Avulsion Fractures of the Ankle
Original Editors - Niels Verbeeck as part of the Vrije Universiteit Brussel Evidence-Based Practice Project
Top Contributors - Niels Verbeeck, Kim Jackson, Admin, Pierreux Maarten, Shaimaa Eldib, Scott Cornish, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Vidya Acharya, Rachael Lowe, Jan Alderweireldt, Claire Knott, Wanda van Niekerk, Lucinda hampton and 127.0.0.1
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
An avulsion fracture is where a fragment of bone is pulled away at the ligamentous or tendinous attachment. It can be caused by traumatic traction (repetitive long-term or a single high-impact traumatic traction) of the ligament or tendon. An avulsion fracture occurs because tendons can bear more load than the bone.[1][2] It can occur at numerous sites in the body, but some areas are more sensitive to these type of fractures than others, such as at the ankle which mostly occurs at the lateral aspect of the medial malleolus or in the foot where avulsion fractures are common at the base of the fifth metatarsal, but also at the talus and calcaneus.[3]
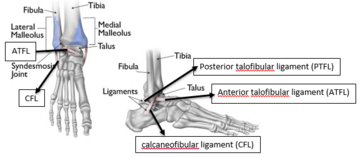
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Taking the example of avulsion fractures at the 5th metatarsal; It is divided into 3 parts: the tuberosity, the metaphysis, and the head. Peroneus Brevis attaches at the lateral side of the tuberosity with peroneus tertius attaching at the dorsal side of the most proximal compartment of the metaphysis. Due to the high traction forces by these structures, tuberosity avulsion fractures commonly occur in an inversion injury.
Epidemiology/ Etiology[edit | edit source]
Avulsion fractures account for 5 to 6% of all fractures in primary settings, a yearly incidence of approximately 67 in 100,000 accounts for fifth metatarsal fracture[4]. The typical cause of injury is an inversion of the foot, generating tension along with the plantar aponeurosis insertion. A twisting injury to the ankle and foot may cause an avulsion fracture at any of these locations. According to Lawrence and Botte’s Classification, three types of proximal fifth metatarsal fractures based on the mechanism of injury, location, treatment options, and prognosis. In the Zone 1 fracture, during the foot inversion, the forces exerted by peroneus brevis or lateral band of the plantar fascia cause avulsion fracture of tuberosity with or without the involvement of the tarsometatarsal articulation.[5] Zone 2 fractures refer to the fractures at the metaphysis-diaphysis junction, extending into the fourth-fifth intermetatarsal facet, caused by forced forefoot adduction with the hindfoot in plantar flexion. Zone 3 fractures refer to proximal diaphyseal fractures, distal to the fourth and fifth metatarsal base articulation caused by excessive bearing of the region or chronic overloading as in stress fractures[5]
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The characteristics of an avulsion fracture differ from those of a ligament rupture. Unlike the non-operative treatment of a lateral ligament rupture, non-operative treatment of avulsion fractures does not yield satisfactory results.[6] Symptoms of an ankle avulsion fracture are very similar to an ankle sprain and it is very difficult to differentiate without an X-ray or an MRI scan.
Pain is usually felt in the ankle immediately post-injury with an immediate onset of swelling. Bruising may develop and the patient will have difficulty walking or weight-bearing on the ankle. If an avulsion fracture is present, there will be immediate pain over the outside aspect of the foot and associated with significant swelling and localised tenderness over the 5th metatarsal. The history of the injury will be similar to that of an ankle sprain (plantarflexor inversion). [7][8][9]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- A Jones fracture occurs as a result of a stress fracture to the 5th metatarsal, due to repetitive loading of the outside part of the foot from the patient’s underlying foot pattern or lower extremity alignment. Unlike a Dancer’s fracture, a Jones fracture may not heal and often requires surgery.[9]
- Stress fractures
- Mid-shaft fractures
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
An X-ray may be ordered by the surgeon. Avulsion fractures can sometimes be overlooked or where an injury to the 5th metatarsal occurs together with an ankle sprain. Other imaging methods are recommended such as MRI, CT Scan or scintigrams. [2] [10] [8]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Examination[edit | edit source]
A history of the injury is taken, such as mechanism, immediate pain levels, and swelling. The Ottawa Ankle Rules can be used to localise the exact area of pain. Palpation may also be useful.
