Flexor Digitorum Longus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
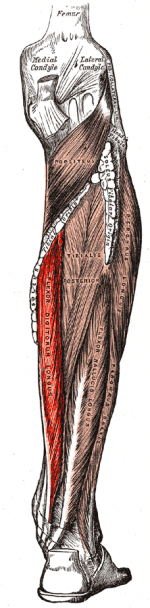
Located at the medial and posterior of the calf, its forms a tendon about 3 fingers breath above the medial malleous which then lies next tibialis posterior tendon. | |||
[[Image:FDL3.png|thumb|right|150px]] | [[Image:FDL3.png|thumb|right|150px]] | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
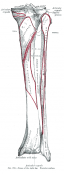
Medial and posterior surface of the body of the tibia. | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
Tibial nerve | Tibial nerve (root L5, S1 and S2). | ||
Cutaneous supply on the medial and posterior aspect of the calf and sole from L4, L5 and S1. | |||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
Posterior tibial artery<ref name="salad">Saladin K. Anatomy & physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2010.</ref> | Posterior tibial artery<ref name="salad">Saladin K. Anatomy &amp; physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2010.</ref> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Flexes phalanges of second to fifth digits as the foot is raised from the ground. Additionally stabilises the metatarsal heads and keeps distal pads of toes in contact with ground in toe-off and when on tip-toe.<ref name="salad" /> | Flexes phalanges of second to fifth digits as the foot is raised from the ground. Additionally stabilises the metatarsal heads and keeps distal pads of toes in contact with ground in toe-off and when on tip-toe.<ref name="salad" /> | ||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 37: | ||
=== Palpation === | === Palpation === | ||
It is near impossible to locate the origin due to it's depth to the soleus muscle. The insertional tendon is also deep but can be identified as it passes alongside the sustentaculum tali. | |||
=== Power === | === Power === | ||
=== Length | Resisted flexion of second to fifth toes with the foot in neutral or dorsiflexion. | ||
=== Length === | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
| Line 68: | Line 76: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
*[[ | *[[Flexor hallucis longus|Flexor hallucis longus]] | ||
*[[The Os Trigonum Syndrome|The Os Trigonum Syndrome]] | *[[The Os Trigonum Syndrome|The Os Trigonum Syndrome]] | ||
*[[Tarsal Tunnel syndrome|Tarsal Tunnel syndrome]] | *[[Tarsal Tunnel syndrome|Tarsal Tunnel syndrome]] | ||
Revision as of 18:30, 11 January 2017
Original Editor - George Prudden
Top Contributors - George Prudden, Kim Jackson, 127.0.0.1, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop, Abbey Wright, Pinar Kisacik and Patti Cavaleri;
Description[edit | edit source]
Located at the medial and posterior of the calf, its forms a tendon about 3 fingers breath above the medial malleous which then lies next tibialis posterior tendon.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Medial and posterior surface of the body of the tibia.
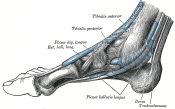
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Plantar surface, base of the distal phalanges of the four lesser digits.
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Tibial nerve (root L5, S1 and S2).
Cutaneous supply on the medial and posterior aspect of the calf and sole from L4, L5 and S1.
Artery[edit | edit source]
Posterior tibial artery[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
Flexes phalanges of second to fifth digits as the foot is raised from the ground. Additionally stabilises the metatarsal heads and keeps distal pads of toes in contact with ground in toe-off and when on tip-toe.[1]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
It is near impossible to locate the origin due to it's depth to the soleus muscle. The insertional tendon is also deep but can be identified as it passes alongside the sustentaculum tali.
Power[edit | edit source]
Resisted flexion of second to fifth toes with the foot in neutral or dorsiflexion.
Length[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Strengthening[edit | edit source]
Stretching[edit | edit source]
Manual techniques[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
|
|
|
File:FDL4.JPG | 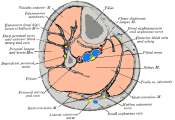
|
See also[edit | edit source]
- Flexor hallucis longus
- The Os Trigonum Syndrome
- Tarsal Tunnel syndrome
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
- Ankle & Foot
- Compartment Syndrome of the Foot
- Ankle Impingement
- Hallux Valgus
- Ankle Joint
- Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV)