot_Examination Ankle & Foot Examination] | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ankle_%26_Foot_Examination Ankle & Foot Examination] | ||
*[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/161739-ankle-assessment Ankle Joint Assessment Video] | *[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/161739-ankle-assessment Ankle Joint Assessment Video]<br> | ||
=== Special Tests === | === Special Tests === | ||
| Line 542: | Line 506: | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Squeeze_Test Squeeze Test]<br> | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Squeeze_Test Squeeze Test]<br> | ||
*[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/161742-talar-tilt-test Talar Tilt Test] | *[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/161742-talar-tilt-test Talar Tilt Test] | ||
*[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/161744-kleiger-test Kleiger Test] | *[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/161744-kleiger-test Kleiger Test]<br> | ||
=== Clinical Predicition Rules === | === Clinical Predicition Rules === | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ottawa_Ankle_Rules Ottawa Ankle Rules] to rule in/out radiography of the ankle after trauma<br> | |||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ottawa_Ankle_Rules Ottawa Ankle Rules] to rule in/out radiography of the ankle after trauma | |||
=== Outcome Measures === | === Outcome Measures === | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Foot_and_Ankle_Disability_Index Foot and Disability Index&]is a 34-item self report questionnaire divided into two subscales: the Foot and Ankle Disability Index and the Foot and Ankle Disability Index Sport<br> | |||
== Pathology/Injury == | |||
== Pathology/Injury | |||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ankle_arthrodesis Ankle Arthrodesis] | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ankle_arthrodesis Ankle Arthrodesis] | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ankle_Impingement Ankle Impingement] | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Ankle_Impingement Ankle Impingement] | ||
| Line 566: | Line 527: | ||
=== Manual Therapy === | === Manual Therapy === | ||
*[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162352-talocrural-joint-posterior-glide-to-promote-dorsiflexion Talocrural Joint Posterior Glide to Promote Dorsiflexion] | *[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162352-talocrural-joint-posterior-glide-to-promote-dorsiflexion Talocrural Joint Posterior Glide to Promote Dorsiflexion] | ||
*[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162355-talocrural-joint-anterior-glide-to-promote-plantarflexion Talocrural Joint Anterior Glide to Promote Plantarflexion] | *[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162355-talocrural-joint-anterior-glide-to-promote-plantarflexion Talocrural Joint Anterior Glide to Promote Plantarflexion] | ||
*[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162347-talocrural-joint-distal-distraction Talocrural Joint Distal Distraction <ref>PT Haven. Talocrural Joint Distal Distraction. Available from: http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162347-talocrural-joint-distal-distraction [last accessed 19/03/2015]</ref>] | *[http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162347-talocrural-joint-distal-distraction Talocrural Joint Distal Distraction <ref>PT Haven. Talocrural Joint Distal Distraction. Available from: http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162347-talocrural-joint-distal-distraction [last accessed 19/03/2015]</ref>] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=== Balance Retraining === | === Balance Retraining === | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Balance Balance] | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Balance Balance] | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Proprioception Proprioception] | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Proprioception Proprioception] | ||
| Line 580: | Line 538: | ||
== Procedures == | == Procedures == | ||