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
An avulsion fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal is usually treated conservatively. If the bone is not displaced, a walking boot or cast can be used, remaining in situ for 4 to 6 weeks. Surgery is only recommended where the bone is displaced from its normal position or where more than 30% of the cubometatarsal joint is involved. The bone will be removed or fixed with osteosynthesis material. Crutches may be used to avoid weight bearing on the injured foot. [11]
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Avulsion fractures are often treated as ankle sprains, with the dysfunctional movement and impairments treated alongside the fracture, so it is important to individualise the treatment plan. [8]Level of evidence: 2B
An inappropriately managed avulsion fracture can lead to significant, long-term functional disability. Most fractures heal well, but following a strict immobilisation period normal arthrokinematics, strength of the lower extremity muscles, proprioception, and functional movement for chosen sport/activities need to be regained.
Rehabilitation following an avulsion fracture consists of 3 phases; the acute, the recovery, and the functional phase:
Acute phase[edit | edit source]
It can begin at 2 weeks postoperatively. This phase can include passive range of motion exercises and cryotherapy and is based on reducing pain, inflammation, and oedema while keeping muscle atrophy of the lower limb to a minimum.
Recovery phase[edit | edit source]
It begins once the goals of the acute phase have been met. This phase can be further divided into 3 stages:
Weeks 0-6: active ROM exercises for the toes and the MPT joints, strengthening exercises for the ankle and foot are still premature, however. In week 2, isometric exercises for the dorsiflexors, plantarflexors, invertors, and evertors of the foot, along with active ankle ROM movements can be started.
Weeks 6-8: Active and passive ROM exercises for the ankle and the subtalar joint with Isometric and isotonic exercises. Exercises for proprioception and proximal strength and control.
At 8-12 weeks: strengthening exercises for the dorsiflexors, plantarflexors, invertors, evertors, long flexors and extensors of the toes are recommended. Full weight-bearing exercises are also permitted.[13][7]
Functional phase[edit | edit source]
Starts at 6 to 8 weeks post-operatively. This phase involves ongoing strength and conditioning of the lower limb, increasing neuromuscular control and utilising sport/activity-specific training. [14]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Cluett J. 2022. Avulsion Fracture Causes and Treaments. Available from: http://orthopedics.about.com/od/brokenbones/a/avulsion.htm (accessed 25 February 2024)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Foot Health Facts. 2024. Fractures of the Fifth Metatarsal. Available from:http://www.foothealthfacts.org/footankleinfo/fifth-metatarsal_fractures.htm (accessed 25 February 2024)
- ↑ McCoy JS, Nelson R. Avulsion Fractures. StatPearls [Internet]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559168/ (accessed 25 February 2024)
- ↑ Vannabouathong C, Ayeni OR, Bhandari M. A Narrative Review on Avulsion Fractures of the Upper and Lower Limbs. Clinical Medicine Insights: Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2018; 11:1179544118809050.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Cheung CN, Lui TH. Proximal fifth metatarsal fractures: anatomy, classification, treatment and complications. Archives of trauma research. 2016 Dec;5(4).:e33298. doi: 10.5812/atr.33298.
- ↑ Hintermann B, Ruiz R. Foot and Ankle Instability A Clinical Guide to Diagnosis and Surgical Management. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Myerson MS, Fisher RT, Burgess AR, Kenzora JE. Fracture dislocations of the tarsometatarsal joints: end results correlated with pathology and treatment. Foot Ankle. 1986 Apr;6(5):225-42. doi: 10.1177/107110078600600504. Level of evidence: 2A
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Haraguchi N, Toga H, Shiba N, Kato F. Avulsion fracture of the lateral ankle ligament complex in severe inversion injury: incidence and clinical outcome. Am J Sports Med. 2007 Jul;35(7):1144-52
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kerkar P. Epainassist, 2023. Ankle Avulsion Fracture: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Recovery Time, Exercises. Available from:http://www.epainassist.com/sports-injuries/ankle-injuries/ankle-avulsion-fracture-symptoms-causes-treatment (accessed 25 February 2024)
- ↑ Pao DG, Keats TE, Dussault RG. Avulsion fracture of the base of the fifth metatarsal not seen on conventional radiography of the foot: the need for an additional projection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Aug;175(2):549-52. doi: 10.2214/ajr.175.2.1750549.
- ↑ Zwitser EW, Breederveld RS. Fractures of the fifth metatarsal; diagnosis and treatment. Injury. 2010 Jun;41(6):555-62. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.05.035.
- ↑ Doncaster and Bassetlaw Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. DBTH VFC Avulsion fracture ankle. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=12pKnQJEmdk[last accessed 24/2/2024]
- ↑ Essentials of Orthopaedics for Physiotherapist, Ebnezar. India: Jaypee, 2003. Level of Evidence: 5
- ↑ http://www.podiatrytoday.com/article/6565 Level of Evidence: 5