*[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Total_Ankle_Arthroplasty Ankle Arthroplasty] | *[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Total_Ankle_Arthroplasty Ankle Arthroplasty] | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855022/ Anatomy of the Ankle Ligaments: A Pictorial Essay] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855022/ Anatomy of the Ankle Ligaments: A Pictorial Essay] | **In this pictorial essay, the ligaments around the ankle are grouped, depending on their anatomic orientation, and each of the ankle ligaments is discussed in detail. | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23980032 The efficacy of manual joint mobilisation/manipulation in treatment of lateral ankle sprains: a systematic review] | |||
*In this pictorial essay, the ligaments around the ankle are grouped, depending on their anatomic orientation, and each of the ankle ligaments is discussed in detail. | **For acute ankle sprains, manual joint mobilisation diminished pain and increased dorsiflexion range of motion. For treatment of subacute/chronic lateral ankle sprains, these techniques improved ankle range-of-motion, decreased pain and improved function. | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24175608 Anterior talocrural joint laxity: diagnostic accuracy of the anterior drawer test of the ankle] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23980032 The efficacy of manual joint mobilisation/manipulation in treatment of lateral ankle sprains: a systematic review] | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25443172 Lower extremity function during gait in participants with first time acute lateral ankle sprain compared to controls] | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25240177 Lower extremity coordination and symmetry patterns during a drop vertical jump task following acute ankle sprain] | |||
*For acute ankle sprains, manual joint mobilisation diminished pain and increased dorsiflexion range of motion. For treatment of subacute/chronic lateral ankle sprains, these techniques improved ankle range-of-motion, decreased pain and improved function. | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25579979 Inter-joint coordination strategies during unilateral stance 6-months following first-time lateral ankle sprain] | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25545409 Single-leg drop landing movement strategies 6 months following first-time acute lateral ankle sprain injury] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24175608 Anterior talocrural joint laxity: diagnostic accuracy of the anterior drawer test of the ankle] | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25225885 Lower Limb Landing Biomechanics in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability] | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25665000 Effect of Tape on Dynamic Postural Stability in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25443172 Lower extremity function during gait in participants with first time acute lateral ankle sprain compared to controls] | *[http://www.hindawi.com/journals/aorth/2015/491976/ Immediate weight-bearing after ankle fracture fixation] | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25598398 Assessment of standing balance in patients after ankle fractures] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25240177 Lower extremity coordination and symmetry patterns during a drop vertical jump task following acute ankle sprain] | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16462563 Functional treatment and early weightbearing after an ankle fracture: a prospective study] | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25765456 Increased treatment durations lead to greater improvements in non-weight bearing dorsiflexion range of motion for asymptomatic individuals immediately following an anteroposterior grade IV mobilisation of the talus.]<br> | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25579979 Inter-joint coordination strategies during unilateral stance 6-months following first-time lateral ankle sprain] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25545409 Single-leg drop landing movement strategies 6 months following first-time acute lateral ankle sprain injury] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25225885 Lower Limb Landing Biomechanics in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25665000 Effect of Tape on Dynamic Postural Stability in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability] | |||
[http://www.hindawi.com/journals/aorth/2015/491976/ Immediate weight-bearing after ankle fracture fixation] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25598398 Assessment of standing balance in patients after ankle fractures] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16462563 Functional treatment and early weightbearing after an ankle fracture: a prospective study] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25765456 Increased treatment durations lead to greater improvements in non-weight bearing dorsiflexion range of motion for asymptomatic individuals immediately following an anteroposterior grade IV mobilisation of the talus.] | |||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | <div class="researchbox"> | ||
<rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1FiYL_imNw8my3flLGuLVj5PfnAf97Jnj2_mfggWWbu3FQPYEE</rss> | <rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1FiYL_imNw8my3flLGuLVj5PfnAf97Jnj2_mfggWWbu3FQPYEE</rss> | ||
</div> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Ankle]] [[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | ||
Revision as of 04:04, 4 August 2017
Original Editor - Naomi O'Reilly
Lead Editors - Naomi O'Reilly, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, Joanne Garvey, Rachael Lowe, Ewa Jaraczewska, Admin, WikiSysop, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Vidya Acharya, Jess Bell, Khloud Shreif, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Olajumoke Ogunleye, Evan Thomas, Sona Eyobe, Oyemi Sillo, Tarina van der Stockt and Rucha Gadgil
Description[edit | edit source]
The Ankle Joint, also known as the Talocrural Articulation, is a synovial hinge joint connecting the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus. The ankle joint is maintained by the shape of the talus and its tight fit between the tibia and fibula. In the neutral position, there are strong bony constraints. With increasing plantar flexion, the bony constraints are decreased and the ligaments are more susceptible to strain and injury. The articulation between the tibia and the talus bears more weight than that between the smaller fibula and the talus. [1]
| [2] | [3] |
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Articulating Surfaces[edit | edit source]
- Trochlea of Talus
- Malleolar Mortis formed by Tibia & Fibula
- Lateral & Medial Malleolus
Joint Capsule[edit | edit source]
The articular capsule surrounds the joints, and is attached, above, to the borders of the articular surfaces of the tibia and malleoli; and below, to the talus around its upper articular surface. The joint capsule anteriorly is a broad, thin, fibrous layer, posteriorly the fibres are thin and run mainly transversely blending with the transverse ligament and laterally the capsule is thickened, and attaches to the hollow on the medial surface of the lateral malleolus. The synovial membrane extends superiorly between Tibia & Fibula as far as the Interosseous Tibiofibular Ligament.[4]
Ligaments[edit | edit source]
Lateral Ligaments of Ankle[edit | edit source]
Reinforce Joint Laterally through three ligaments. These ligaments stabilize the ankle, and serve as a guide to direct ankle motion by attaching the lateral malleolus to the bones below the ankle joint. They are responsible for resistance against inversion and internal rotation stress. [4]
|
LIGAMENT |
DESCRIPTION | PROXIMAL ATTACHMENT | DISTAL ATTACHMENT | ROLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) |
Flat Weak Band that extends Anteriomedially. Most commonly damaged ligament of the ankle. |
Lateral Malleolus | Neck of Talus |
Restrain anterior displacement of the talus in respect to the fibula and tibia. Resists Inversion in planterflexion. |
|
Posterior Talofibular Ligament (PTFL) |
Thick, fairly strong band that runs horizontally medially. This ligament is under greater strain in full dorsiflexion of ankle. Rarely injured because bony stability protects ligaments when ankle in dorsiflexion. |
Malleolar Fossa of Fibula | Lateral Tubercle of Talus |
Forms the back wall of the recipient socket for the talus' trochlea. Resists posterior displacement of the talus. |
|
Calcaneofibular Ligament (CFL) |
Round cord that passes posterioinferiorly | Tip of Lateral Malleolus | Lateral Surface of Calcaneus |
Aids Talofibular stability during Dorsiflexion. Restrain inversion of the calcaneus with respect to the fibula. Prevent Talar tilt into Inversion. |
Medial Ligaments of Ankle[edit | edit source]
Known collectively as the Deltoid Ligament the medial ligaments of the ankle attaches proximally to the Medial Malleolus and fan out to attach distally to the Talus, Calcaneus and Navicular via four adjacent and continuous parts. The deltoid ligament is triangular in shape and consists of a superficial and deep layer which connect the talus to the medial malleolus. It reinforces the joint capsule medially. Stabilise’s the ankle joint during eversion of the foot and prevents subluxation of the ankle joint. [4]
|
LIGAMENTS |
DESCRIPTION | PROXIMAL ATTACHMENT | DISTAL ATTACHMENT | ROLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anterior Tibiotalar Ligament |
Medial Malleolus |
Head of Talus |
Reinforces Ankle Joint. Control Plantarflexion & Eversion | |
|
Posterior Tibiotalar Ligament |
Talus Posteriorly | Control Dorsiflexion | ||
|
Tibionavicular Ligament |
Forms most anterior part of the Deltoid Ligament |
Dorsomedial Aspect of Navicular | Reinforces Ankle Joint | |
|
Tibiocalcaneal Ligament |
Very thin ligament | Sustentaculum Tali | Reinforces Ankle Joint |
Muscles[edit | edit source]
Plantarflexion[edit | edit source]
Muscles which contribute to Plantarflexion
|
MUSCLE |
ACTION | PROXIMAL ATTACHMENT | DISTAL ATTACHMENT | INNERVATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT | ||||
|
SUPERFICIAL | ||||
| Gastrocnemius |
Plantarflexion when Knee Extended Flexion Knee Raises Heel during Walking |
Lateral Head: Lateral Aspect of Lateral Femoral Condyle Medial Head: Popliteal Surface of Femur Superior to Medial Femoral Condyle |
Posterior Surface Calcaneus via Calcaneal Tendon (Achilles Tendon) |
Tibial Nerve S1-S2 |
| Soleus |
Plantarflexion Steadies Leg on Foot |
Posterior Aspect of Head Fibula Superior ¼ Posterior Surface Tibia Soleal Line & Medial Border Tibia | ||
| Plantaris |
Weakly Assists Gastrocnemius in Plantarflexion |
Inferior end Lateral Supracondylar Line of Femur Oblique Popliteal Ligament | ||
|
DEEP | ||||
| Tibialis Posterior |
Plantarflexion Inversion Supports Medial Longitudinal Arch |
Interosseous Membrane Posterior Surface Tibia inferior to Soleal Line Posterior Surface Fibula |
Navicular Tuberosity Cuneiform Cuboid Bases of Metatarsals 2-4 |
Tibial Nerve L4-L5 |
| Flexor Digitorum Longus |
Plantarflexion Flexion Lateral Four Digits Supports Longitudinal Arch |
Medial Part Posterior Surface Tibia inferior to Soleal Line Broad Tendon to Fibula |
Base Distal Phalanges Digits 2-4 |
Tibial Nerve S2-S3 |
| Flexor Hallucis Longus |
Weak Plantarflexion Flexion Big Toe at all Joints Supports Medial Longitudinal Arch |
Inferior 2/3 Posterior Surface Fibula Inferior Part Interosseous Membrane |
Base Distal Phalanx of Big Toe | |
|
LATERAL COMPARTMENT | ||||
|
Peroneus Brevis |
Weak Plantarflexion Eversion |
Inferior 2/3 of Lateral Surface Tibia |
Dorsal Surface Tuberosity of Base 5th Metatarsal |
Superficial Peroneal Nerve (Superficial Fibular Nerve) L5 - S2 |
|
Peroneus Longus |
Weak Plantarflexion Eversion Supports Transverse Arch |
Head & Superior 2/3 of Lateral Surface Tibia |
Base 1st Metatarsal Medial Cuniform | |
Dorsiflexion[edit | edit source]
Muscles which contribute to Dorsiflexion
|
MUSCLE |
ACTION | PROXIMAL ATTACHMENT | DISTAL ATTACHMENT | INNERVATION |
|
ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT | ||||
|
Tibialis Anterior |
Dorsiflexion Inversion Supports Medial Longitudinal Arch |
Lateral Condyle Tibia Superior ½ Lateral Surface Tibia Interosseous Membrane |
Medial & Inferior Surfaces Medial Cuniform Base of 1st Metatarsal |
Deep Peroneal Nerve (Deep Fibular Nerve) L4-L5 |
|
Extensor Digitorum Longus |
Dorsiflexion Extends Lateral Four Digits |
Lateral Condyle Tibia Superior ¾ Anterior Surface Interosseous Membrane |
Middle & Distal Phalanges of Lateral Four Digits |
Deep Peroneal Nerve (Deep Fibular Nerve) L5-S1 |
|
Extensor Hallucis Longus |
Dorsiflexion Extends Big Toe |
Middle Part Anterior Surface Fibula Interosseous Membrane |
Dorsal Aspect of Base Distal Phalanx of Big Toe | |
|
Peroneus Tertius |
Dorsiflexion Aids Eversion |
Inferior 1/3 Anterior Surface Fibula Interosseous Membrane |
Dorsum Base 5th Metatarsal | |
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Derived from Malleolar Branches of:
- Peroneal Artery
- Tibial Artery
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
- Common Peroneal Nerve
- Tibial Nerve
Function[edit | edit source]
Motions Available[edit | edit source]
- Talocrural Joint is a uniaxial hinge joint which has just 1° of Motion
- Dorsiflexion 0° - 20°
- Plantarflexion 0° - 50°
Closed Packed Position[edit | edit source]
- Maximum Dorsiflexion
Open Packed Position[edit | edit source]
- 10° Plantarflexion
Structures Limiting Movement[edit | edit source]
| Movement | Limiting Structures |
|---|---|
| Plantarflexion Posterior & Lateral Compartment |
Anterior Talofibular Ligamanet Anterior Part of Medial Ligament Anterior Joint Capsule Tension Contact of Talus with Tibia Dorsiflexor Tension |
| Dorsiflexion Anterior Compartment |
Medial Ligament Calcaneofibular Ligament Posterior Talofibular Ligament Posterior Joint Capsule Tension Contact of Talus with Tibia Plantarflexors Tension |
Clinical Examination[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Special Tests[edit | edit source]
- Kaltenborn Ankle & Foot Examination
- Anterior Drawer of the Ankle
- Ligament Tests
- Squeeze Test
- Talar Tilt Test
- Kleiger Test
Clinical Predicition Rules[edit | edit source]
- Ottawa Ankle Rules to rule in/out radiography of the ankle after trauma
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
- Foot and Disability Index&is a 34-item self report questionnaire divided into two subscales: the Foot and Ankle Disability Index and the Foot and Ankle Disability Index Sport
Pathology/Injury[edit | edit source]
- Ankle Arthrodesis
- Ankle Impingement
- Ankle Osteoarthritis
- Ankle Osteochondral Lesions
- Ankle Sprain
- Ankle and Foot Fractures
- Ankle and Foot Arthropathies
- Chronic Ankle Instability
Physiotherapeutic Techniques[edit | edit source]
Manual Therapy[edit | edit source]
- Talocrural Joint Posterior Glide to Promote Dorsiflexion
- Talocrural Joint Anterior Glide to Promote Plantarflexion
- Talocrural Joint Distal Distraction [5]
Balance Retraining[edit | edit source]
Procedures[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Anatomy of the Ankle Ligaments: A Pictorial Essay
- In this pictorial essay, the ligaments around the ankle are grouped, depending on their anatomic orientation, and each of the ankle ligaments is discussed in detail.
- The efficacy of manual joint mobilisation/manipulation in treatment of lateral ankle sprains: a systematic review
- For acute ankle sprains, manual joint mobilisation diminished pain and increased dorsiflexion range of motion. For treatment of subacute/chronic lateral ankle sprains, these techniques improved ankle range-of-motion, decreased pain and improved function.
- Anterior talocrural joint laxity: diagnostic accuracy of the anterior drawer test of the ankle
- Lower extremity function during gait in participants with first time acute lateral ankle sprain compared to controls
- Lower extremity coordination and symmetry patterns during a drop vertical jump task following acute ankle sprain
- Inter-joint coordination strategies during unilateral stance 6-months following first-time lateral ankle sprain
- Single-leg drop landing movement strategies 6 months following first-time acute lateral ankle sprain injury
- Lower Limb Landing Biomechanics in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability
- Effect of Tape on Dynamic Postural Stability in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability
- Immediate weight-bearing after ankle fracture fixation
- Assessment of standing balance in patients after ankle fractures
- Functional treatment and early weightbearing after an ankle fracture: a prospective study
- Increased treatment durations lead to greater improvements in non-weight bearing dorsiflexion range of motion for asymptomatic individuals immediately following an anteroposterior grade IV mobilisation of the talus.
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1FiYL_imNw8my3flLGuLVj5PfnAf97Jnj2_mfggWWbu3FQPYEE: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Allen F. Anderson Sports Medicine. Anatomy Ankle Available from: http://www.drallenfanderson.com/ankle/anatomy [last accessed 20/03/2015]
- ↑ Anatomy Zone. Ankle Joint - 3D Anatomy Tutorial. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lPLdoFQlZXQ [last accessed 19/03/2015]
- ↑ AnimatedBiomedical. Ankle Joint, Bones of the Foot - 3D Medical Animation. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X-eAXKS4pJM [last accessed 19/03/2015]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinial Anatomy. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2011.
- ↑ PT Haven. Talocrural Joint Distal Distraction. Available from: http://www.pthaven.com/page/show/162347-talocrural-joint-distal-distraction [last accessed 19/03/2015]